In today’s fast-paced world, consumers are constantly seeking convenience and efficiency in their daily lives. Enter Instacart, a revolutionary grocery delivery app that has redefined how people shop for essentials. Since its inception, Instacart has grown exponentially, becoming a leader in the on-demand delivery app market by launching Instacart clone app . By seamlessly connecting customers with personal shoppers and local retailers, the platform has transformed the grocery shopping experience.
But what makes Instacart so successful? It’s more than just a delivery service—Instacart’s business model is built on a sophisticated yet user-friendly approach that benefits customers, gig workers, and retail partners alike. As the demand for online grocery delivery continues to rise, Instacart’s unique marketplace model offers a scalable solution, making it a major player in the evolving grocery delivery platform industry. This blog will explore how Instacart works, why it’s successful, and the secrets behind its innovative business model.
How Instacart Works: Step-by-Step Overview
Instacart operates through a straightforward yet effective process, offering a seamless experience for both customers and retailers. The platform serves three key stakeholders: customers, shoppers, and retailers. Let’s break down how the Instacart delivery process works.
1. Customers Place Orders via the Instacart App
Customers start by selecting their favorite local grocery stores from the available options on the Instacart app. They then browse through products, add them to their cart, and choose a delivery time that best suits their schedule. The platform offers flexibility, allowing customers to pick a delivery window within the same day or even schedule it for later in the week.
2. Personal Shoppers Fulfill the Orders
Once an order is placed, a gig economy worker, or personal shopper, is assigned to the task. These shoppers visit the selected store, pick the items, and handle any last-minute adjustments such as product replacements. Instacart’s real-time communication feature allows shoppers to stay in touch with customers throughout the shopping process, ensuring any substitutions are approved before proceeding. Instacart’s use of gig economy workers, which Investopedia defines as independent contractors engaged in short-term, flexible work, has been key to its operational efficiency.
3. Shoppers Deliver the Groceries
After completing the order, the shopper delivers the groceries directly to the customer’s doorstep. Instacart provides real-time tracking, so customers know exactly when their groceries will arrive. With contactless delivery becoming increasingly popular, Instacart offers the option for a no-contact drop-off, which has gained traction during the pandemic.
Instacart’s crowdsourced delivery model keeps operational costs low while ensuring quick, efficient deliveries. The platform’s ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences, such as contactless delivery, is one of its biggest strengths in the competitive grocery delivery platform market.
Instacart Business Model Explained
Instacart operates on a multi-sided marketplace model that brings together customers, personal shoppers, and retailers in a seamless digital ecosystem. Unlike traditional grocery stores, Instacart does not own any inventory or warehouses. Instead, it acts as an intermediary between customers and local retailers, making it highly scalable and cost-effective. Here’s a deeper look into how Instacart’s business model works.
| Stakeholder | Role in Instacart’s Ecosystem | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Customers | Place grocery orders through the Instacart app | Convenience, flexible delivery, access to multiple stores |
| Retailers | Provide inventory and partner with Instacart | Access to Instacart’s customer base, increased sales |
| Personal Shoppers | Shop and deliver groceries to customers | Flexible work, gig economy opportunities, immediate payouts |
1. Online Marketplace Model
At the core of Instacart’s success is its online marketplace model. The platform partners with local grocery stores, supermarkets, and retailers, allowing customers to order groceries online from their preferred locations. By leveraging these partnerships, Instacart can offer a wide selection of products without managing its own inventory. This minimizes overhead costs and gives the company flexibility to operate in multiple regions.
Instacart’s marketplace functions by listing products from partnered retailers on its app. Customers can browse available stores in their area, select items, and place an order. The platform charges a markup on some items, which serves as one of its revenue streams.
2. Crowdsourced Delivery
A key element of Instacart’s business model is its reliance on the gig economy. Rather than employing full-time delivery drivers, Instacart uses independent contractors, known as personal shoppers, to fulfill and deliver customer orders. This crowdsourced delivery model keeps operating costs low, as Instacart only pays shoppers when they are actively fulfilling orders. The use of gig workers allows the company to scale its operations quickly, especially in high-demand periods.
By tapping into the gig economy, Instacart avoids the need for a large workforce on its payroll, making it agile and adaptable to market fluctuations. This flexibility is crucial in maintaining profitability while keeping delivery fees competitive.
