In recent years, food delivery apps have redefined the way we enjoy meals, offering unparalleled convenience. Among these platforms, Uber Eats has emerged as a dominant player, serving millions globally. Its success is attributed not only to its seamless user interface but also to an intricate monetization strategy that transforms each order into revenue.
By leveraging existing infrastructure, such as Uber’s driver network, and exploring multiple revenue streams—like delivery fees, commissions, and in-app promotions—Uber Eats has built a resilient business model. Understanding how these elements fit together provides valuable insights for businesses aiming to replicate this model or compete in the growing on-demand economy. Here you can explore our pre-built Uber like app
This article will explore Uber Eats’ core revenue model, partnerships with restaurants and delivery personnel, innovative pricing strategies, and future growth prospects, ensuring a comprehensive look at how the platform sustains profitability in a highly competitive market.
The Core Monetization Model of Uber Eats
| Revenue Stream | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Commissions | Percentage charged to restaurants for orders received. | 30% for Uber driver deliveries, 16% for restaurant staff. |
| Delivery Fees | Variable fee charged to customers based on distance and location. | $5 during normal hours, $8 during surge. |
| Surge Pricing | Increased delivery fees during high-demand periods. | Fees 1.5x to 3x normal delivery costs. |
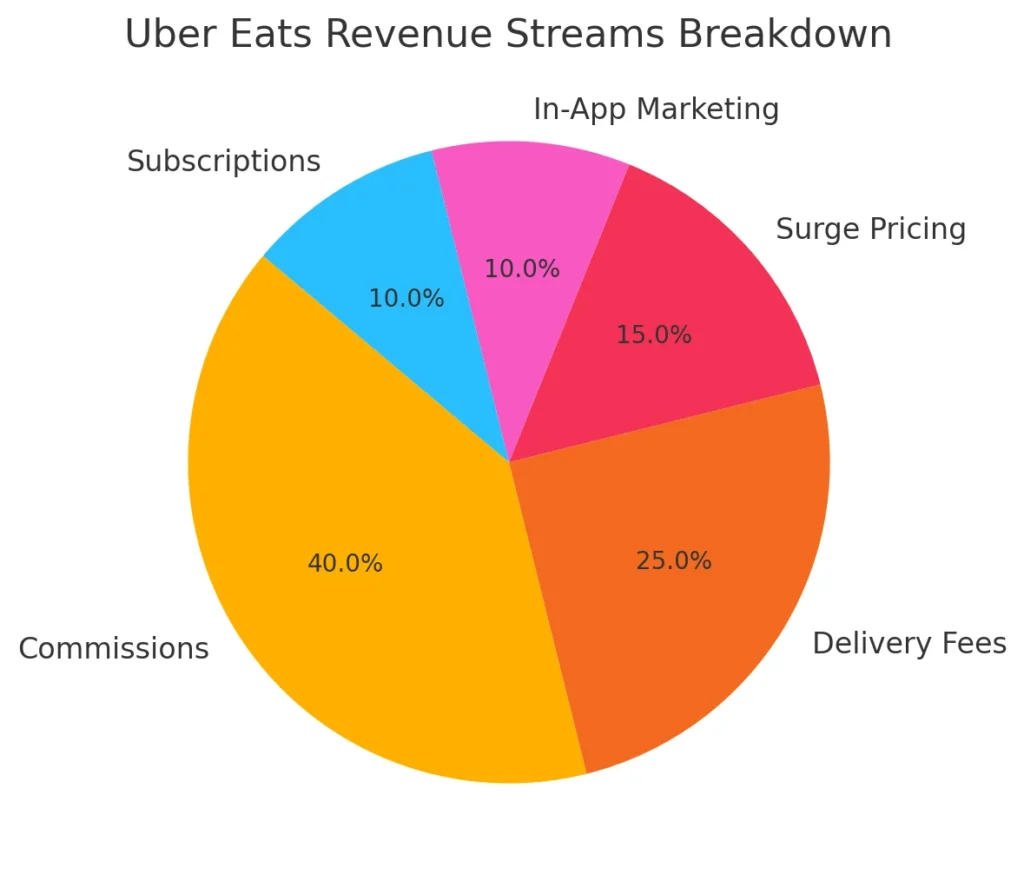
Uber Eats employs a multi-revenue model that relies on key strategies to generate profits:
- Commissions from Restaurant Partners
- Uber Eats charges restaurants a commission fee for each order. This fee varies based on who handles the delivery: 30% for Uber drivers, 16% for restaurant staff, and a smaller fee for customer pickups.
