In the ever-growing ride-hailing market, platforms like Uber and Indrive have revolutionized transportation by providing convenience, flexibility, and affordability to users. As these services gain more popularity, startups and businesses are increasingly seeking to replicate their success with Uber clone and Indrive clone solutions—customized apps designed to mimic the core functionalities of these giants.
However, choosing between an Uber clone and an Indrive clone is not merely about aesthetics or user interface. A critical factor for long-term success is scalability. Scalability ensures that a ride-hailing platform can handle increased demand, expand geographically, and adapt to new technological advancements. But which platform is better equipped to scale effectively? In this detailed analysis, we’ll dive into the business models, feature comparisons, architecture, and much more to help you make an informed decision.
Understanding the Business Models: Uber Clone vs. Indrive Clone
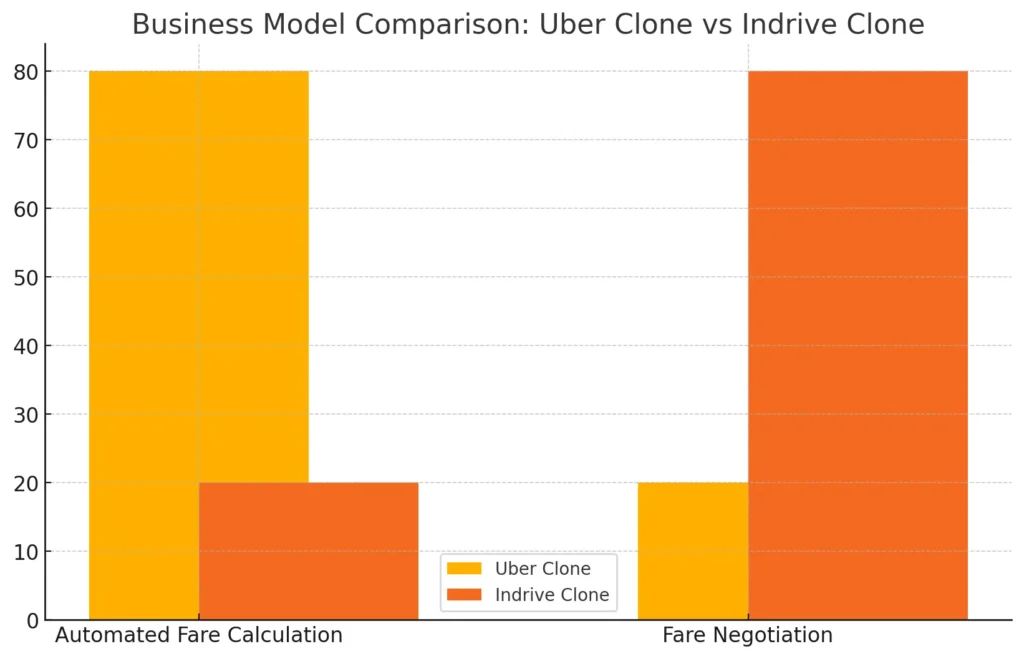
The business model is the foundation of any ride-hailing app, and both Uber clone and Indrive clone operate on distinct frameworks, offering unique advantages.
Uber’s Business Model
The Uber clone is built around a centralized, algorithm-based system that automatically determines ride fares based on variables such as distance, time, and demand. This model promotes consistency and reliability, making it scalable for large, urban markets where seamless user experience and speed are critical. Uber clones rely on fixed pricing, surge pricing, and a commission-based revenue stream from drivers. This system works effectively in cities where users prefer a predictable and automated process.
Indrive’s Business Model
On the other hand, the Indrive clone introduces a more flexible, decentralized pricing model. It operates on a fare negotiation basis, allowing drivers and passengers to agree on a ride price instead of relying on fixed algorithms. This model offers flexibility, especially in markets where haggling or adjusting to local economic conditions is crucial. Indrive’s approach has found success in markets where passengers value the ability to set their own prices and negotiate with drivers.
Business Model Comparison
When comparing the scalability of these models, Uber clones are better suited for rapid scaling in metropolitan areas where a structured, consistent pricing model is favored. In contrast, the Indrive clone’s decentralized system may require more customization to local market conditions, making it highly adaptable but potentially slower to scale in new regions.
Which is better for scalability?
