Uber has redefined transportation, evolving from a humble ride-hailing startup to a multi-billion-dollar tech giant operating across 10,000+ cities worldwide. Founded in 2009, Uber’s innovative approach to transportation didn’t just disrupt the taxi industry but created new standards for convenience and on-demand services. Many aspiring entrepreneurs and businesses have been inspired by this success, leading to the rise of the “Uber clone,” which replicates its business model to cater to various industries But what drives Uber’s incredible success and revenue?
In this article, we dive into Uber’s monetization model to understand how it capitalizes on rides, partnerships, and dynamic pricing to generate billions annually. We’ll explore the technology, business strategies, and revenue streams that make Uber a leader in the ride-hailing industry while also addressing its challenges and future opportunities.
Let’s uncover how Uber transformed the way the world moves and how it continues to thrive despite market disruptions.
Uber’s Core Business Model and Its Foundation
At the heart of Uber’s success is its multi-sided platform, which connects drivers and riders through a seamless mobile app interface. Uber’s business model operates within the on-demand economy framework, providing users with instant access to transportation while creating earning opportunities for drivers. The core foundation lies in Mobility-as-a-Service (MaaS), where Uber facilitates mobility without owning physical vehicles.
Key Components of Uber’s Platform
- Drivers as Partners: Uber doesn’t employ drivers but allows individuals with eligible vehicles to work as independent partners, offering flexibility.
- Riders as Consumers: Riders benefit from affordable, real-time ride-hailing services with multiple vehicle options (UberX, Uber Black, etc.).
- Technology as a Facilitator: Uber leverages GPS tracking and algorithmic matching to minimize wait times and enhance efficiency.
This foundational model offers a win-win solution—providing flexible work opportunities for drivers and reliable transportation for riders.
Also Read:- Monetization Models for Super Apps
Key Revenue Streams That Drive Uber’s Earnings
Uber’s monetization strategy is built on multiple revenue streams, ensuring financial stability and flexibility. Here’s how the company generates billions annually:
| Revenue Stream | Description | Contribution to Revenue |
|---|---|---|
| Ride Commissions | Uber takes a 15% to 30% commission per ride. | Core revenue driver |
| Surge Pricing | Dynamic pricing increases fares during high demand. | Boosts earnings in peak times |
| Premium Rides | Offers luxury rides at higher prices. | Attracts high-end customers |
| Cancellation Fees | Fees charged when riders cancel late. | Compensates drivers & Uber |
| In-app Advertising | Promotes third-party services within the app. | Non-fare revenue stream |
1. Ride Commissions
Uber takes a commission cut ranging from 15% to 30% of the fare for each ride. Drivers earn the remaining portion, creating an incentive to stay active on the platform. The commission-based model provides consistent revenue from daily transactions across markets.
2. Surge Pricing
During high-demand periods, Uber implements surge pricing, where fares increase to reflect market conditions. This not only ensures quicker availability of drivers but also maximizes revenue by leveraging peak times such as holidays or major events.
3. Premium Rides and Services
Uber offers premium services like Uber Black and Uber SUV at higher fares. These luxury options attract customers seeking exclusive experiences and contribute to higher margins.
4. Cancellation Fees
If a rider cancels a booking after a set period, Uber charges a cancellation fee. This adds a small but significant revenue stream and compensates drivers for lost time.
5. Advertising Revenue
In-app advertising allows Uber to promote third-party services, adding a non-fare revenue stream. Businesses pay to reach Uber’s vast user base, further boosting income.
Uber’s ability to diversify its revenue streams strengthens its financial position and ensures sustainability even during economic fluctuations.