3. Partnership with Retailers
Instacart’s relationships with retailers are central to its business model. The company forms strategic partnerships with local and national grocery chains, such as Costco, Kroger, and Safeway, enabling customers to shop from multiple stores within a single order. These partnerships provide retailers with an additional revenue stream through online sales without investing in their own on-demand delivery app infrastructure.
Retailers benefit from increased visibility and access to Instacart’s large customer base, while Instacart earns commissions from each order placed through its platform. The app-based business model allows Instacart to serve as a bridge between physical retail and e-commerce, which is especially appealing in a market where more consumers are turning to online grocery delivery.
4. Data-Driven Operations
Instacart’s success is also tied to its use of data and technology. The company employs sophisticated data analytics to optimize delivery routes, improve order accuracy, and personalize the shopping experience. By analyzing customer purchase patterns, Instacart can offer personalized recommendations, driving higher customer engagement and repeat business. Data-driven insights also help Instacart identify new opportunities for growth and efficiency, making its business model increasingly robust.
In summary, Instacart’s multi-sided marketplace and gig economy workforce allow it to scale rapidly while keeping costs low. By partnering with retailers and leveraging data analytics, Instacart has created a flexible and profitable app-based business model that has proven highly successful in the competitive delivery app market.
Revenue Streams: How Instacart Makes Money
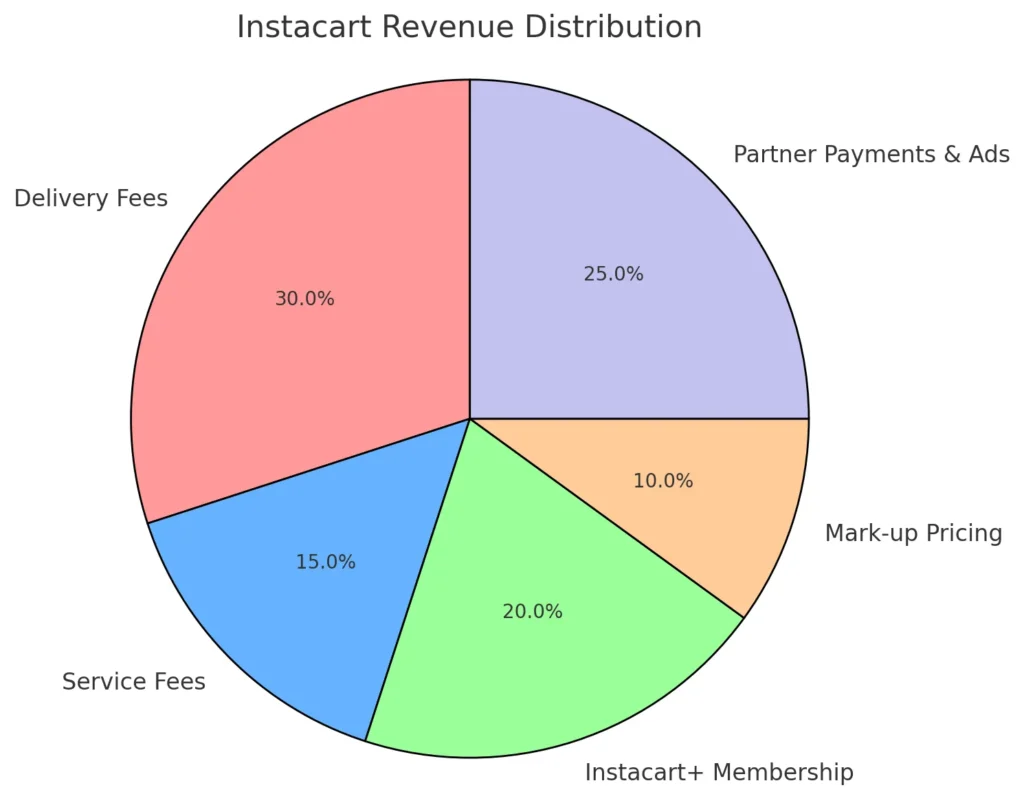
Instacart’s business model is not just about connecting customers with retailers; it’s also a sophisticated platform for generating multiple streams of revenue. From delivery fees to partnerships with brands, Instacart has built a comprehensive approach to monetizing its operations. Here’s a breakdown of how Instacart makes money:
1. Delivery Fees
One of Instacart’s primary revenue streams comes from charging delivery fees. Customers pay a fee based on factors such as the size of their order and the selected delivery window. Standard delivery fees typically range from $3.99 to $9.99, depending on whether the customer opts for same-day delivery or schedules it for a later date. By offering various delivery options, Instacart caters to both budget-conscious users and those who prioritize speed and convenience.
