Worldpay processes over $2.3 trillion in annual payment volume across 140+ countries, making it one of the most powerful yet least visible players in global commerce. While consumers may never interact with Worldpay directly, millions of businesses rely on its infrastructure every day to accept payments seamlessly—online, in-store, and across borders. This scale alone makes the business model of Worldpay worth close study.
Unlike flashy consumer fintech apps, Worldpay grew by mastering the unglamorous but mission-critical layers of payments. Originally spun out of Royal Bank of Scotland, later acquired by Vantiv and then integrated into FIS, Worldpay scaled through strategic acquisitions, deep compliance expertise, and enterprise-grade technology. Its evolution highlights how B2B platforms can dominate markets by prioritizing reliability, trust, and ecosystem alignment.
In 2026, as digital commerce, embedded finance, and global marketplaces accelerate, the business model Worldpay offers founders a clear lesson: sustainable scale comes from owning critical infrastructure. For entrepreneurs building fintech, SaaS, or marketplace platforms, Worldpay demonstrates how strong backend systems unlock massive front-end growth—an approach Miracuves helps founders implement every day.
How the Worldpay Business Model Works
Worldpay operates as a global payments infrastructure platform, not a consumer-facing app. Its business model is designed to enable, route, secure, and monetize digital and physical transactions for businesses at scale .At its core, Worldpay sits between merchants, consumers, banks, card networks, and regulators, ensuring that every transaction is authorized, processed, settled, and compliant—within milliseconds.
High-Level Overview
Worldpay’s model is best described as a Hybrid B2B Payments Platform, combining:
- Payment processing
- Financial technology services
- Compliance and risk management
- Value-added data and optimization tools
Unlike simple payment gateways, Worldpay owns deep layers of the stack—technology, acquiring licenses, global compliance, and enterprise integrations—making it extremely hard to replace once embedded.
Key Business Model Components
1. Type of Business Model
- Primary Model: B2B Payments Infrastructure Platform
- Supporting Models:
- Transaction-based pricing
- Enterprise SaaS-like service contracts
- Embedded finance enabler for platforms and marketplaces
- Transaction-based pricing
This hybrid approach allows Worldpay to earn revenue every time money moves, while also locking in long-term enterprise relationships.
2. Value Proposition by User Segment
Worldpay creates tailored value for multiple stakeholders:
- Merchants & Enterprises
- Accept payments globally (cards, wallets, BNPL, local methods)
- Higher authorization rates through smart routing
- Reduced fraud and chargebacks
- One integration, global reach
- Accept payments globally (cards, wallets, BNPL, local methods)
- SMEs & Digital Businesses
- Fast onboarding and scalable payment tools
- Subscription and recurring billing support
- Omnichannel (online + in-store) payments
- Fast onboarding and scalable payment tools
- Platforms & Marketplaces
- Split payments and payouts
- Embedded compliance and KYC
- White-labeled payment infrastructure
- Split payments and payouts
- Banks & Financial Institutions
- Outsourced acquiring and processing capabilities
- Regulatory-grade infrastructure without rebuilding internally
- Outsourced acquiring and processing capabilities
3. Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
Worldpay’s ecosystem stays balanced through clearly defined roles:
- Merchants: Generate transaction volume (core revenue driver)
- Consumers: Initiate payments (indirect users)
- Issuing Banks: Approve or decline transactions
- Card Networks: Visa, Mastercard, AmEx, etc.
- Regulators: Enforce compliance across regions
- Technology Partners: POS systems, eCommerce platforms, APIs
Worldpay’s success depends on trust and reliability across all these actors.
4. Evolution of the Model
Worldpay’s business model has evolved significantly:
- Early Phase: Basic card payment processing
- Growth Phase: Global acquiring + enterprise focus
- Platform Phase (2020–2026):
- Embedded payments
- Omnichannel commerce
- Advanced fraud, data, and optimization layers
- Support for digital wallets, BNPL, and real-time payments
- Embedded payments
Each evolution added new revenue layers without breaking the core transaction engine.
5. Why the Model Works in 2026
Worldpay’s model aligns perfectly with current market dynamics:
- Explosion of cross-border eCommerce
- Rise of subscription and usage-based billing
- Growth of platform economies and marketplaces
- Increasing regulatory complexity, which favors large, compliant players
- Demand for high uptime and low latency payment systems
The more complex the ecosystem becomes, the more valuable a trusted platform intermediary gets.