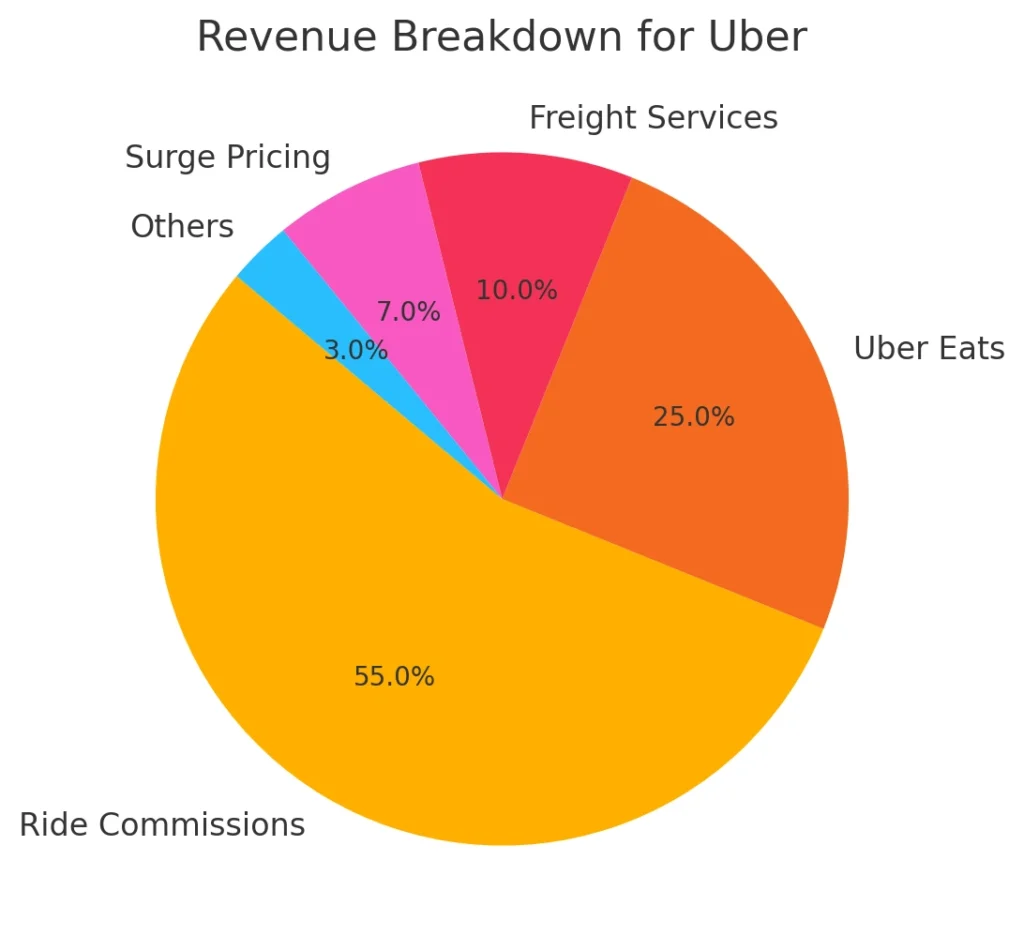
Expansion of Revenue Streams Beyond Ride-Hailing
Uber has evolved beyond its core ride-hailing service by strategically diversifying into new sectors. This has unlocked additional revenue streams and ensured its relevance in a rapidly shifting market.
| Service | Description | Revenue Model |
|---|---|---|
| Uber Eats | Food delivery service | Commission per order, delivery fees |
| Uber Freight | Logistics and freight transportation | Freight fees |
| Uber Direct | Same-day and scheduled package deliveries | Delivery charges |
| Premium Memberships | Subscription plans offering ride discounts | Recurring monthly revenue |
1. Uber Eats and Food Delivery
With the launch of Uber Eats, the company tapped into the booming food delivery industry. This platform connects restaurants, couriers, and customers, charging a commission on orders and delivery fees, creating a significant income source.
2. Uber Freight
Through Uber Freight, the company entered the logistics space, allowing businesses to connect with freight carriers. Uber earns from freight fees, similar to its ride-sharing commission model. This expansion reinforces its presence in transportation while diversifying revenue streams.