2. Service Fees
In addition to delivery fees, Instacart charges service fees for handling and processing orders. These fees generally account for operating costs such as paying personal shoppers and maintaining the app. Service fees typically range from 5% to 10% of the total order value, but this can vary depending on the location and demand. While service fees are an additional cost for customers, they allow Instacart to keep its operational costs sustainable without raising the base price of products.
3. Instacart Express Membership
Instacart offers a subscription-based service called Instacart Express. For a monthly fee of $9.99 or an annual fee of $99, members receive free delivery on all orders over a certain amount (typically $35). This membership option encourages customer loyalty and repeat orders while providing Instacart with a steady stream of subscription revenue. Instacart Express has been instrumental in boosting customer retention by providing value for frequent users of the service.
4. Retailer Partnerships
Instacart forms partnerships with grocery retailers, allowing them to extend their reach to customers without developing their own on-demand delivery app. Instacart earns a commission from each sale made through its platform, typically taking a percentage of the total order value. This partnership model benefits both parties: retailers gain access to a growing base of online shoppers, while Instacart earns revenue without managing inventory.
5. Advertising Revenue
Another growing revenue stream for Instacart comes from advertising. Brands can pay for premium placement within the app to ensure their products are more visible to customers. Sponsored products and in-app promotions are commonly used by food and beverage companies to increase sales. This advertising model has proven to be highly profitable, particularly as more brands seek to reach online grocery shoppers.
6. Peak Pricing
During periods of high demand, such as holidays or severe weather, Instacart applies peak pricing, where delivery and service fees are temporarily increased. This strategy not only helps manage order volume but also creates an additional revenue source during busy times when customers are willing to pay extra for timely delivery.
| Revenue Stream | Description | Key Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Fees | Charged per order for standard or expedited delivery | Provides flexibility in pricing, catering to different user needs |
| Service Fees | Additional fees for processing and handling orders | Helps cover operational costs without increasing product prices |
| Instacart Express Membership | Monthly or annual subscription for unlimited free deliveries | Encourages customer loyalty and repeat business |
| Retailer Commissions | Percentage of sales made through the platform | Adds an additional income stream from retailers |
| Advertising Revenue | Brands pay for premium placement in the app | Provides a growing source of income through promotions |
| Peak Pricing | Higher fees during high-demand times (e.g., holidays) | Captures additional revenue when demand is high |
Instacart’s ability to generate income from multiple sources—delivery fees, service fees, subscriptions, retailer partnerships, and advertising—gives it a diverse revenue model that keeps the business profitable even as it scales.
Want to launch an on-demand grocery delivery app like Instacart?
We help businesses build feature-rich, scalable, and
user-friendly platforms.
Why Instacart is Successful: Key Factors
Instacart’s meteoric rise in the grocery delivery app industry is no accident. The platform’s success is driven by a combination of strategic decisions, technology innovations, and customer-centric features. Here are the key factors that have contributed to Instacart’s success:
1. Convenience and Flexibility
One of Instacart’s greatest strengths is the convenience it offers. Customers can shop for groceries from the comfort of their homes and have them delivered in as little as an hour. The on-demand delivery app caters to a wide range of users, from those needing quick deliveries to others who prefer scheduling a time slot that fits their schedule. Instacart’s flexible delivery windows give it an edge over traditional grocery shopping, appealing to busy customers looking for time-saving solutions.
2. Gig Economy Workforce
Instacart’s use of gig economy workers plays a crucial role in its operational efficiency. By relying on independent contractors, or personal shoppers, Instacart can keep its staffing costs low while quickly scaling up during periods of high demand. This crowdsourced delivery model allows Instacart to expand its services to new markets without the overhead of employing a large, full-time workforce. It’s a win-win model: shoppers get flexible work, and Instacart maintains a lean operational structure.
3. Scalability and Market Penetration
The online marketplace model has enabled Instacart to scale rapidly across multiple regions. Because Instacart doesn’t own any physical stores or inventory, it can quickly expand into new cities by partnering with local retailers. This scalability has allowed Instacart to penetrate markets where traditional grocery stores have struggled to implement their own delivery services. By forming partnerships with national and local retailers, Instacart ensures widespread availability, making it the go-to solution for online grocery delivery.