- Delivery Fees for Users
- The app charges end-users a delivery fee that adjusts based on distance, location, and driver availability.
- Surge Pricing Mechanism
- During periods of high demand, Uber Eats introduces surge pricing to encourage more drivers to become available, ensuring timely deliveries.
Also Read:- Build an App Like Instacart
Operational Partners Driving Profitability
- Restaurant Partnerships
- Uber Eats allows restaurants to extend their reach without the need for individual apps, offering exposure through its in-app marketing tools and increasing sales.
- Delivery Partners
- The platform relies on independent contractors (delivery drivers) who earn through a combination of base pay, bonuses, and surge pricing. This decentralized workforce helps Uber Eats scale efficiently.
- End Users
- For customers, Uber Eats offers a smooth experience through features like live order tracking, scheduled deliveries, and multiple payment options, ensuring satisfaction and retention.
Additional Revenue Streams and Innovations
- In-App Marketing and Promotions
- Uber Eats generates extra revenue by allowing restaurants to pay for sponsored listings and enhanced visibility within the app.
- Subscription Services (Uber Eats Pass)
- Uber Eats offers premium subscriptions, providing customers with discounts and free deliveries, encouraging long-term loyalty.
- Grocery Delivery Expansion
- Beyond food delivery, Uber Eats now offers grocery services in select regions, diversifying its revenue streams and expanding market share.
Also Read:- DoorDash Monetization Model & Growth Strategy
Looking to replicate UberEats’ business model?
We can help you design a profitable structure with delivery fees, restaurant partnerships, and customer loyalty programs.
Competitive Landscape and Market Share
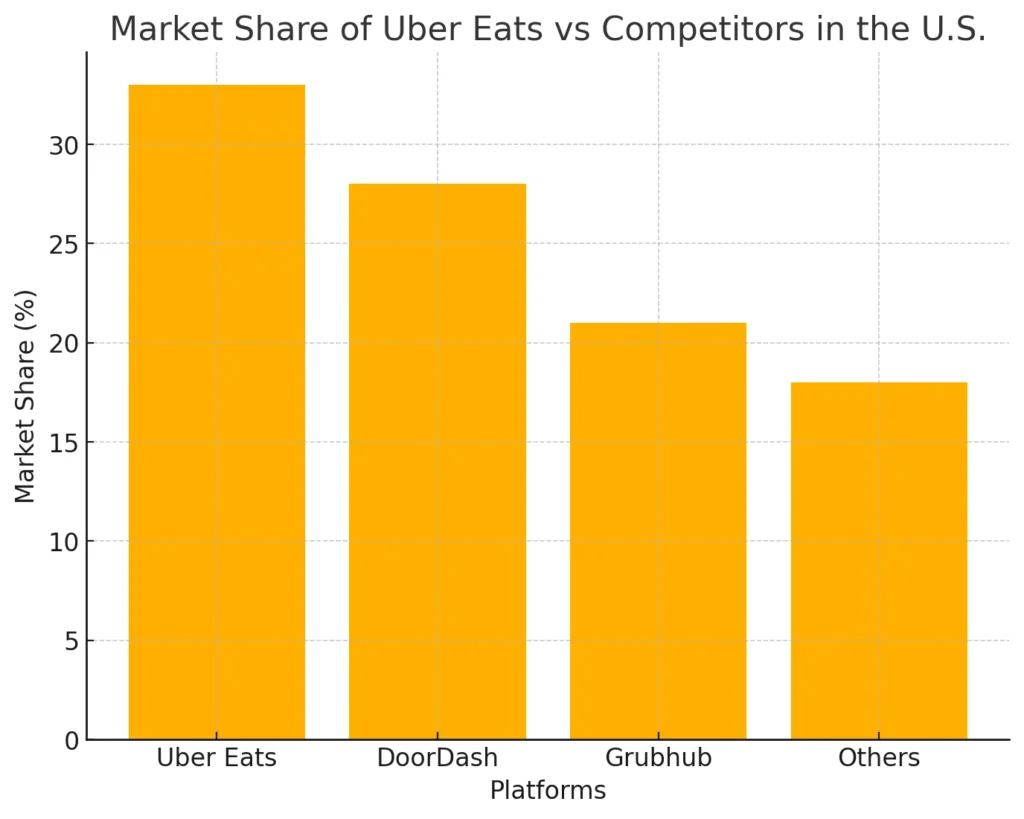
Uber Eats operates in an increasingly competitive food delivery industry, vying for dominance with other major players like DoorDash and Grubhub. As of the latest market analysis, Uber Eats holds approximately 33% market share in the U.S., just ahead of DoorDash with 28%.