This is exactly the type of infrastructure-led thinking Miracuves applies when designing future-proof, scalable platforms for global markets.
Read more: What is Worldpay and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Worldpay’s growth isn’t driven by mass consumer adoption—it’s powered by carefully segmented business customers with high transaction intensity. Instead of chasing millions of small users, Worldpay optimizes for volume, longevity, and ecosystem lock-in.
This segmentation strategy allows Worldpay to serve startups and global enterprises within the same infrastructure, while monetizing them very differently.
Primary & Secondary Customer Segments
Primary Segments
- Large Enterprises & Global Merchants
- Industries: Retail, Airlines, Hospitality, Gaming, Travel, SaaS, Fintech
- Characteristics:
- Millions of transactions per day
- Multi-country operations
- High regulatory exposure
- Millions of transactions per day
- Why they choose Worldpay:
- Global acquiring licenses
- High authorization rates
- Enterprise-grade SLAs and uptime
- Global acquiring licenses
- Industries: Retail, Airlines, Hospitality, Gaming, Travel, SaaS, Fintech
- Digital-First Platforms & Marketplaces
- Examples: eCommerce platforms, on-demand apps, SaaS marketplaces
- Needs:
- Split payments and payouts
- Embedded KYC and compliance
- Scalable APIs
- Split payments and payouts
- Strategic value:
- These clients grow transaction volume exponentially, compounding Worldpay’s revenue.
- These clients grow transaction volume exponentially, compounding Worldpay’s revenue.
- Examples: eCommerce platforms, on-demand apps, SaaS marketplaces
Secondary Segments
- SMEs and Mid-Market Businesses
- Online merchants and omnichannel retailers
- Subscription-based businesses
- High-growth startups
- Online merchants and omnichannel retailers
- Financial Institutions
- Banks outsourcing payment processing
- Fintechs leveraging Worldpay’s acquiring backbone
- Banks outsourcing payment processing
Customer Journey: Discovery → Conversion → Retention
Worldpay’s customer journey is consultative, not viral:
- Discovery
- Enterprise sales teams
- Strategic partnerships (eCommerce platforms, POS providers)
- Industry events and fintech alliances
- Enterprise sales teams
- Conversion
- Technical evaluations and pilots
- Proof of authorization-rate improvement
- Compliance and risk assessments
- Technical evaluations and pilots
- Retention & Expansion
- Deep API integrations (high switching costs)
- Continuous optimization tools
- Cross-selling fraud prevention, analytics, and new payment methods
- Deep API integrations (high switching costs)
Once integrated, merchants rarely leave—payments are too mission-critical to switch casually.
Acquisition Channels by Segment
- Enterprises
- Direct sales and account-based marketing
- Long-term contracts (3–7 years)
- Direct sales and account-based marketing
- Platforms & Marketplaces
- Developer-focused documentation
- Partner referrals
- Embedded payment offerings
- Developer-focused documentation
- SMEs
- Channel partnerships
- White-label integrations
- Channel partnerships
Worldpay optimizes customer lifetime value (LTV) by expanding payment types, regions, and services over time.
Market Positioning & Competitive Edge
Worldpay positions itself as:
- “The payments engine behind global commerce”
- Reliable, invisible, and deeply embedded
Differentiation Strategy
- Operates in 140+ markets
- Supports 300+ payment methods
- Strong compliance footprint across regions
- Enterprise-scale reliability with platform flexibility
In terms of market share, Worldpay consistently ranks among the top global acquirers by transaction volume, especially strong in North America, Europe, and high-regulation industries.