4. Pandemic-Driven Growth
The COVID-19 pandemic had a significant impact on consumer behavior, accelerating the adoption of online grocery delivery services. Instacart was well-positioned to capitalize on this shift, experiencing a surge in demand during lockdowns and social distancing periods. As more people turned to online shopping, Instacart rapidly expanded its workforce, onboarding thousands of new personal shoppers. This growth allowed Instacart to not only meet demand but also establish itself as a household name in the delivery app market. According to a report by Statista, the global online grocery market is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, fueled by the demand for convenience and digital solutions.
5. Strong Customer Engagement and Personalization
Instacart excels at maintaining customer engagement through features like personalized product recommendations, loyalty programs, and easy reordering options. The platform uses data analytics to understand customer preferences and offers tailored suggestions, improving the user experience. Additionally, Instacart’s mobile app allows for real-time communication between shoppers and customers, ensuring a smooth shopping and delivery experience. By offering personalized touches and responsive service, Instacart keeps users coming back.
6. Partnerships with Retail Giants
Instacart’s ability to form strategic partnerships with major retailers like Costco, Kroger, and Safeway has been a key factor in its success. These partnerships give Instacart access to an extensive inventory of products and enable it to serve millions of customers across the U.S. and Canada. For retailers, partnering with Instacart offers a low-risk way to tap into the growing online grocery delivery market without the need to invest in their own digital infrastructure.
| Success Factor | Description | Instacart Implementation Example |
|---|---|---|
| Convenience | Provides flexible delivery times and easy ordering | Same-day delivery, real-time tracking, scheduled delivery |
| Scalability | Expands easily without owning physical stores | Partnerships with local and national retailers |
| Gig Economy Workforce | Leverages a flexible workforce for cost-effective delivery | Uses independent contractors for personal shopping |
| Customer Engagement | Ensures high retention through personalization and ease | Personalized product recommendations, loyalty programs |
| Partnerships with Retailers | Forms alliances with grocery chains to expand product access | Partners with retailers like Kroger, Costco, Safeway |
Instacart’s success is fueled by its customer-centric approach, efficient use of the gig economy, and the scalability of its online marketplace model. These factors, combined with its ability to adapt to changing consumer preferences, have made Instacart a dominant player in the grocery delivery platform space.
Comparison with Competitors
The grocery delivery app market is highly competitive, with major players like Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery, and Shipt vying for consumer attention. While each platform offers similar services, Instacart has distinguished itself through strategic decisions and a unique operational model. Here’s how Instacart compares to its key competitors.
| Feature | Instacart | Amazon Fresh | Walmart Grocery | Shipt |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Partnership Model | Partners with local/national stores | Owns inventory, fulfillment centers | Owns inventory, store-based | Partnered with retailers, Target-focused |
| Delivery Workforce | Gig workers (personal shoppers) | Amazon drivers | Walmart staff + third-party | Gig workers |
| Membership | Instacart Express ($9.99/month) | Included with Amazon Prime | No membership required | Shipt membership ($99/year) |
| Availability | Nationwide across various stores | Limited to Prime locations | Nationwide | Nationwide, Target-focused |
| Product Variety | Wide variety, based on local stores | Limited to Amazon inventory | Walmart-only products | Limited to partnered stores |
1. Instacart vs. Amazon Fresh
Amazon Fresh leverages its parent company’s vast logistics network and infrastructure to deliver groceries efficiently. However, unlike Instacart, Amazon Fresh has its own inventory and operates through fulfillment centers. This can limit Amazon Fresh’s ability to provide access to a wide variety of local grocery stores, a key advantage of Instacart’s online marketplace model. Instacart’s partnerships with local retailers allow it to offer more variety and cater to customers looking for specific regional products.
Another distinction is that Amazon Fresh is available primarily to Amazon Prime members, whereas Instacart offers its services to a broader audience, with the option to subscribe to Instacart Express for free delivery.
2. Instacart vs. Walmart Grocery
Walmart Grocery benefits from Walmart’s vast store network, enabling it to offer lower prices and a wide selection of products. While Walmart focuses on a streamlined, cost-effective approach, it lacks the same variety of store options that Instacart provides. Instacart’s ability to connect customers with a range of local and niche retailers, in addition to large chains, makes it more appealing to users looking for specific products or brands.