- Global Reach
- Unlike many competitors, Uber Eats capitalizes on international markets. With operations in over 11,000 cities worldwide, it leverages Uber’s ride-hailing infrastructure to streamline operations.
- Adapting to Regional Competitors
- Despite its global footprint, Uber Eats faces challenges from local delivery platforms with aggressive pricing and specialized marketing strategies. This competition forces Uber Eats to innovate and expand offerings continuously.
Uber Eats continues to hold a significant portion of the U.S. market share, closely competing with DoorDash and Grubhub, as shown in recent data.” For a detailed market analysis, visit 6sense.
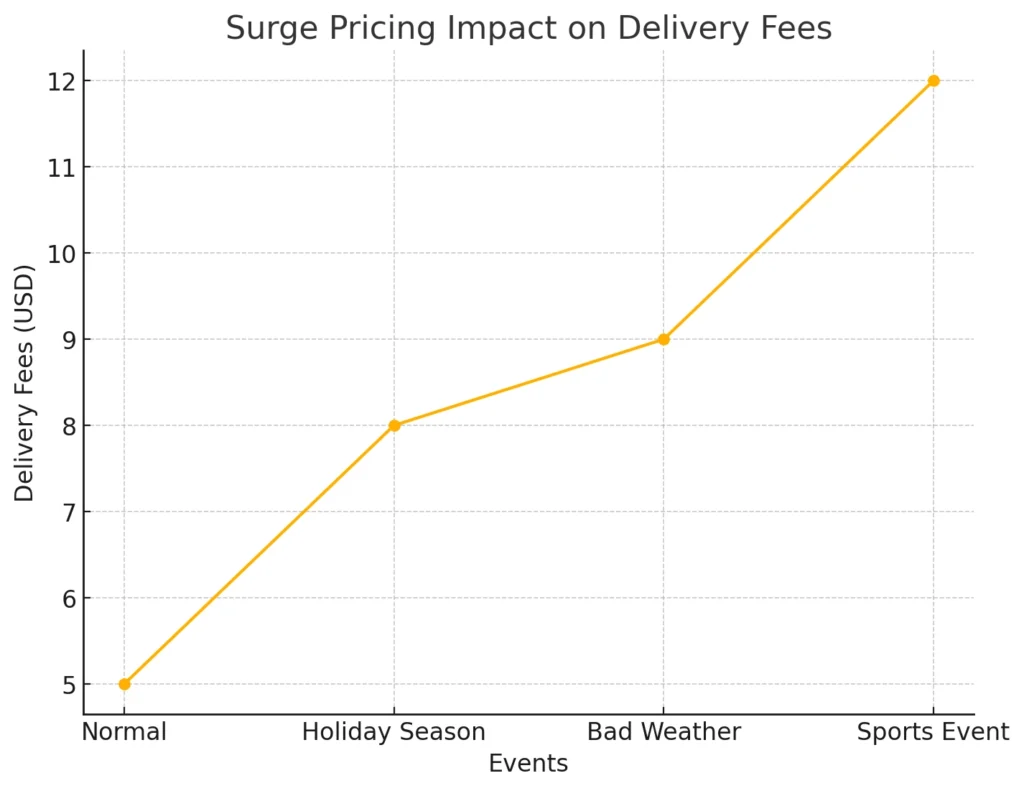
Real-World Examples of Surge Pricing
| Event | Surge Pricing Factor | Impact on Fees |
|---|---|---|
| Holiday Season | High order volume, limited drivers | 2x increase in delivery fees |
| Bad Weather | Fewer drivers available | 1.8x normal fees |
| Sports Finals | Peak demand from group orders | Up to 3x normal delivery fee |
- Impact of Peak Demand
- During high-demand events like holidays, sporting events, or storms, Uber Eats uses surge pricing to incentivize more drivers to come online. This ensures prompt deliveries even during busy periods.
- Dynamic Fee Structure
- For example, a delivery that typically costs $5 may increase to $8 or more during peak times. The platform calculates these fees based on driver availability and order density within specific locations.
- Customer Behavior
- While surge pricing boosts driver participation, it can discourage customers from placing smaller orders due to higher fees, influencing order patterns and delivery efficiency.
