Grab has transformed from a humble ride-hailing service into Southeast Asia’s leading super app, offering a wide array of services, from transportation to food delivery and financial services. Launched in 2012 as GrabTaxi, the company has since expanded across eight countries, providing users with seamless access to multiple daily needs, all through one app. Its evolution has inspired many entrepreneurs to explore similar solutions, leveraging platforms like a Grab clone to build versatile on-demand apps tailored to regional needs.
In this article, we will delve deep into how Grab works, explore its business model, and analyze the multiple revenue streams that have driven its success in the on-demand economy.
What is Grab?
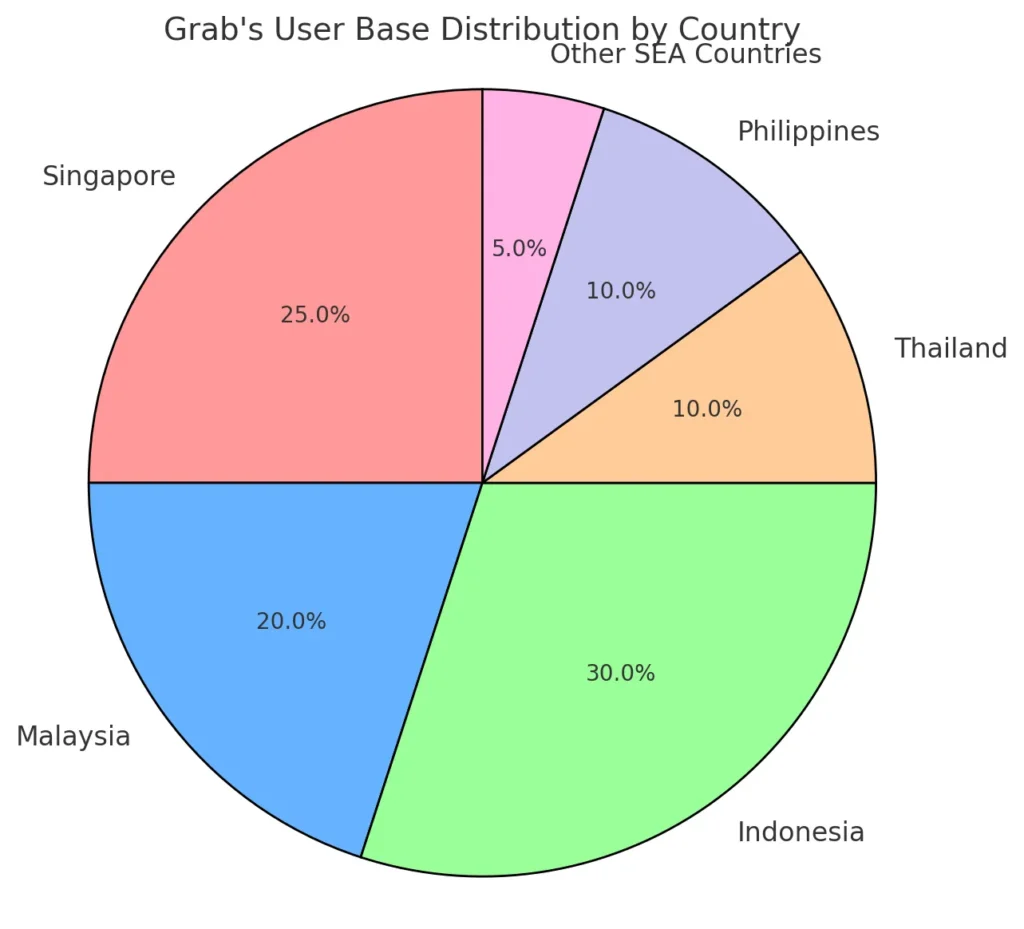
Grab started in 2012 as GrabTaxi, founded by Anthony Tan and Tan Hooi Ling, to improve the taxi industry in Malaysia by addressing issues like safety and reliability. Initially a ride-hailing service, Grab has evolved into Southeast Asia’s largest super app, offering a broad spectrum of services beyond transportation. These include GrabFood (food delivery), GrabMart (grocery delivery), GrabPay (digital payments), and GrabExpress (parcel delivery), among others. Today, it operates in over 400 cities across eight countries, serving millions of users with various on-demand services all in one platform.
Since its inception, Grab has raised billions in funding, contributing to its rapid expansion across Southeast Asia. The company has secured significant investments, with detailed funding rounds listed on Crunchbase.
How Does Grab Work?
