In 2007, a small Tel-Aviv startup set out to democratize financial markets. By 2025, eToro had grown from a niche social trading platform into a multi-billion-dollar global fintech ecosystem — and the Business Model of eToro became one of the most talked-about case studies in modern platform-based finance.
With over 30 million registered users across 140+ countries and annual revenue nearing $1 billion, eToro scaled by combining hybrid brokerage services, copy-trading innovation, and multi-asset diversification. Instead of relying on a single revenue stream, it built a monetization engine powered by spreads, platform activity, and user retention loops.
eToro’s evolution matters because it reimagined how people invest — shifting trading from isolated screens to a social, community-driven experience where users learn, share, and even replicate others’ strategies. For founders building tomorrow’s platforms — whether in fintech, marketplaces, or social communities — eToro’s model blends technology, network effects, and regulatory agility in ways that are highly relevant for 2026 and beyond.
How the eToro Business Model Works
eToro’s business model is a hybrid of online brokerage and social trading, designed to make financial markets accessible, interactive, and community-driven. Instead of just providing trading tools, it blends elements of social networking, education, and investing marketplaces, creating a platform where users both trade assets and learn from each other’s behavior.
1. Type of Model
- Multi-Asset Online Brokerage: Core functionality lets users trade stocks, ETFs, cryptocurrencies, forex, commodities, and more through eToro’s trading infrastructure.
- Social Trading / Matchmaking Marketplace: Users can follow, interact, and copy trades of experienced traders, transforming investing into a social, participatory activity.
- Hybrid Model: Revenue is generated from both transaction-linked fees and community-driven engagement rather than heavy reliance on commissions alone.
2. Value Proposition
eToro’s value for each stakeholder:
- Retail Investors:
- Access: Simplified access to global markets with low entry barriers.
- Education & Insight: Social feeds, performance stats, and community tools help novices learn from pros.
- Copy Trading: Ability to mirror successful investor strategies automatically.
- Access: Simplified access to global markets with low entry barriers.
- Experienced Traders:
- Monetization: Earn through Popular Investor programs and performance recognition.
- Exposure: Community visibility builds reputation and influence.
- Monetization: Earn through Popular Investor programs and performance recognition.
- Institutional Partners:
- API Integrations: Data feeds, partnership integrations (e.g., market data with social platforms).
- Expanded Distribution: Joint marketing and co-branded educational initiatives.
- API Integrations: Data feeds, partnership integrations (e.g., market data with social platforms).
3. Stakeholders
- End Users: Retail traders & investors of all experience levels.
- Top Traders / Influencers: Serve as nodes for community activity and generate network effects.
- Regulators & Exchanges: Compliance across regions ensures operational legitimacy.
- Partners: Market data providers, fintech partners, social networks, educational partners.
4. Evolution Over Time
- 2007–2010: Laid foundation as a standard online brokerage.
- 2010: Introduced OpenBook — pioneering social trading and copy trading.
- 2010–2020s: Expanded asset classes (stocks, ETFs, crypto), mobile apps, and global market access.
- 2024–2025: Increased partnerships (e.g., with exchanges and social platforms) and IPO, signaling maturity.
5. Why It Works in 2026
- Network Effects: The more users and top traders join, the richer the data and insights, making the platform more valuable.
- Shift to Community-Driven Finance: Retail investors increasingly seek social proof and shared learning over traditional siloed trading.
- Multi-Asset Access: With crypto and fractional investing popular among younger demographics, eToro’s broad asset suite increases relevance.
Read more : What is eToro App and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
eToro’s growth didn’t come from chasing “everyone who trades.”
It came from something much smarter: owning a specific kind of investor mindset — the person who wants to invest, but also wants to learn, copy, and feel confident doing it.
That positioning makes eToro less like a traditional brokerage… and more like a social-finance ecosystem.
Primary Customer Segments (Core Growth Engine)
1) New-to-Investing Retail Users (Beginners)
These are people who:
- are curious about investing
- feel overwhelmed by charts and jargon
- want to start small and learn fast
Why they stay:
- CopyTrading reduces anxiety
- social feeds create “I’m not alone” confidence
- the app feels more like a community than a terminal
2) Self-Directed Traders (Intermediate Investors)
This segment already understands trading basics and wants:
- multi-asset access (stocks, crypto, ETFs, commodities)
- a simple UI
- lower friction execution than legacy brokers
Why they stay:
- asset diversity inside one wallet-like platform
- cross-market flexibility
- fast discovery of trending assets via community signals
Secondary Segments (Retention + Monetization Layer)
3) Advanced Traders / High-Performers (“Popular Investors”)
These are eToro’s “supply-side creators.”