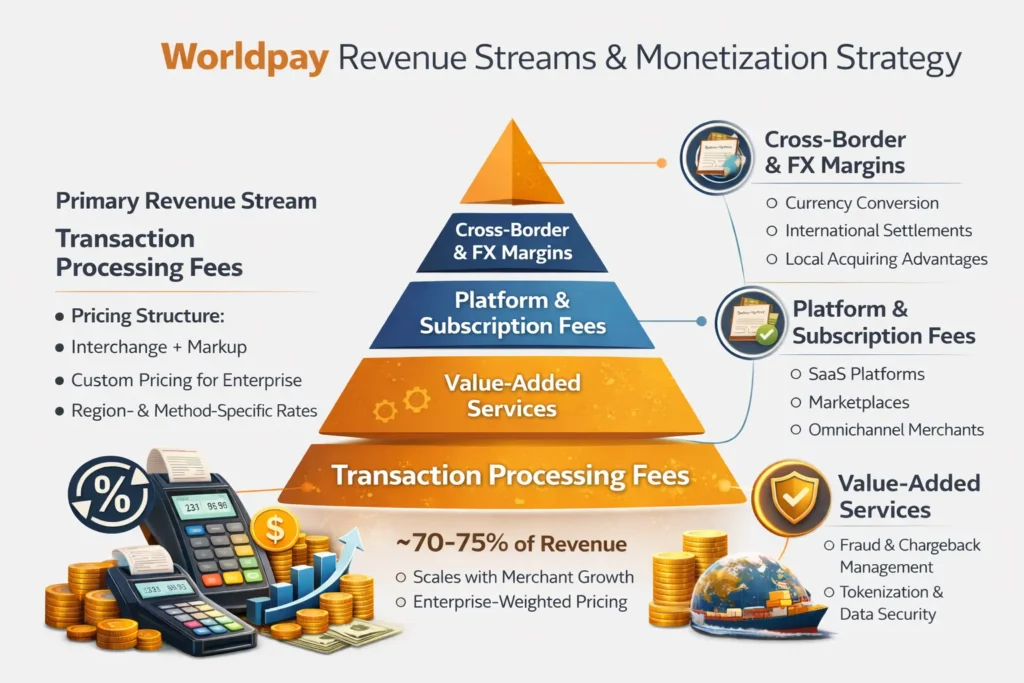
Revenue Streams & Monetization Design
Worldpay’s monetization strategy is built on a simple truth:
If you power every transaction, even small fees compound into massive revenue at scale.
Instead of relying on one revenue lever, Worldpay uses a layered monetization architecture that earns from volume, value-added services, and long-term contracts.
Primary Revenue Stream: Transaction Processing Fees
This is Worldpay’s core engine.
How it works:
- Worldpay earns a fee every time a transaction is processed.
- Fees are typically a mix of:
- Percentage of transaction value
- Fixed per-transaction fee
- Percentage of transaction value
Pricing Structure (Enterprise-Weighted):
- Interchange + markup model
- Custom pricing for high-volume merchants
- Region- and payment-method–specific pricing
Why it scales so well:
- As merchants grow, Worldpay’s revenue grows automatically.
- Cross-border and alternative payment methods carry higher margins.
Estimated Contribution:
- ~70–75% of total revenue
- Strong correlation with global eCommerce growth
Secondary Revenue Streams
1. Value-Added Services
High-margin, stickiness-driven revenue.
- Fraud detection & prevention
- Chargeback management
- Tokenization and data security
- Smart routing and authorization optimization
These services:
- Improve merchant ROI
- Increase switching costs
- Drive margin expansion
2. Subscription & Platform Fees
Especially relevant for:
- SaaS platforms
- Marketplaces
- Omnichannel merchants
Examples:
- Monthly platform access fees
- Advanced reporting dashboards
- Developer tool access
3. Cross-Border & FX Margins
Worldpay earns from:
- Currency conversion
- International settlement
- Local acquiring advantages
This is one of the fastest-growing revenue segments in 2026 due to global digital commerce.
4. Embedded Payments for Platforms
Worldpay acts as the payments backbone for:
- Marketplaces
- Vertical SaaS products
- On-demand platforms
Revenue comes from:
- Revenue-sharing agreements
- Per-user or per-merchant fees
This stream is strategically important because it creates indirect scale through partners.
Overall Monetization Strategy
Worldpay’s monetization works because:
- Core transaction fees ensure predictable, recurring revenue
- Value-added services increase margins and retention
- Platform partnerships unlock exponential volume growth
- Pricing is aligned with merchant success, not usage friction
Psychologically, Worldpay’s pricing:
- Feels “invisible” to end consumers
- Feels justified to merchants because it directly impacts revenue performance
- Rewards long-term volume commitments
This layered approach is exactly what Miracuves recommends to founders building:
- Marketplaces
- Subscription platforms
- Fintech and SaaS ecosystems
Monetize the core action — then build premium layers around it.
Operational Model & Key Activities
Worldpay’s business model only works because of industrial-grade operations running quietly in the background. Payments demand speed, uptime, security, and compliance—simultaneously. There’s no room for error.