It depends on the target market. The Uber clone offers easier scalability in markets that demand automation and speed. Indrive clones, with their flexible fare system, excel in regions where local economic nuances and negotiation culture are key.
Both Uber and Indrive follow distinct business models that shape their operations and scalability. Learn more about the underlying structure of ride-hailing platforms here.
Also Read :- Future of Indrive Clone Apps
Feature Comparison: Uber Clone vs. Indrive Clone
| Feature | Uber Clone | Indrive Clone |
|---|---|---|
| Business Model | Automated fare calculation and fixed pricing | Fare negotiation between rider and driver |
| Ride Matching | Algorithm-based, fast ride assignment | Manual fare agreement before ride confirmation |
| Scalability | Easily scalable with cloud infrastructure | Customizable for niche/local markets |
| User Verification | Automated (2FA, biometric login) | Manual or automated (depending on customization) |
| Backend Infrastructure | Centralized, robust backend for large user base | Decentralized, adaptable for local requirements |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher initial costs due to complex features | More flexible with lower upfront costs |
| Sustainability Integration | Easily integrates EVs and shared rides globally | More localized sustainability options |
When it comes to building a successful ride-hailing platform, the features integrated into the app play a vital role in its scalability and user experience. Let’s dive into the key feature comparisons between the Uber clone and Indrive clone and explore how they impact the platform’s overall scalability and success.
User Experience and Interface
Both clones offer intuitive, user-friendly interfaces designed to streamline the ride-booking process, but they differ significantly in how the user experience is structured:
- Uber Clone: Prioritizes automation, allowing users to book rides in just a few taps. Uber clones usually come with real-time ride tracking, upfront fare calculations, and integrated payment options. The app is structured to minimize human interaction, ensuring that the process is smooth, efficient, and scalable, particularly in high-demand markets.
- Indrive Clone: Offers a more interactive approach, with its negotiation feature being a standout aspect. Users can propose a fare to the driver, and drivers can accept, reject, or counter the offer. While this adds flexibility and user control, it can slow down the booking process, especially in markets where users are accustomed to automated fare systems like Uber’s.
Driver and Rider Features
- Matching Algorithms: Uber clones rely heavily on automated matching algorithms that connect drivers and passengers based on proximity, traffic conditions, and demand, enabling the platform to handle large volumes of requests efficiently. This system is critical for scalability in dense urban areas where demand can fluctuate rapidly.
- Fare Negotiation: Indrive clones, on the other hand, depend on a manual fare negotiation process. This offers flexibility and adaptability, particularly in regions where local economic conditions vary, but may limit scalability in fast-paced environments due to the added step in the transaction process.
Ride-Hailing Platform Architecture
- Uber Clone: Built on a centralized architecture, the Uber clone uses advanced algorithms to automate everything from fare calculation to ride assignment, making it highly efficient and scalable. The cloud-based infrastructure used by Uber clones allows for rapid expansion to new markets, as it can easily handle increased traffic and user demand.
- Indrive Clone: Uses a decentralized architecture, giving more control to the drivers and passengers during fare negotiations. While this offers greater flexibility and customization for local markets, it may introduce complexity when scaling in regions that demand speed and efficiency, as it relies more on manual inputs.
Performance Under Load
- Uber Clone: Scales more effectively in high-demand scenarios due to its automated fare and ride-matching systems. For example, Uber’s surge pricing ensures that there are always enough drivers available during peak hours, which reduces the likelihood of service outages or delays.
- Indrive Clone: While it can handle significant loads, the fare negotiation process could slow down ride-matching during peak times, making it less efficient in extremely busy markets.
Which features are more scalable? The Uber clone takes the lead in terms of scalability due to its automated systems, making it easier to scale in urban areas with high demand. The Indrive clone excels in flexibility but may require more customization to scale effectively in regions with different economic structures.
A successful ride-hailing platform requires a carefully selected set of features tailored to user expectations and market demands. For Uber clones, the emphasis on automation and scalability supports high-demand areas by providing a smooth, reliable experience across vast user bases. Discover more about the features of a successful Uber clone to see how these elements drive efficiency. On the other hand, Indrive clones prioritize user control and flexibility, a valuable approach in regions where fare negotiation is customary. Explore the key elements of an Indrive clone to understand how this model adapts to diverse economic environments and offers a personalized touch to ride-hailing.