Moreover, Walmart employs its own delivery staff and third-party services, which can sometimes lead to delays. Instacart’s crowdsourced delivery model, on the other hand, ensures that orders can be fulfilled quickly by personal shoppers, particularly during peak hours.
3. Instacart vs. Shipt
Shipt, owned by Target, operates similarly to Instacart with a focus on same-day delivery. Shipt’s strength lies in its strong partnership with Target, offering exclusive benefits to Target shoppers. However, Shipt’s retail partnerships are more limited compared to Instacart’s expansive network, which spans multiple grocery chains, pharmacies, and specialty stores.
Where Instacart truly shines in comparison is its data-driven personalization and customer experience. Instacart’s use of data analytics to offer personalized product recommendations and its real-time communication between customers and personal shoppers provide a superior shopping experience compared to Shipt.
4. Instacart’s Competitive Edge
Instacart’s unique value proposition lies in its diverse retailer partnerships, crowdsourced delivery model, and customer-centric features. While other competitors may excel in logistics or pricing, Instacart’s wide reach and ability to offer products from both large chains and local retailers make it stand out. Additionally, its flexible delivery options, integration with the gig economy, and use of technology for personalized service give it a significant advantage in the rapidly evolving delivery app market.
Instacart continues to lead by prioritizing flexibility, variety, and user experience, maintaining its position as a top choice for online grocery delivery.
Instacart’s App Features and User Experience
Instacart’s app is designed with simplicity, functionality, and user convenience in mind. It offers a host of features that cater to both customers and personal shoppers, making the shopping experience smooth and enjoyable. Here’s a breakdown of the most important Instacart app features that drive customer engagement and enhance the user experience.
1. User-Friendly Interface
The app’s clean and intuitive design ensures that users can easily browse through products, select stores, and manage their carts. Customers can quickly search for items using the search bar, filter results by store, or explore curated categories such as “Fresh Produce” or “Best Deals.” This easy navigation minimizes friction, ensuring a seamless shopping experience from start to finish.
2. Personalized Recommendations
Instacart uses data-driven insights to offer personalized product recommendations based on users’ shopping history and preferences. When customers log into the app, they’re greeted with suggestions for frequently purchased items, relevant seasonal products, and brand promotions. These personalized touches not only enhance the shopping experience but also encourage customers to make repeat purchases, boosting customer loyalty.
3. Real-Time Order Tracking
One of Instacart’s standout features is its real-time order tracking. From the moment the order is accepted by a personal shopper, customers can track every stage of the shopping process. The app provides updates as the shopper picks items in-store, communicates with the customer regarding substitutions, and delivers the groceries. This transparency ensures that customers are always informed, improving trust and satisfaction.
4. In-App Communication
To further enhance the shopping experience, Instacart allows for in-app communication between shoppers and customers. If a product is unavailable, the shopper can suggest a substitution through the app, and the customer can approve or reject it in real-time. This feature ensures that shoppers can make quick decisions on behalf of the customer, ensuring that orders are fulfilled to the customer’s satisfaction.
5. Scheduled Deliveries and Flexibility
Instacart offers a variety of delivery options to suit different customer needs. Whether users need their groceries within an hour or prefer to schedule their delivery for a later date, the app provides flexibility. Additionally, customers can opt for contactless delivery, which has become increasingly popular in the wake of the COVID-19 pandemic.
6. Shopper-Friendly Features
For personal shoppers, the Instacart app includes features designed to improve efficiency. Shoppers receive detailed instructions for each order, along with suggested routes to navigate the store. They also receive instant payment through the app after completing deliveries, making it an attractive platform for gig economy workers.
In conclusion, Instacart’s app excels by combining user-friendly design, real-time communication, and personalized recommendations. These features ensure a positive and efficient shopping experience for both customers and shoppers, contributing to the platform’s success in the grocery delivery app market.
Lessons Other Businesses Can Learn from Instacart
Instacart’s success offers valuable insights for businesses looking to adopt or enhance their own app-based business models. By understanding what has made Instacart a dominant force in the online grocery delivery space, companies across industries can apply these lessons to improve their own operations and strategies. Here are some key takeaways:
1. Scalable Marketplace Model
One of Instacart’s greatest strengths lies in its scalable marketplace model. Instead of managing its own inventory or warehouses, Instacart partners with existing retailers to offer a vast selection of products. This eliminates the need for costly infrastructure, allowing the business to expand rapidly across regions. Other companies can adopt similar marketplace models, where they serve as an intermediary between sellers and buyers without holding inventory. This approach minimizes operational costs and risks while allowing for quick scalability.