3. Uber Direct and Package Deliveries
Uber Direct focuses on same-day and scheduled deliveries for e-commerce businesses and retailers. By offering last-mile delivery solutions, Uber taps into retail partnerships, further expanding its portfolio beyond transportation.
4. In-App Advertising and Sponsorships
Uber’s app serves as a platform for advertising and sponsored content, with businesses paying to promote their products and services to Uber’s extensive user base. This adds a lucrative advertising stream to Uber’s income portfolio.
By capitalizing on these diverse industries, Uber ensures steady growth while minimizing reliance on a single market segment.
Uber Eats continues to expand aggressively, taking advantage of the booming food delivery industry, which is experiencing rapid growth in regions like India. This market shift has increased opportunities for on-demand platforms to diversify revenue streams and reach new customer segments (Statista).
Also Read:- Dynamic Pricing Strategies in On-Demand Services
Uber’s Pricing and Payment Strategies
Uber’s pricing and payment models are designed to enhance user convenience while maximizing revenue. These strategies ensure that the platform remains competitive and profitable.
1. Surge Pricing Algorithm
Uber’s dynamic surge pricing kicks in during periods of high demand—such as rush hours or events—by temporarily raising fares. This not only ensures driver availability but also boosts revenue during peak times.
2. Transparent Fare Estimation
Uber provides users with upfront fare estimates, ensuring transparency and eliminating surprises. Riders know the cost before confirming a trip, improving trust and satisfaction.
3. Flexible Payment Options
The app supports multiple payment methods, including credit cards, digital wallets, and in-app payment systems. This flexibility makes transactions smoother and encourages seamless adoption across regions.
4. Subscription Plans
Uber also offers subscription models, such as Uber Pass, giving users discounted rides for a fixed monthly fee. These plans help build user loyalty and provide predictable recurring revenue.
By combining dynamic pricing, payment flexibility, and subscriptions, Uber creates a seamless financial experience for users while maximizing its profitability.
Uber leverages its pricing power to adjust fares dynamically through surge pricing, especially during peak demand periods. This strategy allows Uber to maintain profitability while ensuring availability of drivers by encouraging them to operate during high-demand hours (Investopedia).
Thinking of launching a ride-sharing service?
Let us help you implement Uber-inspired business
strategies, from revenue-sharing models to ride pricing.
The Role of Technology in Uber’s Success
Uber’s technological infrastructure plays a pivotal role in enhancing the efficiency and scalability of its platform. Through innovative solutions, Uber ensures smooth operations for both drivers and riders while setting new standards in the transportation industry.
1. Driver Matching Algorithms
Uber’s algorithm-based matching ensures that riders are paired with the nearest available drivers. This minimizes wait times and optimizes driver availability, enhancing user satisfaction and boosting efficiency.
2. Real-time GPS Tracking
Uber’s live tracking system offers users visibility of their driver’s location, estimated time of arrival (ETA), and route. This feature builds trust, providing transparency and convenience to both drivers and riders.
3. Autonomous Vehicles and Future Technologies
Uber is actively investing in autonomous vehicles and flying taxis. While still in development, these technologies could reduce costs and create new revenue opportunities in the coming years, keeping Uber ahead of the innovation curve.
4. Integration with Third-Party Platforms
The platform’s integration with services like Spotify enhances the rider experience by offering personalized features. This synergy between technology and user experience strengthens customer loyalty.
By continually investing in cutting-edge technology, Uber ensures operational efficiency and sets the stage for future innovation.
Challenges and Obstacles in Uber’s Business Model
Despite its innovative business model, Uber faces several challenges that impact its growth and profitability. Managing these obstacles is crucial for sustaining its position in the competitive ride-hailing market.
1. Regulatory and Legal Issues
Uber often encounters regulatory challenges in different markets, including disputes with local governments and taxi unions. These issues can result in restrictions, fines, or even temporary bans, impacting its operations.
2. Driver Retention and Satisfaction
Uber’s reliance on drivers as partners presents challenges, as driver turnover remains high. Competitors like Lyft offer incentives to attract drivers, making retention difficult. Balancing driver satisfaction with operational costs remains a critical challenge.
