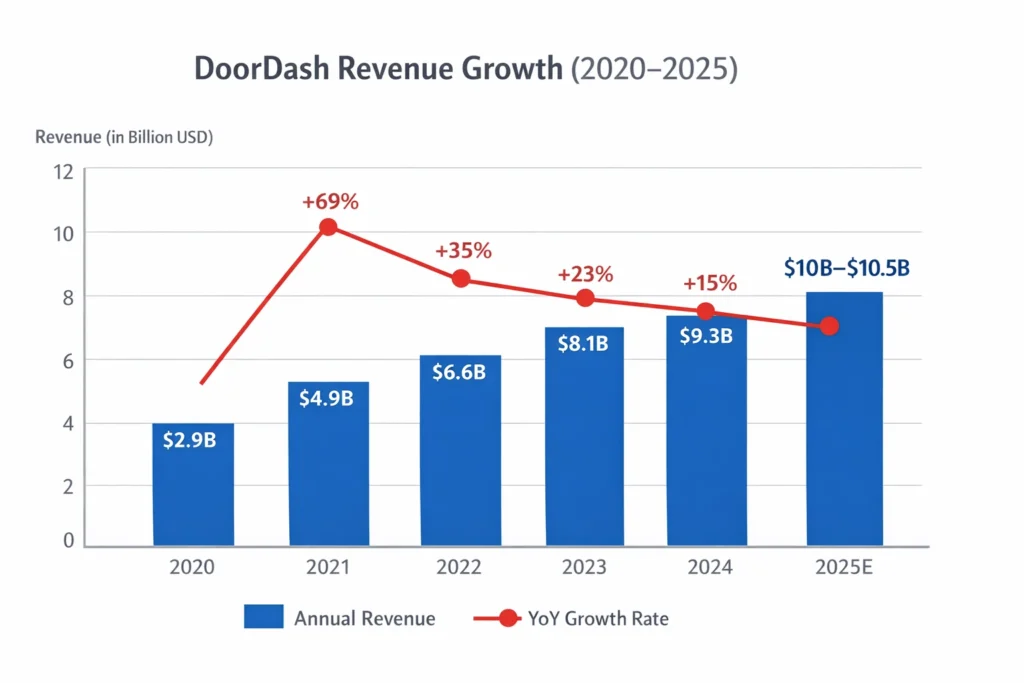
DoorDash reported approximately $10–10.5 billion in revenue in 2025, and within that massive figure, DashMart has quietly evolved into one of the company’s most strategic growth engines. While restaurant delivery fueled DoorDash’s early scale, DashMart represents its shift toward higher-margin, repeat-use commerce built around everyday essentials.
Unlike traditional food delivery marketplaces that depend heavily on commissions from third-party restaurants, DoorDash Mart operates as an inventory-owned instant commerce model. By owning the products, pricing, and fulfillment flow, DoorDash captures retail margins, controls customer experience, and reduces its dependence on partner fees—fundamentally changing its unit economics.
For entrepreneurs and founders, DashMart offers a powerful lesson in modern commerce. It shows how owning supply chains, leveraging demand data, and optimizing hyperlocal fulfillment can transform delivery platforms from low-margin intermediaries into scalable, profit-oriented retail businesses within the quick commerce ecosystem.
DoorDash Mart Revenue Overview – The Big Picture
DoorDash Mart, commonly branded as DashMart, is DoorDash’s network of dark stores offering groceries, snacks, beverages, alcohol, and daily essentials with ultra-fast delivery.
In 2025, DashMart contributed an estimated 8–12% of DoorDash’s total revenue, but more importantly, it delivered significantly higher gross margins than restaurant delivery.
DoorDash’s overall valuation in 2025 hovered around $60–65 billion, supported by diversification beyond food delivery. DashMart’s year-over-year growth is estimated at 35–40%, driven by repeat usage and subscription customers.
Revenue is heavily concentrated in the United States, with limited international expansion. Gross margins range between 30–40%, outperforming third-party marketplace delivery. Competitors include GoPuff, Getir, Instacart Express, and Uber Eats convenience verticals.
Read More: How Safe is a White-Label DoorDash App? Security Guide 2025
Primary Revenue Streams Deep Dive
DashMart’s monetization strategy is built around margin ownership and frequency, not commissions.
Revenue Stream #1: Inventory Sales & Retail Margins
DashMart purchases goods wholesale and sells them directly to consumers.