Worldpay operates more like a global utility than a traditional tech company, with systems designed for 24/7 reliability across continents.
Core Operations
Worldpay’s daily operations revolve around five critical pillars:
- Platform & Infrastructure Management
- High-availability payment gateways
- Redundant global data centers
- Real-time transaction routing and settlement
- High-availability payment gateways
- Risk, Fraud & Compliance
- Machine-learning fraud detection
- PCI-DSS, GDPR, PSD2, SOC2 compliance
- KYC/AML enforcement across regions
- Machine-learning fraud detection
- Merchant Support & Account Management
- Enterprise account teams
- Technical onboarding and integration support
- SLA-driven incident response
- Enterprise account teams
- Product & Payment Method Expansion
- Adding local payment methods and wallets
- Supporting BNPL and real-time payments
- Continuous API enhancements
- Adding local payment methods and wallets
- Sales & Go-to-Market Operations
- Enterprise sales cycles
- Partner enablement
- Industry-specific solutions
- Enterprise sales cycles
Resource Allocation Strategy
Worldpay’s resource deployment reflects its infrastructure-first mindset:
- Technology & Engineering: ~35–40%
- Platform reliability
- Security and scalability
- Data analytics and optimization tools
- Platform reliability
- Risk, Compliance & Legal: ~15–20%
- Regulatory readiness
- Regional licensing
- Ongoing audits
- Regulatory readiness
- Sales, Marketing & Partnerships: ~20–25%
- Enterprise acquisition
- Platform partnerships
- Vertical-specific solutions
- Enterprise acquisition
- Customer Support & Operations: ~10–15%
- Merchant success teams
- Global support coverage
- Merchant success teams
- R&D & Innovation: ~10%
- AI-driven fraud systems
- Embedded finance capabilities
- New market payment rails
- AI-driven fraud systems
This disciplined allocation ensures stability first, innovation second, and growth third—the reverse of most startups, but essential at scale.
Why This Operational Model Works
- High uptime builds institutional trust
- Compliance becomes a competitive moat
- Deep integrations create long-term retention
- Operational excellence reduces churn to near-zero
For founders, this is a critical insight:
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Worldpay doesn’t try to own every part of the payments value chain. Instead, it orchestrates an ecosystem where partners extend reach, deepen functionality, and reinforce its market position.
Its partnership philosophy is simple but powerful:
Be the most reliable payments layer that others want to build on.
Collaboration Philosophy
Worldpay focuses on:
- Long-term, high-trust partnerships
- Deep technical integrations (not surface-level affiliations)
- Mutual value creation, not one-sided distribution deals
This approach turns partners into growth multipliers, not just resellers.
Key Partnership Types
1. Technology & API Partners
Worldpay integrates with:
- eCommerce platforms (e.g., global storefront builders)
- POS systems and retail software
- ERP and accounting systems
- Fraud and identity verification providers
Value Created:
- Faster merchant onboarding
- Embedded payments inside third-party platforms
- Lower acquisition costs
2. Payment Networks & Financial Alliances
Core infrastructure relationships include:
- Card networks (Visa, Mastercard, AmEx)
- Local payment schemes
- Issuing and acquiring banks
These alliances ensure:
- Global acceptance
- Higher authorization rates
- Regional compliance coverage
3. Payment, Wallet & BNPL Partnerships
To stay relevant in 2026 consumer behavior, Worldpay partners with:
- Digital wallets
- Buy Now, Pay Later providers
- Real-time payment networks
This expands merchant revenue while giving Worldpay access to higher-margin transaction flows.
4. Marketing & Distribution Partners
Worldpay leverages:
- Platform resellers
- Industry-specific solution partners
- Vertical SaaS providers
Instead of direct marketing to every merchant, Worldpay embeds itself where merchants already operate.
5. Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Local regulators and compliance bodies
- Regional financial institutions
- Government-led digital payment initiatives
These partnerships lower market-entry friction and protect long-term operations.
Ecosystem Strategy Insights
Worldpay’s ecosystem creates durable advantages:
- Network Effects:
More partners → more merchants → more transactions → better data → stronger platform. - Monetization Leverage:
Revenue is shared, but total volume grows faster than standalone acquisition. - Competitive Moats:
Deep partner integrations make replacement costly and risky.
This is a key lesson for Miracuves clients:
Platforms scale faster when partners carry distribution, compliance, and context.