Also Read :- Guide for Building an Uber Clone
Scalability Factors in Ride-Hailing Apps
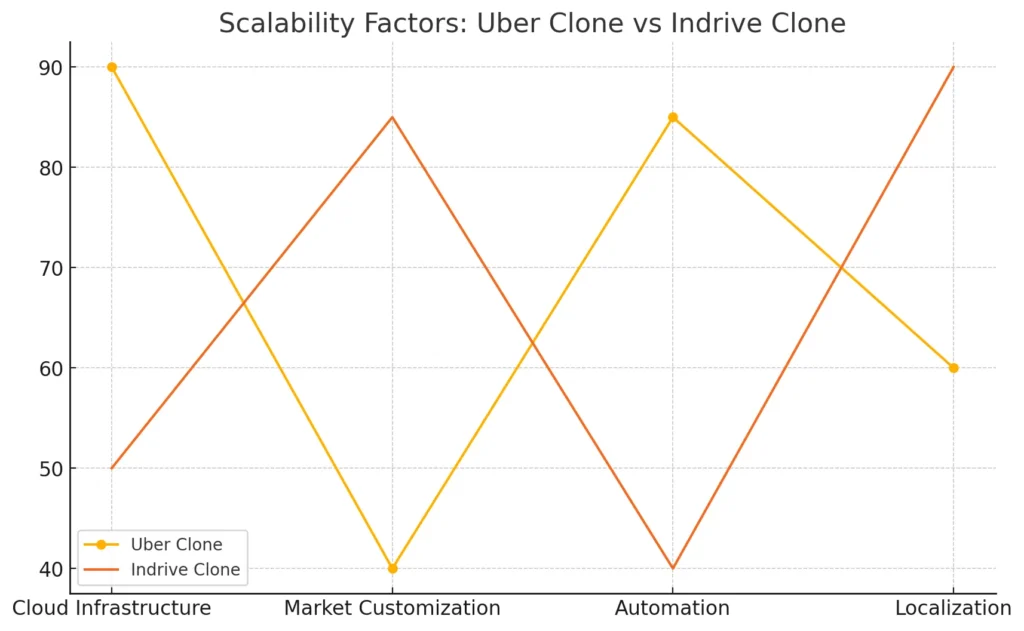
Scalability is a critical consideration when choosing between an Uber clone and an Indrive clone. The infrastructure behind these platforms plays a significant role in determining how well the app can handle increasing demand, geographical expansion, and future growth.
Backend Infrastructure
- Uber Clone: Uber clones are built on cloud-based infrastructures that allow for horizontal scaling. This means they can easily handle large increases in traffic and user data without compromising performance. The centralized architecture used in Uber clones also supports seamless scaling across multiple regions.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones, while also cloud-based, often need additional customizations depending on the market. Their decentralized approach makes them more adaptable to smaller, niche markets but can introduce complexities when scaling up in highly populated areas.
Performance Under Load
- Uber Clone: Uber’s reliance on automated algorithms for ride matching and fare calculation ensures smooth performance during high-demand periods. The platform can handle millions of requests per second, ensuring that both riders and drivers experience minimal latency even during peak times.
- Indrive Clone: While Indrive clones are designed to manage demand, their reliance on manual fare negotiations may slow down the user experience under heavy load. This can be a limiting factor in scaling, especially in busy urban markets where efficiency and speed are crucial.
Data Handling and Analytics
- Uber Clone: Uber clones often come with advanced analytics and AI-driven insights to help optimize operations. These systems can analyze user behavior, predict demand, and offer personalized recommendations, improving both user experience and operational efficiency. This capability ensures that as the platform grows, it can maintain high levels of performance and user satisfaction.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones tend to have simpler data handling mechanisms, as the decentralized model relies more on manual interactions. However, it can still integrate analytics for monitoring user activity, though it may not be as advanced or automated as in an Uber clone.
API Integration and Extensions
- Uber Clone: Uber clones are typically built with a robust API infrastructure that allows for easy integration of third-party services, such as map services (Google Maps, Mapbox), payment gateways (Stripe, PayPal), and other extensions. This makes it easy to scale and add new features as the platform grows.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones also support API integration, though the emphasis is on customization to support local services and payment methods. This adaptability is an advantage in emerging markets, but the process may require additional development time.
Which platform scales better?