2. Leverage the Gig Economy
Instacart’s reliance on the gig economy has given it the flexibility to scale its workforce up or down based on demand. By using independent contractors as personal shoppers, Instacart has significantly reduced its staffing overhead while maintaining a responsive delivery system. Businesses can follow this model by integrating crowdsourced labor into their operations. Whether for delivery, customer service, or on-demand support, leveraging the gig economy can help reduce fixed costs while maintaining operational flexibility.
3. Prioritize Customer-Centric Features
Instacart’s customer-centric approach is evident in its app design, which focuses on ease of use, personalization, and real-time communication. Businesses should focus on building digital platforms that prioritize customer experience. Offering personalized product recommendations, providing real-time updates, and enabling direct communication between service providers and customers are features that can significantly enhance user satisfaction and retention.
4. Form Strategic Partnerships
Instacart’s success is largely due to its ability to form strategic partnerships with retailers, allowing it to offer a broad product range without managing inventory. Businesses can apply this strategy by partnering with complementary companies to offer a more comprehensive service to customers. For example, e-commerce platforms can partner with logistics companies to offer faster deliveries, or tech startups can collaborate with established brands to enhance their credibility and reach.
5. Data-Driven Decision Making
Instacart excels at using data analytics to improve its operations, from optimizing delivery routes to providing personalized recommendations to customers. Businesses should invest in data-driven strategies to gain insights into customer behavior, streamline operations, and identify new growth opportunities. Data is a powerful tool for improving customer experience and operational efficiency, and companies that harness it effectively can stay ahead of the competition.
6. Adaptability to Market Changes
Finally, Instacart has shown remarkable adaptability, particularly during the COVID-19 pandemic when demand for online grocery delivery surged. Instacart quickly scaled its operations and introduced new features like contactless delivery to meet changing customer preferences. Businesses must remain agile and ready to adapt to market shifts. This means staying attuned to customer needs and being prepared to implement changes rapidly in response to new trends or disruptions.
By adopting these key lessons—scalability, customer focus, strategic partnerships, and data-driven operations—businesses can position themselves for success in today’s competitive digital marketplace.
Challenges and Future Outlook
While Instacart has achieved significant success in the grocery delivery app space, it faces several challenges that could impact its growth and profitability in the future. Understanding these obstacles, along with Instacart’s strategies for overcoming them, can provide a roadmap for businesses navigating similar markets.
1. Increasing Competition
As the demand for online grocery delivery continues to grow, Instacart faces stiff competition from giants like Amazon Fresh, Walmart Grocery, and Target’s Shipt. These companies have the advantage of owning their supply chains, which allows them to offer lower prices and faster delivery. While Instacart’s strength lies in its partnerships with local retailers, competitors are investing heavily in improving logistics, delivery speed, and customer service. To maintain its market share, Instacart must continue innovating, potentially by expanding its retail partnerships or enhancing its technology.
2. Gig Economy Regulations
One of the biggest challenges facing Instacart is the evolving regulatory landscape surrounding the gig economy. Laws such as California’s Assembly Bill 5 (AB5) have raised concerns about the classification of gig workers as independent contractors. If more regions adopt similar laws, Instacart may be forced to reclassify its personal shoppers as employees, which would significantly increase operational costs. The company is already facing legal battles and labor disputes, which could impact its scalability and flexibility.
3. Profitability Concerns
Despite its rapid growth, Instacart has struggled to achieve consistent profitability. The platform operates on thin margins, with significant costs tied to logistics, delivery, and customer acquisition. While Instacart Express subscriptions and advertising revenue have provided new income streams, maintaining profitability remains a challenge. As competitors streamline their operations and increase delivery efficiency, Instacart will need to find ways to reduce its own operational costs, possibly through innovations like automated delivery or more efficient shopper logistics.
4. Logistical Challenges
Managing deliveries, particularly in densely populated urban areas or during peak demand periods, is a constant logistical challenge for Instacart. The company must balance customer expectations for quick delivery with the complexities of coordinating personal shoppers, store inventories, and traffic patterns. To overcome these challenges, Instacart could invest further in data-driven logistics optimization or explore partnerships with last-mile delivery solutions like autonomous vehicles or drones.