Worldpay proves that ecosystem-first thinking is how infrastructure businesses dominate global markets.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Worldpay’s growth story is about compounding volume, not chasing users. Its strategy focuses on expanding where transactions happen, not just how many customers it has.
In 2026, Worldpay grows by embedding deeper into commerce flows, expanding globally, and enabling new payment behaviors.
Core Growth Engines
1. Embedded Scale via Platforms
Worldpay fuels growth by becoming the default payments layer for:
- Marketplaces
- Vertical SaaS products
- Global commerce platforms
As these platforms grow, Worldpay’s transaction volume scales automatically, without additional sales effort.
2. Organic Expansion Through Merchant Success
Instead of aggressive upselling, Worldpay grows through:
- Adding new payment methods
- Expanding merchants into new regions
- Increasing authorization and conversion rates
When merchants make more money, Worldpay does too.
3. Strategic Paid Acquisition (Enterprise-Focused)
- Account-based marketing
- Industry-specific sales teams
- Long sales cycles, high contract values
This keeps customer acquisition costs high—but LTV multiples higher.
4. Product-Led Expansion
New offerings in 2025–2026 include:
- Real-time payments
- Advanced fraud AI
- Embedded payouts and treasury services
Each product adds another revenue layer on the same infrastructure.
5. Geographic Expansion Model
Worldpay expands through:
- Local acquiring licenses
- Regional banking partnerships
- Compliance-first market entry
Rather than “launch fast,” Worldpay launches correctly, ensuring long-term viability.
Scaling Challenges & How Worldpay Solved Them
Challenge 1: Operational Complexity
- Multiple currencies, regulations, and payment rails
- Solution: Modular architecture + regional compliance teams
Challenge 2: Infrastructure Load
- Peak transaction volumes during global events
- Solution: Redundant systems and real-time failover
Challenge 3: Regulatory Barriers
- Constantly evolving fintech regulations
- Solution: Proactive regulatory partnerships and audits
Challenge 4: Competitive Pressure
- Fintech startups competing on price
- Solution: Enterprise-grade reliability and bundled value services
Why Worldpay’s Scaling Strategy Works
- Growth is low-churn and compounding
- New revenue doesn’t require rebuilding infrastructure
- Expansion strengthens—not weakens—core stability
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Payments is a brutal arena—thin margins, regulatory pressure, and nonstop innovation. Worldpay survives and wins not by being the cheapest, but by being the hardest to replace.
Its competitive strategy is built around depth, trust, and embedded advantage.
Core Competitive Advantages
1. Network Effects & Switching Barriers
- More merchants → more transaction data → better routing and fraud detection
- Deep API integrations create high switching costs
- Multi-region compliance makes migration risky for enterprises
Once Worldpay is embedded, replacing it is a multi-year decision.
2. Brand Equity & Institutional Trust
Worldpay is trusted by:
- Global enterprises
- Regulated industries (gaming, travel, finance)
- High-risk verticals that need proven reliability
In payments, trust beats novelty every time.
3. Technology & Infrastructure Depth
- Real-time authorization optimization
- Smart transaction routing
- AI-driven fraud prevention
- Near-zero downtime architecture
This tech depth is invisible—but decisive.
4. Data-Driven Personalization
Worldpay leverages transaction-level data to:
- Improve approval rates
- Reduce fraud false-positives
- Customize payment experiences by region
Data becomes both a performance enhancer and a moat.
Market Defense Tactics
1. Handling New Entrants
- Competes on value, not price
- Bundles fraud, compliance, and optimization
- Emphasizes enterprise reliability over discounts
2. Pricing & Margin Defense
- Tiered pricing by volume and complexity
- Long-term contracts with negotiated margins
- Premium pricing justified by ROI improvements
3. Strategic Feature Timing
- Releases features when markets are ready—not early
- Prioritizes stability over experimentation
- Aligns roadmaps with regulatory timelines
4. Partnerships & Acquisitions
- Acquires or partners rather than competes directly
- Uses ecosystem relationships to neutralize threats
- Expands defensively into high-growth payment rails
Strategic Insight for Founders
Worldpay proves that:
The strongest competitive advantage is being operationally indispensable.
At Miracuves, we help founders design platforms with:
- High switching costs
- Ecosystem dependencies
- Long-term defensibility baked into architecture
Read more : Best Worldpay Clone Scripts 2025: Launch Your Own Global Payment Gateway
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Think of Worldpay as a masterclass in building a boring-looking but billion-dollar business. It didn’t win by being trendy—it won by being essential.