The Uber clone is generally more scalable due to its automated systems and centralized architecture, which support rapid scaling across large markets with minimal need for manual intervention. The Indrive clone is more customizable but requires more manual processes, making it suitable for smaller, more flexible markets.
Cloud-based infrastructure plays a crucial role in ensuring the platform can scale rapidly to meet increasing demand. Discover more about the importance of cloud scalability here.
Launching a ride-sharing app with Uber/Indrive features?
Book a demo to see how we can help you implement real-time ride tracking, custom pricing, and seamless payment options—just like the pros.
Security and Privacy Considerations
In today’s digital world, security and privacy are non-negotiable aspects of any online platform. Both the Uber clone and Indrive clone need to ensure that user data is protected, and the platforms are secure from breaches. However, the implementation and approach to security may differ between these clones.
Data Security
- Uber Clone: Uber clones often rely on high-end encryption protocols to secure user data, including sensitive information such as payment details and location history. End-to-end encryption ensures that all communications between users, drivers, and servers remain protected from third-party attacks. Uber clones are typically built with GDPR compliance and other regional data protection laws in mind, which is critical for global scalability.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones may also use encryption technologies but may require additional customization to meet regional data protection requirements, especially in markets where privacy regulations differ. The flexibility of the Indrive clone’s architecture allows for tailored security measures in various regions but may require additional effort to ensure compliance with global standards.
User Verification
- Uber Clone: User verification is typically automated in Uber clones, using methods such as two-factor authentication (2FA), identity verification through documents, and biometric login options. These security measures help reduce fraud, ensure the safety of both riders and drivers, and provide a layer of trust necessary for scaling in various regions.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones may incorporate similar user verification mechanisms, but the manual aspects of fare negotiation could introduce additional vulnerabilities, such as potential exploitation or misrepresentation of identity. Extra verification steps might be needed to ensure that both drivers and passengers are legitimate users of the platform.
Payment Security
- Uber Clone: With in-app payments as a standard feature, Uber clones implement PCI-DSS compliance to safeguard payment transactions. Users can securely store payment methods, and the system can handle various payment gateways, ensuring secure transactions at scale.
- Indrive Clone: Payment security in Indrive clones is equally crucial, especially in regions where users prefer cash payments or local payment systems. Though it may support both in-app payments and cash, special attention must be given to ensuring that all payment data is encrypted and secure from potential fraud.
Which platform is more secure? Both platforms are secure, but the Uber clone takes the lead with more automated security protocols and compliance with global privacy laws. The Indrive clone offers flexibility but may require more region-specific customizations to meet security and privacy standards.
Customer Support and Community Building
As a ride-hailing platform scales, managing customer support and fostering community engagement becomes critical for long-term success. Both the Uber clone and Indrive clone platforms must consider these factors as they grow their user bases.
Scalable Customer Support
- Uber Clone: Uber clones are built with automated support systems like chatbots and AI-driven help desks to manage a high volume of support requests. These automated systems can handle common queries such as fare disputes, driver concerns, and ride cancellations, significantly reducing the need for human intervention. This is crucial for scalability as it helps the platform support large user bases without overwhelming customer service teams.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones may incorporate similar automated support systems, but their reliance on manual fare negotiations means more nuanced issues can arise. Drivers and passengers may need more personalized support, especially when disputes over fare negotiations occur. While this ensures a more human touch in resolving issues, it can become a challenge to scale in larger markets where more automated solutions are necessary.
Feedback Systems
- Uber Clone: The Uber clone features a built-in rating system for both riders and drivers. This feedback loop is essential for maintaining service quality, helping to identify poor-performing drivers or problematic riders quickly. The scalability of this system ensures that, as the platform grows, it continues to self-regulate by relying on user feedback.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones also offer feedback mechanisms but may require more community-driven approaches to ensure transparency and trust. The negotiation-based model could potentially lead to disputes over fare agreements, so robust feedback systems that emphasize transparency between riders and drivers are essential.
Community Engagement
- Uber Clone: Uber clones typically focus on offering rewards or loyalty programs to engage users. These systems can be easily scaled across different regions, helping to retain both riders and drivers.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones can leverage their negotiation-based model to foster stronger community engagement. By allowing users to have more control over their ride fares, the platform can create a more personalized experience that appeals to local cultures. However, maintaining this community-driven approach at scale may require careful attention to regional differences.