Grab operates as a digital aggregator, connecting service providers (drivers, restaurants, couriers) with users, all through one app. Here’s how each core service works:
- GrabRides: Users book taxis or personal rides via the app, selecting from cars, bikes, and even pet-friendly options.
- GrabFood: Customers order food from nearby restaurants, with delivery managed by local couriers.
- GrabPay: A digital wallet that allows users to make cashless payments for rides, food, or at partnered merchants.
Want to build a successful super app like Grab?
Our experts will help you design a winning business model
and development strategy.
Grab Business Model
Grab operates on a super app model, integrating multiple services into one platform, which reduces the need for separate apps. This strategy allows users to access a wide range of services—ride-hailing, food delivery, grocery delivery, and digital payments—all from a single app. By doing so, Grab maximizes user engagement and retention. Its business model thrives on a commission-based system, where it takes a percentage from service providers for each transaction, whether it’s a ride, a meal, or a financial service.
Key Components of Grab’s Business Model:
- Multi-Service Integration: Grab’s platform brings together services that cater to various aspects of daily life. Whether it’s booking a ride, ordering food, delivering groceries, or making cashless payments, users can do it all within the Grab app. This comprehensive service offering increases user stickiness, as customers are more likely to use the app frequently for different needs.
- User-Centric Experience: Grab’s business model revolves around providing a seamless user experience. By integrating features like real-time tracking, cashless payments through GrabPay, and personalized offers via GrabRewards, the app ensures that users remain engaged and satisfied. The super app model also makes it easy for users to transition between services, such as moving from ride-hailing to food ordering within seconds, enhancing convenience and speed.
- Commission-Based Revenue: A significant part of Grab’s revenue comes from its commission-based model. For every transaction made on the platform—whether it’s a ride, food delivery, or grocery order—Grab takes a percentage from the service providers. For example, drivers or restaurants pay a commission to Grab for facilitating the connection with the customer. The commission rates typically vary between 16% to 30%, depending on the service and region. This model allows Grab to generate consistent revenue across its service lines.
- Service Provider Partnerships: Grab works with a large network of drivers, restaurants, grocery stores, and merchants who deliver services to customers. For drivers, Grab provides a flexible platform where they can set their own working hours while earning extra income. Similarly, restaurants and other merchants benefit from increased visibility and a broader customer base. Grab’s ability to connect service providers with a vast user base makes it a valuable partner for businesses looking to expand their reach.
- Data-Driven Insights: Grab leverages data analytics to enhance its services and optimize its operations. By tracking user behavior, preferences, and patterns, Grab can provide targeted offers, personalized experiences, and recommendations. For instance, GrabAds uses user data to help businesses connect with the right audience through highly targeted advertising, both online and offline. This creates an additional revenue stream for Grab while offering businesses valuable marketing opportunities.
- Diversified Revenue Streams: While commissions remain the core revenue generator, Grab has diversified its income sources to include financial services (like loans and insurance), advertising (through GrabAds), and premium services (such as GrabFinance). These revenue channels have allowed Grab to scale its business beyond traditional ride-hailing and food delivery services. For example, GrabPay facilitates digital transactions, generating additional income from merchant fees, and GrabFinance offers small business loans, expanding into fintech services.
- Local Market Adaptation: One of Grab’s major strengths is its ability to adapt to the specific needs of the Southeast Asian market. This includes offering services tailored to local preferences, such as GrabBike for motorbike transportation in congested cities like Jakarta and Bangkok, and GrabMart for grocery delivery in urban areas with limited access to physical stores. By localizing its offerings, Grab ensures it meets the unique demands of each market, which is critical to its success in a region as diverse as Southeast Asia.
- Super App Strategy: Grab’s goal is to become the “everyday everything” app for its users. This means not just offering a variety of services but also making sure those services are integrated into users’ daily routines. By keeping users within the Grab ecosystem for various needs—whether it’s commuting, dining, or banking—the app ensures higher customer retention and loyalty. This also creates cross-service synergies where a user booking a ride might also be tempted to order food, leading to multiple transactions within a single user session.
- Sustainable Growth and Community Impact: Beyond profitability, Grab’s business model emphasizes sustainable economic empowerment in Southeast Asia. By creating employment opportunities for drivers, delivery partners, and merchants, Grab contributes to the local economy while also addressing the region’s transportation and service challenges. This focus on sustainability and community impact is a key part of Grab’s long-term vision, helping it build strong relationships with governments, local businesses, and consumers.