5. The Future of Grocery Delivery
The future of online grocery delivery is promising, and Instacart is well-positioned to remain a dominant player. The industry is expected to continue growing as consumer preferences shift toward convenience and digital solutions. Instacart’s focus on data, technology, and scalability provides a solid foundation for future growth. To stay ahead, the company may explore new features such as subscription-based meal kits, partnerships with emerging grocery brands, or expanding its services beyond groceries into new categories like home goods or health products.
In conclusion, while Instacart faces significant challenges—ranging from regulatory issues to profitability concerns—the company has proven its adaptability and resilience. By continuing to innovate and respond to market changes, Instacart can overcome these challenges and remain a leader in the grocery delivery platform space.
Conclusion
Instacart’s journey from a simple grocery delivery app to a dominant force in the on-demand delivery market demonstrates the power of innovation, scalability, and customer-centric strategies. Its online marketplace model, combined with a gig economy workforce and strategic retailer partnerships, has reshaped how consumers shop for groceries.
The platform’s success is driven by its ability to offer flexibility, convenience, and personalized experiences to customers while maintaining operational efficiency through its crowdsourced delivery system. Despite facing challenges from growing competition, regulatory hurdles, and profitability concerns, Instacart’s focus on data-driven innovation and adaptability ensures it remains a major player in the evolving delivery app market.
As the industry continues to grow, Instacart’s future looks promising, with opportunities to expand its services and explore new markets. Businesses looking to replicate Instacart’s success can learn valuable lessons from its business model, customer focus, and ability to leverage the gig economy.
Instacart’s story is one of agility, strategic partnerships, and a deep understanding of evolving consumer needs—a blueprint for success in the digital economy.
Miracuves: Your Partner in On-Demand App Development
If you’re inspired by Instacart’s success and looking to create your own on-demand delivery app, Miracuves can help turn your vision into reality. With our expertise in developing cutting-edge grocery delivery platforms, gig economy solutions, and marketplace models, we are here to guide you every step of the way.
Whether you’re launching a grocery delivery app like Instacart or exploring other on-demand delivery niches, our team at Miracuves has the experience and technology to build a solution tailored to your business needs. From design to deployment, we ensure your app meets industry standards and provides a seamless experience for your users.
Don’t wait to transform your business—contact Miracuves today and take the first step toward developing a scalable, profitable, and innovative app!
Our grocery delivery solution is built for success.
From smart cart functionality to real-time order tracking
FAQs
What is Instacart’s business model?
Instacart operates on an online marketplace model, connecting customers, local retailers, and personal shoppers. It earns revenue through delivery fees, service fees, retailer partnerships, advertising, and subscriptions via Instacart Express.
How does Instacart make money?
Instacart generates revenue through delivery and service fees, commissions from retailers, Instacart Express subscriptions, and advertising revenue from brands that promote their products within the app.
How does Instacart differ from competitors like Amazon Fresh or Walmart Grocery?
Unlike Amazon Fresh or Walmart Grocery, which own their inventory, Instacart partners with local and national retailers, offering a wide range of products through crowdsourced delivery using gig workers.
Who are Instacart’s customers?
Instacart’s customers are individuals seeking convenient, on-demand grocery delivery. It serves consumers who prefer online shopping and fast delivery from local grocery stores through its app.
How does Instacart use the gig economy?
Instacart relies on gig economy workers (personal shoppers) to fulfill orders and deliver groceries. This model provides flexibility for workers and allows Instacart to keep its operational costs low.
Why is Instacart so successful?
Instacart’s success comes from its scalable business model, strategic partnerships with retailers, customer-centric features, and effective use of the gig economy for fast and efficient delivery.
Check out the top-rated grocery delivery solutions offered by Miracuves – built for performance and scale:
- Blinkit like script – Hyperlocal, real-time grocery delivery with live order tracking
- Instacart like script – Includes shopper assignment, scheduling, and multi-store support
- Uber Delivery like script – Designed for fast-paced local logistics and seamless deliveries
- UberEats like script – A flexible platform supporting both restaurant meals and grocery orders
- Fresh Direct like script – A powerful all-in-one platform for fresh groceries, meal kits, and household essentials —delivered straight to your door.