Which platform handles customer support and community building better? The Uber clone has the advantage of automated systems that scale easily across regions, while the Indrive clone offers a more personalized approach but may require additional effort to scale efficiently.
Also Read :- Building a Successful Ride-Hailing App Like Via
Sustainability and Environmental Impact
As ride-hailing platforms expand, the focus on sustainability and environmental impact becomes increasingly crucial. Both Uber clone and Indrive clone solutions need to consider eco-friendly practices to meet the growing demand for greener alternatives.
Eco-Friendly Practices
- Uber Clone: Uber clones often integrate electric vehicles (EVs) and ride-sharing options to reduce the carbon footprint. Many Uber clone platforms offer eco-friendly ride choices, such as electric or hybrid vehicles, to help cities reduce emissions. With increasing demand for sustainability, EV partnerships can scale globally, enhancing the platform’s reputation.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones can also integrate EVs, but due to the decentralized model, adopting sustainable practices may depend more on local markets and driver preferences. However, the negotiation-based model can encourage riders to opt for eco-friendly options when available, potentially incentivizing drivers to use EVs or more fuel-efficient vehicles.
Sustainable Growth
- Uber Clone: As an automated and centralized system, Uber clones can more easily implement green initiatives on a global scale. For example, Uber has launched initiatives in various regions that focus on sustainability by promoting shared rides and transitioning to a fully electric fleet in specific markets. This kind of strategy can be scaled across different countries, ensuring that the platform grows sustainably without compromising environmental goals.
- Indrive Clone: While Indrive clones offer flexibility in terms of market-specific sustainability practices, their decentralized nature might mean slower adoption of global eco-friendly initiatives. Localized approaches, such as partnering with government programs to promote sustainable transport options, may be necessary but could take longer to implement at scale.
Which platform supports sustainability better? The Uber clone is more likely to lead in scalability and sustainability initiatives, as its centralized model allows for easier integration of global green efforts. The Indrive clone can support sustainability, but the decentralized, negotiation-driven model may require more localized efforts to implement environmentally conscious options effectively.
Cost of Development and Maintenance
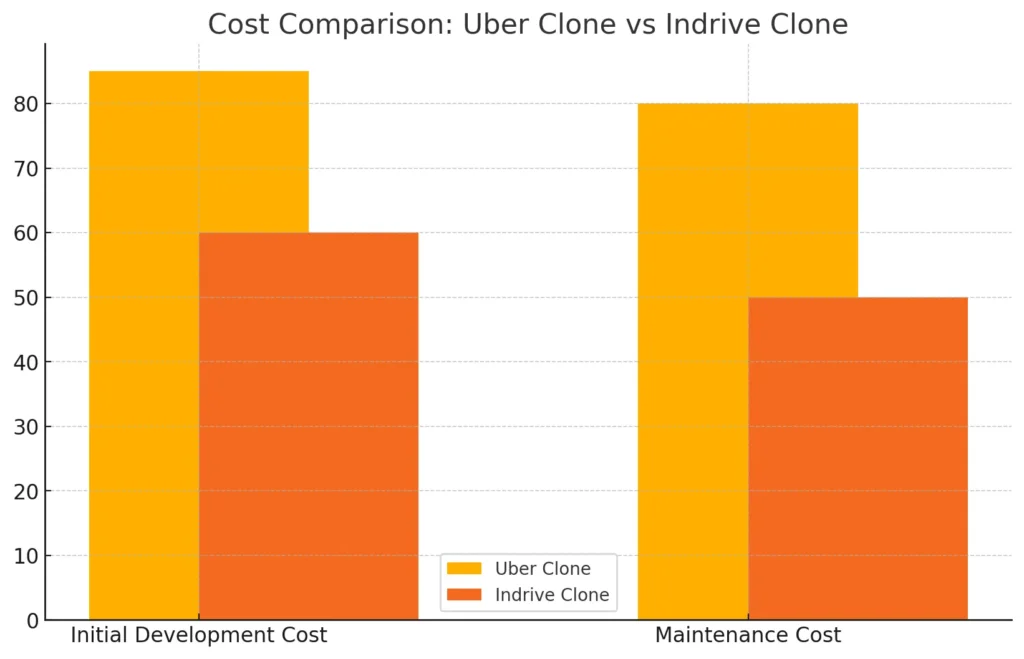
When evaluating cost efficiency in Uber clones, it’s clear that their automated features and scalable architecture offer long-term growth potential, especially for businesses targeting high-demand urban markets. However, the initial investment is higher due to advanced functionalities. In contrast, maintenance strategies for Indrive clones focus on customization for local markets, often requiring manual updates that adapt to regional needs. This flexibility can be beneficial but might involve increased complexity in ongoing support, particularly in diverse or evolving markets.