They:
- trade seriously
- build follower trust
- become copyable portfolios
Why they stay:
- direct monetization through eToro incentive programs
- reputation + audience growth
- status and visibility inside the platform
4) Crypto-First Investors
These users often come in for:
- Bitcoin, Ethereum, altcoins
- quick exposure without complex exchanges
Why they stay:
- multi-asset expansion (they later buy stocks/ETFs)
- simplified custody and UI
- social proof during volatile cycles
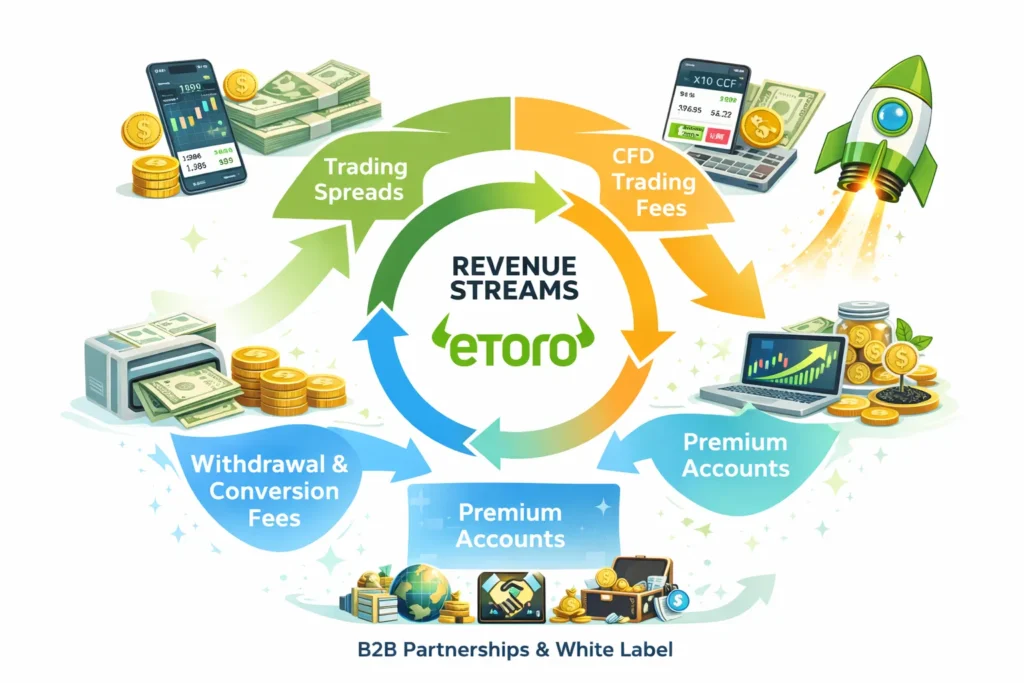
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Now we get to the fun part: how money actually flows through eToro.
eToro’s monetization is clever because it’s not built on one stream. It’s built like a fintech flywheel — where trading behavior, user trust, and asset expansion all feed revenue.
Instead of charging a visible “subscription fee” like Netflix, eToro monetizes through embedded financial mechanics — spreads, fees, and conversion layers that scale as user activity grows.
Primary Revenue Stream #1: Trading Spreads (Core Engine)
The biggest and most consistent revenue driver for eToro is the spread — the difference between the buy and sell price of an asset.
How it works
- User buys an asset at slightly above market price
- User sells at slightly below market price
- eToro captures the margin
Why it scales
Spreads scale beautifully because:
- they grow with trading volume
- they don’t feel like “fees” to most users
- they apply across multiple asset classes (forex, crypto, CFDs)
Primary Revenue Stream #2: CFD Trading Fees (High Margin Segment)
In many regions, eToro offers CFDs (Contracts for Difference) — which are leveraged instruments.
This segment is highly profitable because it includes:
- leverage fees
- overnight financing charges
- higher trading frequency
- higher risk tolerance users
Key point
Even if only a minority of users trade CFDs, they often represent a disproportionate share of revenue.
Secondary Revenue Streams
1) Withdrawal Fees
A classic fintech monetization layer.
- Users pay a flat fee when withdrawing funds
- It monetizes the “exit moment”
- It discourages frequent withdrawals, increasing platform float
2) Currency Conversion Fees
Because eToro operates globally, it frequently converts:
- local currencies → USD base currency
- crypto → fiat
- asset-to-asset trades
This generates recurring revenue, especially as the platform expands into emerging markets.
3) Premium Accounts / Club Tiers
eToro also uses a “status ladder” model through eToro Club.
Higher tiers often unlock:
- reduced fees
- dedicated account managers
- premium research and signals
- exclusive assets or early access features
This is smart because it:
- increases retention
- drives higher deposits
- makes high-value customers feel “VIP locked-in”
4) Crypto Staking / Yield Products (Selective Regions)
In some markets, eToro has offered staking-like products where users earn yields.
Even when yield goes to the user, eToro can monetize via:
- spread capture
- custody fees
- partner revenue shares
5) B2B Partnerships + White Label Infrastructure
While not always publicly emphasized, eToro’s technology and brand partnerships (including with financial institutions and sports sponsorships) create indirect monetization:
- co-branded acquisition campaigns
- affiliate commissions
- institutional integrations
Operational Model & Key Activities
If eToro’s business model is the blueprint, its operational model is the machine.