3. Public Backlash Over Surge Pricing
While surge pricing increases revenue, it has faced public criticism for being unfair during emergencies or high-demand events. This has negatively impacted Uber’s public image at times, leading to customer dissatisfaction.
4. IPO Pressures and Profitability Concerns
Since Uber went public in 2019, the company has faced pressure from investors to achieve profitability. Balancing growth investments with the demand for profit remains an ongoing struggle.
By addressing these challenges, Uber aims to sustain its market dominance while ensuring operational efficiency and stakeholder satisfaction.
How Uber Drives Growth through Partnerships and Expansion
Uber’s success lies not only in its ride-hailing operations but also in strategic partnerships and continuous expansion into new markets and sectors.
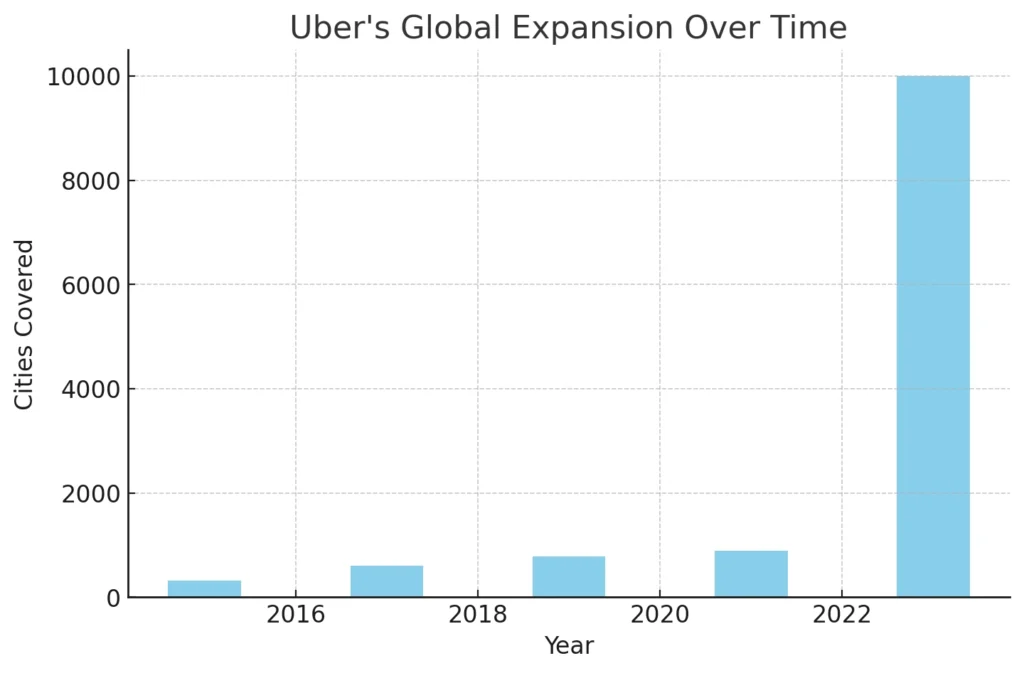
1. Strategic Partnerships
Uber forms alliances with local businesses to promote its services. For example, partnerships with fitness centers offer rides to customers, and integrations with apps like Spotify provide personalized music for riders. These collaborations help Uber build deeper connections with users.
2. Global Market Expansion
Uber aggressively expands into new cities and countries, adapting its services to meet local regulations and cultural expectations. As of now, Uber operates in over 900 metropolitan areas, leveraging global presence to increase revenue streams.
3. Introduction of New Services
To diversify its offerings, Uber has introduced platforms like Uber Eats for food delivery and Uber Freight for logistics. Each new service taps into a different market, expanding Uber’s influence beyond transportation.
4. Embracing Sustainability
Uber is also focusing on sustainability initiatives by introducing electric vehicles and Uber Green services. These efforts align with environmental trends, helping Uber maintain a positive brand image while reducing its carbon footprint.