Initial Development Costs
- Uber Clone: Developing an Uber clone often comes with higher initial development costs due to its sophisticated backend infrastructure, automation features, and advanced algorithms. The cost increases when integrating AI-driven functionalities, cloud-based architecture, and real-time analytics. These features are essential for scalability in large, high-demand markets.
- Indrive Clone: The development cost for an Indrive clone can be more flexible. While it requires a functional backend for fare negotiation and basic ride-hailing features, the decentralized architecture and lower reliance on complex algorithms may result in reduced upfront costs. However, the level of customization needed for fare negotiations and local market requirements could add to the development expenses.
Long-Term Maintenance and Updates
- Uber Clone: Due to the complexity of features, maintaining an Uber clone involves regular updates to improve ride-matching algorithms, ensure payment security, and optimize real-time tracking. Additionally, continuous updates are needed to integrate new technologies like autonomous driving and AI-powered analytics, which can increase long-term maintenance costs.
- Indrive Clone: Indrive clones may require less frequent updates than Uber clones, but maintenance costs could increase in markets that require region-specific customizations. Since fare negotiations are more manual, updates to the system may focus on enhancing user experience, community engagement, and localized payment integrations.
Which platform has better cost efficiency?
- Uber clone: The upfront development costs are higher due to advanced features, but the platform’s scalability potential and automation help maintain long-term growth.
- Indrive clone: Offers more flexibility in terms of initial costs, but the need for localized customizations and manual processes could make maintenance more complex over time.
Conclusion:
In summary, choosing between an Uber clone and an Indrive clone depends largely on your market focus and growth strategy. Uber clones are better suited for rapid, large-scale expansion in urban settings, while Indrive clones offer flexibility and adaptability in niche or developing markets where fare negotiation and local customization are valued.
Both platforms offer scalable solutions but come with different challenges and advantages in terms of cost, feature integration, scalability, and market adaptability. Identifying your target audience, budget, and long-term goals will help determine which clone aligns best with your business needs.
At Miracuves, we specialize in delivering highly customizable, scalable solutions like Uber clones and Indrive clones. Whether you’re looking to dominate urban markets with advanced automation or target niche regions with flexible fare negotiations, we have the expertise to bring your vision to life.
Take the first step toward transforming your ride-hailing business today. Contact Miracuves for a free consultation and see how we can create the perfect solution tailored to your needs!
Visit Miracuves.com to learn more and get started!
Want to start your own Uber/Indrive-like ride-sharing app?
Our expert team can help you create a customized platform with features like real-time ride tracking, driver profiles, and user-driven pricing models.
FAQs
What is the difference between an Uber clone and an Indrive clone?
Uber clones use a centralized, automated fare system, while Indrive clones offer a decentralized, negotiation-based model allowing users to agree on fares with drivers.
Which is more scalable: Uber clone or Indrive clone?
Uber clones tend to be more scalable in high-demand urban markets due to their automated systems, while Indrive clones excel in localized markets requiring fare flexibility.
How much does it cost to develop an Uber clone vs. an Indrive clone?
Uber clones typically have higher upfront development costs due to advanced features and algorithms. Indrive clones can be more cost-effective but may require customizations for local markets.
What are the key features of an Uber clone?
Uber clones include automated fare calculations, real-time tracking, in-app payments, and surge pricing algorithms for scalability and efficiency in high-demand areas.
How does fare negotiation work in an Indrive clone?
Indrive clones allow passengers to propose a fare, and drivers can accept, reject, or negotiate the amount, offering flexibility in regions where fixed pricing isn’t favorable.
Are Uber and Indrive clones eco-friendly?
Both platforms can integrate electric vehicles and eco-friendly ride options. Uber clones often scale green initiatives globally, while Indrive clones may adopt sustainability efforts locally.