Grab’s super app business model is a highly effective strategy that combines user convenience, service provider engagement, and multiple revenue streams. By continuously expanding its services and integrating new verticals like finance and advertising, Grab has positioned itself as a market leader in Southeast Asia. The platform’s ability to adapt to local markets, coupled with its data-driven insights and strong partnerships, ensures its continued growth and success in the on-demand economy.
Revenue Channels
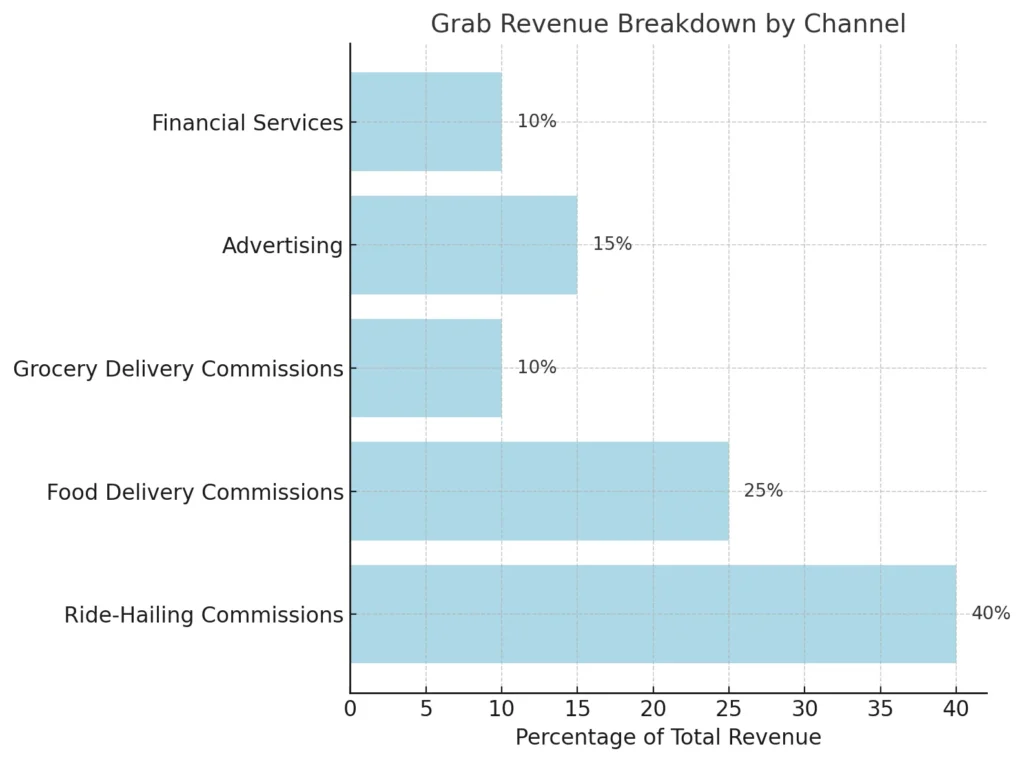
Grab has developed diverse revenue streams to support its super app ecosystem:
- Commissions: The core revenue source, Grab earns a percentage (typically 16-30%) from services like rides, food delivery, and groceries. For each transaction, a portion is taken from service providers.
- Advertising: Through GrabAds, businesses pay for exposure to millions of users within the app, using targeted advertising based on user behavior and location.
- Financial Services: Grab generates income through GrabPay and GrabFinance, offering payment solutions and lending services, with additional revenue from transaction fees and interest on loans.
| Revenue Channel | Description | Revenue Source |
|---|---|---|
| Ride-Hailing Commissions | Grab takes a commission (16-25%) on each ride completed | Fees from drivers and passengers |
| Food Delivery Commissions | 20-30% commission on food delivery orders | Partner restaurants and delivery fees |
| GrabAds | Advertising platform for businesses to reach users | Ad fees from businesses |
| Financial Services | Revenue from GrabPay, loans, and insurance | Transaction fees, loan interest, insurance fees |
| Grocery Delivery | Commissions from grocery delivery services through GrabMart | Partner stores and delivery charges |
Grab’s Competitors
Grab faces tough competition from other ride-hailing and super apps, notably Uber and GoJek.
| Company | Founded | Countries | Core Services | Monthly Users | Revenue Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Grab | 2012 | 8 | Ride-Hailing, Food Delivery, Payments | 187 million | Commissions, Ads, Financial Services |
| Uber | 2009 | 70+ | Ride-Hailing, Food Delivery | 110 million | Commissions, Ads |
| GoJek | 2010 | 5 | Ride-Hailing, Payments, Delivery | 38 million | Commissions, Ads, Financial Services |
- Uber: A global ride-hailing giant, Uber operates on a similar business model but focuses more on transportation and food delivery in fewer regions in Southeast Asia.