By leveraging partnerships, global growth, and new services, Uber continues to strengthen its market presence and enhance its appeal across diverse customer segments.
Also Read:- How to Build a Grocery Delivery App Like FreshDirect: Features, Tech, and Cost
Lessons from Uber’s Monetization Model for Aspiring Businesses
Uber’s monetization model offers valuable insights for entrepreneurs and businesses looking to replicate its success. Here are some key takeaways:
1. Prioritize Customer Experience
Uber’s seamless user interface, real-time tracking, and multiple payment options enhance the user experience, ensuring customer satisfaction and loyalty. A similar focus on convenience can elevate any on-demand business.
2. Leverage Dynamic Pricing Models
Uber’s surge pricing strategy maximizes earnings during high demand. Implementing flexible pricing models based on market dynamics can help businesses optimize revenue and manage supply-demand efficiently.
3. Build Strong Partnerships
Strategic collaborations with businesses and local stakeholders allow Uber to expand and diversify its offerings. Entrepreneurs can benefit by forming alliances within their industries to extend market reach.
4. Balance Innovation with Regulation
Uber’s struggles with legal challenges highlight the importance of compliance and adaptability. Balancing innovative strategies with regulatory requirements ensures smoother market entry and sustainability.
5. Diversify Revenue Streams
Uber’s ventures into food delivery, freight, and package services have reduced its reliance on ride-hailing. Businesses can secure their future by exploring additional revenue streams and diversifying operations.
Aspiring entrepreneurs can apply these lessons to their ventures, creating sustainable, growth-oriented business models inspired by Uber’s strategy.
Conclusion
Uber’s ability to evolve from a ride-hailing startup to a multi-service giant showcases the power of innovation, adaptability, and smart monetization strategies. By continuously refining its business model and venturing into food delivery, freight logistics, and sustainable transportation, Uber ensures it stays relevant in a fast-changing market.
However, challenges such as regulatory hurdles, driver retention issues, and public criticism must be navigated carefully. Uber’s success will rely on its ability to balance profitability with customer satisfaction, innovation with compliance, and market expansion with sustainable practices.
With investments in autonomous vehicles and green initiatives, Uber is poised to lead the next wave of transformation in mobility. For entrepreneurs, Uber’s story offers valuable lessons in diversification, customer-centricity, and strategic growth—a blueprint for building successful, future-ready businesses.
Looking to develop your own on-demand service platform? Partner with Miracuves to build innovative, scalable solutions inspired by Uber’s success and accelerate your journey in the competitive on-demand economy.
Want to see how Uber’s business model works in action?
Explore how we can help you build an app with commission-based
revenue, surge pricing, and other monetization strategies that
power successful platforms like Uber.
FAQs
How does Uber’s monetization model work?
Uber generates revenue through multiple streams, including commissions from rides, surge pricing, premium services, and cancellation fees. It also earns from ventures like Uber Eats, Uber Freight, and in-app advertising.
What is surge pricing, and how does it benefit Uber?
Surge pricing is a dynamic fare model where prices increase during high-demand periods, such as peak hours or events. This strategy ensures driver availability and maximizes Uber’s revenue during busy times.
How does Uber maintain profitability despite challenges?
Uber balances profitability by diversifying into multiple sectors, such as food delivery and freight logistics. It also manages operational costs through partnerships, technology investments, and dynamic pricing strategies.
What role do partnerships play in Uber’s success?
Uber collaborates with local businesses and integrates with platforms like Spotify to enhance user experiences. These strategic partnerships drive customer engagement and extend Uber’s reach into new markets.
How can businesses apply Uber’s strategies to their models?
Businesses can replicate Uber’s success by focusing on customer convenience, using dynamic pricing, leveraging partnerships, and exploring new revenue streams. Entrepreneurs can also consult with experts like Miracuves to build on-demand solutions tailored to their industry needs.