Also Read:- Build a Food Delivery App Like Uber Eats
Challenges with Independent Contractors
- Gig Economy Regulations
- Uber Eats’ reliance on independent drivers faces growing scrutiny, with legal battles around driver classification (employee vs. contractor). Changes in regulations could affect labor costs and profitability.
- Driver Turnover
- High turnover rates among drivers present operational challenges, affecting delivery times and service quality. Maintaining a reliable delivery workforce requires balancing pay incentives and fair working conditions.
- Managing Driver Satisfaction
- Dissatisfied drivers can impact customer experience, as delays or poor service could lead to negative reviews and harm Uber Eats’ reputation.
The gig economy, while providing flexible work opportunities, has introduced challenges around labor regulations and worker classification, impacting companies like Uber Eats.” Learn more about the rise of gig work and its implications here from Sodales Solutions.
Deeper Insight into Grocery Expansion
- Impact on the Business Model
- Expanding into grocery delivery adds new revenue streams, helping Uber Eats diversify beyond food orders. This move strengthens its position against delivery-only grocery platforms like Instacart.
- Operational Challenges
- Managing groceries requires different logistics, such as cold storage for perishables and more precise delivery windows, adding complexity to operations.
- Market Competition
- Uber Eats competes with well-established grocery platforms. Its ability to leverage existing infrastructure and cross-promote with Uber rides provides a competitive edge.
Key Challenges in Monetization
- Operational Risks
- As Uber Eats relies on drivers and restaurants, inconsistent service quality—such as late deliveries or incorrect orders—can negatively impact customer satisfaction and retention.
- Intense Market Competition
- Competing platforms like DoorDash and local delivery services adopt aggressive marketing tactics, including lower fees, forcing Uber Eats to continuously innovate to stay ahead.
- Reputation Management
- Uber Eats must manage the risk of negative reviews and delivery complaints, which can harm brand perception and reduce customer trust.
Future Growth Prospects and Trends
- AI and Tech Innovations
- Uber Eats is actively exploring AI-powered order management and drone deliveries to reduce delivery times and costs, staying at the forefront of technology.
- Subscription and Loyalty Programs
- Expanding programs like Uber Eats Pass with exclusive discounts strengthens customer retention and boosts recurring revenue.
- Expansion into New Delivery Verticals
- Uber Eats is venturing into retail and pharmacy deliveries, adding diversity to its platform and enhancing its competitive edge in the evolving on-demand economy.
Conclusion
Uber Eats has transformed food delivery by leveraging a multi-revenue model that includes commissions, delivery fees, surge pricing, and in-app promotions. Its success lies in balancing operational efficiency with innovative expansions like grocery delivery and premium subscriptions. However, challenges such as driver turnover, competition, and evolving gig economy regulations present hurdles.
Looking ahead, Uber Eats’ growth will depend on its ability to adopt new technologies, expand into new delivery verticals, and enhance customer loyalty through subscriptions and rewards programs. Continuous innovation will be essential to maintain its competitive edge in the dynamic on-demand market.
Ready to build your own on-demand delivery app like Uber Eats? Miracuves offers customizable, ready-to-launch solutions tailored to your business needs. Leverage our expertise to develop feature-rich platforms with advanced order management and seamless delivery capabilities. Whether it’s food delivery, grocery services, or retail, we’ve got you covered with cutting-edge technology and personalized support.
Visit Miracuves today and discover how we can help turn your business ideas into a thriving reality!
Related Posts:-
- Create a Food Delivery App Like Swiggy
- BigBasket Business Model Explained
- Create a Delivery App Like Rappi
Want to launch your own food delivery platform like UberEats?
Our pre-built solution comes with real-time order tracking,
restaurant management, and secure payment options.
FAQs
How does Uber Eats generate its primary revenue?
Uber Eats earns revenue through commissions from restaurants, delivery fees from customers, and surge pricing during peak hours.
What is surge pricing on Uber Eats?
Surge pricing increases delivery fees based on high demand, limited driver availability, or specific events, encouraging drivers to accept more orders.
How do drivers earn through Uber Eats?
Drivers are paid per order, including base fees, distance-based fees, and surge bonuses. They can also receive customer tips.
What benefits do restaurants get by partnering with Uber Eats?
Restaurants gain increased visibility, access to in-app marketing, and an expanded customer base without needing their own delivery infrastructure.
How has Uber Eats expanded beyond food delivery?
Uber Eats has expanded into grocery, retail, and pharmacy deliveries to diversify revenue and meet evolving customer demands.