This allows DoorDash to capture retail margins similar to convenience stores while leveraging its logistics network. Markups vary by category, with snacks, beverages, and private-label products generating the highest margins.
This stream alone accounts for more than half of DashMart’s total revenue.
Revenue Stream #2: Delivery Fees
Customers pay delivery fees on each order unless covered by DashPass.
Fees are dynamically adjusted based on demand, time of day, and distance. While lower than restaurant delivery fees, the volume makes this a meaningful contributor.
Revenue Stream #3: DashPass Subscriptions
DashPass offers free or discounted delivery for a monthly fee of around $9.99.
Subscribers order more frequently, increasing overall lifetime value and stabilizing revenue. DashPass also reduces price sensitivity across other revenue streams.
Revenue Stream #4: Advertising & Sponsored Listings
Consumer packaged goods brands pay to promote products within DashMart.
Sponsored listings, banner placements, and targeted ads turn DashMart into a retail media network, one of the fastest-growing monetization layers.
Revenue Stream #5: High-Value Categories & Add-ons
Alcohol, health products, and late-night essentials carry higher average order values and margins, boosting profitability per delivery.
Revenue Streams Breakdown
| Revenue Stream | Share of DashMart Revenue |
|---|---|
| Inventory margins | 55–60% |
| Delivery fees | 14–16% |
| DashPass subscriptions | 9–11% |
| Advertising & promotions | 8–10% |
| Alcohol & premium add-ons | 5–7% |
The Fee Structure Explained
DashMart’s fee model is intentionally simple for users but layered underneath.
User-Side Fees
Customers may pay a delivery fee, a small service fee, and surge pricing during peak hours. These fees are often waived or reduced for DashPass members.
Provider-Side Fees
There are no merchant commissions because DoorDash owns the inventory directly.
Hidden Revenue Layers
DashMart benefits from wholesale rebates, supplier-funded promotions, and private-label margins that are invisible to end users.
Regional Pricing Variations
Urban areas typically feature lower delivery fees but higher order frequency, while suburban regions rely on higher fees and larger basket sizes.
Fee Structure by User Type
| User Type | Fees Paid | Monetization Logic |
|---|---|---|
| Regular customers | Delivery + service fees | Transaction-based revenue |
| DashPass members | Subscription fee | Recurring revenue + higher LTV |
| Brands & suppliers | Ad spend | High-margin retail media income |
How DoorDash Mart Maximizes Revenue Per User
DashMart is engineered to increase order frequency rather than order size alone.
Customer segmentation targets late-night users, families, and repeat essentials buyers. Upselling is driven through smart bundles, while cross-selling integrates DashMart items into restaurant orders.
Dynamic pricing adjusts delivery fees and product pricing in real time. Retention is powered by DashPass, which locks users into habitual ordering behavior.
Psychological pricing strategies such as $9.99 bundles, free-delivery thresholds, and limited-time deals increase conversion. DashPass users place more than twice as many monthly orders compared to non-subscribers.
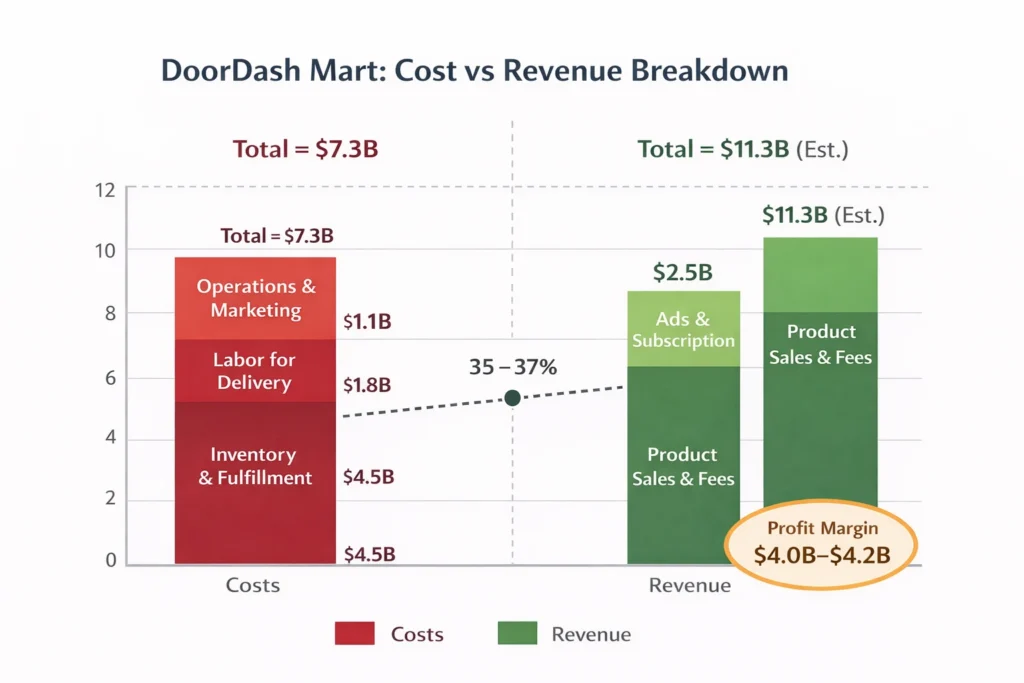
Cost Structure & Profit Margins
DashMart’s cost structure is heavier than a marketplace but more defensible.