Here’s what founders can take away and apply immediately.
Key Factors Behind Worldpay’s Success
- Infrastructure First, Experience Second
Worldpay perfected reliability, compliance, and scale before layering UX and analytics. - Monetize the Core Action
Every transaction creates value—Worldpay simply takes a small, justified cut. - High Switching Costs by Design
Deep integrations + compliance = long-term customer lock-in. - Ecosystem Over Ownership
Partnerships expand reach faster than direct expansion. - Enterprise Trust as a Growth Lever
In regulated markets, trust compounds faster than marketing spend.
Replicable Principles for Startups
You don’t need Worldpay’s scale to apply its model:
- Start with a single critical workflow
- Design for volume-based monetization
- Add premium layers (analytics, automation, compliance)
- Build APIs early to enable partnerships
- Treat compliance and reliability as features, not costs
These principles work especially well for:
- Marketplaces
- Fintech apps
- SaaS platforms
- On-demand ecosystems
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Competing only on price
- Ignoring compliance until late stages
- Overbuilding features before stabilizing the core
- Underestimating operational complexity
- Treating partnerships as optional
Worldpay succeeded by doing the opposite.
Adapting the Model for Local or Niche Markets
Founders can localize this approach by:
- Focusing on one industry vertical
- Supporting regional payment behaviors
- Partnering with local institutions
- Scaling geography only after operational maturity
Implementation & Investment Priorities
Phase 1 :
- Core platform build
- MVP compliance setup
- Single-region launch
Phase 2 :
- Add monetization layers
- Secure strategic partnerships
- Expand payment methods or services
Phase 3 :
- Geographic expansion
- Advanced analytics and automation
- Ecosystem monetization
Ready to implement Worldpay’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps.
Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion
Worldpay’s business model proves a powerful truth about the modern digital economy:
the most valuable companies are often the least visible to consumers.By focusing on infrastructure, trust, and ecosystem enablement, Worldpay turned payments—a commodity on the surface—into a deeply defensible, high-scale platform business. Its success didn’t come from rapid experimentation or viral growth, but from relentless execution, regulatory mastery, and long-term thinking.
As we move into 2026 and beyond, platform economies will favor businesses that power critical workflows, reduce complexity for others, and scale through partnerships—not noise—proving that when founders build what others depend on, sustainable growth follows, the same philosophy Miracuves applies to designing future-ready platforms across markets and regulations
FAQs
What type of business model does Worldpay use?
Worldpay operates a B2B payments infrastructure platform model. It earns revenue mainly through transaction-based fees and value-added financial services for businesses.
How does Worldpay’s business model create value?
Worldpay simplifies global payments by managing authorization, settlement, fraud prevention, and compliance. This lets businesses scale faster without handling payment complexity.
What are Worldpay’s key success factors?
Its success is driven by global acquiring licenses, high system reliability, strong compliance expertise, enterprise partnerships, and a scalable API-driven architecture.
How scalable is Worldpay’s business model?
The model is highly scalable because revenue increases automatically with transaction volume. Marginal costs per transaction remain low as scale grows.
What are the biggest challenges in this model?
Major challenges include regulatory complexity, infrastructure uptime requirements, cybersecurity risks, and pricing pressure from fintech competitors.
How can entrepreneurs adapt Worldpay’s model to their region?
Founders can localize the model by targeting a specific industry, supporting regional payment behaviors, ensuring compliance, and leveraging strategic partnerships.
How has Worldpay’s business model evolved over time?
Worldpay evolved from basic card processing into a full-stack global payments platform, adding fraud management, data intelligence, embedded finance, and omnichannel support.
What are alternatives to Worldpay’s business model?
Alternatives include payment aggregators, subscription-based fintech tools, and vertical SaaS platforms with embedded payments, trading scale for simplicity.
Related Article :
- What is PayPal and How Does It Work?
- What is Razorpay and How Does It Work?
- Best Remitly Clone Scripts 2025: Launch Your Global Remittance App Faster & Smarter
- Best Stripe Clone Scripts 2025: Build a Scalable Global Payment Infrastructure for Your Startup
- Best PayPal Clone Scripts 2025 Launch a Secure Global Digital Payment Platform