- GoJek: Another Southeast Asian super app, GoJek offers similar services like ride-hailing, food delivery, and digital payments. GoJek and Grab compete heavily in Indonesia, with GoJek also expanding into financial services.
This competition drives innovation and service quality improvements in the region.
The ride-hailing industry continues to experience massive growth, with platforms like Uber, GoJek, and Grab leading the market. According to Statista’s ride-hailing data, this market is expected to see substantial expansion globally.
Future of Grab
Grab’s future is focused on expanding its services and further dominating Southeast Asia’s digital economy. The company is pushing to strengthen its foothold in financial services through GrabPay and GrabFinance, providing loans, insurance, and payments to a wider customer base. Additionally, Grab aims to introduce more on-demand services like healthcare and logistics, while expanding into new territories beyond Southeast Asia. With constant innovation and a growing super app ecosystem, Grab is poised to continue its upward trajectory.
Value Proposition of Grab
Grab offers a one-stop solution for users and businesses, making it an essential app for daily needs. Users choose Grab for its convenience, combining multiple services (transportation, food delivery, payments) into a single app. Its cashless payments and secure transactions enhance user trust, while tailored services (e.g., GrabFood, GrabRides) save time and effort. For businesses, Grab offers a vast customer base, enabling growth through digital payments, advertising (GrabAds), and efficient delivery services, making it a critical partner for growth.
Challenges Grab Faces
Grab faces several operational challenges, including navigating local regulations, particularly in diverse markets with varying laws for ride-hailing and financial services. Scaling issues also arise as it expands across multiple countries, requiring efficient management of logistics, payments, and customer service. Additionally, increasing competition from local and global players, such as GoJek and Uber, forces Grab to constantly innovate to retain market share. Maintaining consistent service quality and user trust while growing its user base presents another ongoing challenge.
How to Build a Grab Clone App
For entrepreneurs inspired by Grab’s success, Miracuves offers a Grab clone solution designed to help you build your own on-demand service platform. With features like ride-hailing, food delivery, and digital payments, the Grab clone is fully customizable, enabling you to tailor it to your business needs. Miracuves provides end-to-end support, ensuring you have the technology and tools to launch quickly and scale efficiently. This ready-made solution accelerates your go-to-market strategy and gives you a competitive edge.
Conclusion
Grab’s journey from a simple ride-hailing service to a comprehensive super app is a testament to the power of on-demand services. Its business model, which integrates transportation, food delivery, and financial services, has reshaped the way users in Southeast Asia engage with daily necessities. For entrepreneurs, this presents a lucrative opportunity. With Miracuves’ Grab clone solution, you can launch your own multi-service app, leveraging proven strategies to capture a piece of the growing on-demand market.
Ready to launch your app? Contact Miracuves to start your journey today!
Launch your Grab-style business fast with our ready-to-deploy super app!
Start your Grab-inspired multi-service business in days, not months. Our pre-built solution is fully customizable and market-ready.
FAQs About Grab’s Business Model
What services does Grab offer?
Grab provides a variety of services including ride-hailing, food delivery, grocery shopping, digital payments, parcel delivery, insurance, and more, all integrated into one super app.
How does Grab make money?
Grab earns through commissions on rides, food deliveries, groceries, and advertising via GrabAds. It also generates revenue from financial services like GrabPay and GrabFinance.
Who are Grab’s main competitors?
Grab competes with Uber and GoJek, particularly in the Southeast Asian market.
What are the challenges Grab faces?
Grab struggles with regulatory hurdles, scaling across different countries, and competition in its markets.
How can I build a Grab-like app?
Entrepreneurs can use Miracuves’ Grab clone solution, a customizable and scalable app designed for launching multi-service platforms quickly.
Check out our popular super app solutions offered by Miracuves – built for versatility, performance, and scale:
- Super App Like Gojek – A powerful all-in-one super app offering ride-hailing, food delivery, courier, payments, and more
- Super App Like Glovo – An on-demand delivery app covering food, groceries, pharmacy, and courier services in one platform
- Super App Like Grab – A comprehensive app solution combining transportation, delivery, digital payments, and everyday services