Key costs include dark-store leases, utilities, cold storage, last-mile delivery incentives, inventory spoilage, and technology investments. Marketing spend focuses on in-app promotions rather than external advertising, lowering CAC over time.
With average order values between $28–35, mature DashMart locations achieve positive contribution margins. Profitability improves with store density, private-label expansion, and automation in fulfillment.
Read More: Best DoorDash Clone Script 2025 — Launch Your Food Delivery App
Future Revenue Opportunities & Innovations
DashMart’s future lies in scaling efficiency and data monetization.
AI-driven demand forecasting reduces inventory waste. Private-label expansion improves margins. Advertising is expected to exceed 15% of DashMart revenue by 2027.
Expansion into health, wellness, and B2B essentials presents new growth channels. Automation and micro-fulfillment centers will further reduce per-order costs.
For founders, the biggest opportunity lies in localized instant commerce platforms outside saturated metro markets.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Your Opportunity
DashMart proves that owning supply chains unlocks margin control.
Founders can replicate dark-store logistics, focus on high-frequency SKUs, and bundle subscriptions for predictable revenue. Major gaps exist in Tier-2 cities and vertical-specific quick commerce like pharmacy, office supplies, and campus delivery.
Platforms that prioritize frequency and convenience can scale faster than traditional marketplaces.
Want to build a platform with DoorDash Mart’s proven revenue model? Miracuves helps entrepreneurs launch revenue-generating platforms with built-in monetization systems. Our DoorDash Mart–style clone solutions come with flexible revenue models you can customize. Some clients see revenue within 30 days of launch, and if you want it, we may arrange and deliver it in 3–6 days with guaranteed delivery.
If you want advanced language-level scripts or enhanced versions, Miracuves provides those too.
Final Thought
DashMart proves that delivery platforms don’t need to depend on commissions forever. By owning inventory, pricing, and fulfillment, DoorDash Clone shifted from being a middleman to becoming a retail operator with stronger control over margins and customer experience.
The real advantage lies in frequency. Daily essentials, fast fulfillment, and subscription-driven behavior turn occasional users into habitual buyers, significantly improving lifetime value and reducing long-term acquisition costs.
For entrepreneurs, DashMart highlights the power of vertical focus and localized execution. Success doesn’t require national scale from day one—dense coverage, smart SKU selection, and operational efficiency matter more.
FAQs
1. How much does DoorDash Mart make per transaction?
Around $8–12 gross profit per order in mature markets.
2. What’s DashMart’s most profitable revenue stream?
Inventory margins, especially private-label products.
3. How does DashMart’s pricing compare to competitors?
Slightly higher than supermarkets but competitive with GoPuff.
4. What percentage does DoorDash take from providers?
None, as DoorDash owns the inventory.
5. How has DashMart’s revenue model evolved?
From delivery commissions to margin-led retail and advertising.
6. Can small platforms use similar models?
Yes, especially in focused local markets.
7. What’s the minimum scale for profitability?
Dense urban coverage with repeat users.
8. How to implement similar revenue models?
Combine dark stores, subscriptions, and data-driven pricing.
9. What are alternatives to DashMart’s model?
Pure marketplace delivery or hybrid commission-retail models.
10. How quickly can similar platforms monetize?
Many begin generating revenue within weeks of launch.