And here’s the thing most founders miss:
eToro isn’t just “an app where people trade.”
It’s a regulated, real-time, always-on financial operating system — running across multiple countries, asset classes, and compliance environments.
That operational complexity is exactly why eToro’s model is hard to copy… and why it’s such a powerful case study for entrepreneurs.
1) Core Operations (What eToro Runs Daily)
A) Platform & Infrastructure Management
This is the engine behind everything:
- real-time price feeds
- order execution systems
- portfolio tracking
- uptime reliability (finance apps can’t “go down” casually)
- risk monitoring + fraud detection
For fintech platforms, this is where scalability is won or lost.
B) Regulatory Compliance + Licensing
eToro operates under strict regulations across regions.
That means daily operational work includes:
- KYC (Know Your Customer)
- AML (Anti-Money Laundering)
- transaction monitoring
- audit trails
- region-specific product availability (e.g., CFDs allowed in some markets, restricted in others)
This is not a one-time setup — it’s continuous operations.
C) Liquidity & Market Access
eToro must maintain relationships and systems that support:
- stock execution routing
- crypto custody and liquidity
- forex liquidity providers
- pricing feeds and spread management
This layer is invisible to users — but it’s where a lot of the platform’s trust comes from.
D) Customer Support + Trust Operations
In finance, support is not “nice to have.”
It directly affects:
- churn
- reputation
- regulatory exposure
- deposit volume
Support includes:
- dispute resolution
- withdrawal issues
- verification/KYC delays
- account security incidents
E) Community Moderation + Social Integrity
Because eToro has a social feed, it must manage:
- spam and scams
- fake performance claims
- misinformation
- pump-and-dump behavior in crypto discussions
This is a huge operational challenge unique to social trading.
2) Key Activities (What Creates Business Value)
eToro’s key activities fall into 3 major buckets:
1) Financial Transaction Enablement
- trading execution
- asset custody
- order matching / routing
- pricing and spreads
2) Network Effects & Social Engagement
- CopyTrading systems
- Popular Investor incentives
- social feeds + performance transparency
- trader discovery and ranking algorithms
3) Retention + Monetization Optimization
- tiered membership (Club)
- cross-asset nudges (crypto → stocks)
- portfolio product packaging
- behavioral analytics for LTV growth
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
eToro didn’t become a global fintech brand by building everything alone.
Its real superpower is that it behaves like a platform company, not just a brokerage — meaning it grows by stitching together an ecosystem of:
- liquidity providers
- banks and payment rails
- market data partners
- regulators and licensed entities
- marketing and distribution allies
And in 2026, ecosystem-building is the way platforms defend themselves in competitive, regulated industries.
Key Partnership Types That Power eToro
1) Technology & API Partners
These partnerships strengthen:
- real-time market data
- charting and analytics layers
- security systems
- trading infrastructure integrations
Why this matters:
In finance, milliseconds and reliability are part of the product.
2) Payment, Banking & Liquidity Alliances
To operate globally, eToro needs:
- payment processors (card, bank transfer, local methods)
- currency conversion rails
- banking partners for custody and settlement
- liquidity providers for forex and CFD markets
- crypto custody infrastructure in compliant regions
Why this matters:
This is how eToro reduces friction in deposits/withdrawals — which directly increases conversion and retention.
3) Marketing & Distribution Partnerships
eToro has used partnerships like:
- affiliate networks
- finance influencers
- media + education collaborations
- high-trust sponsorships (sports, global events)
This is not “branding fluff.”
In fintech, sponsorships function like trust acceleration — they reduce user fear around depositing money.
4) Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
This is the most underrated part.
To expand into new countries, eToro often needs:
- licensed entities
- local compliance frameworks
- region-specific legal infrastructure
- partnerships that reduce time-to-market
In regulated industries, expansion is as much legal as it is product.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
eToro didn’t scale like a traditional financial company.
It scaled like a modern consumer platform — closer to how TikTok or Airbnb grows — but inside the rules of a regulated financial world.
That’s what makes its growth story so interesting:
it combines viral network effects with fintech trust-building.
Growth Engines (How eToro Expands in 2026)
1) Organic Virality + Social Referral Loops
eToro’s biggest growth advantage is that it bakes sharing into the product.
When users:
- follow investors
- copy portfolios
- comment on trades
- share performance
…it creates constant “social proof” loops.
This turns investing into something people discuss publicly — which is rare in finance.
Result: the product becomes a marketing channel.
2) CopyTrading as a Built-In Acquisition System
CopyTrading is not just a feature.
It’s a growth engine because it solves the #1 friction point in investing:
“I don’t know what I’m doing.”
So instead of leaving the platform to learn somewhere else, beginners stay inside eToro and copy others.
That creates:
- faster activation
- higher retention
- more trading volume
- deeper network effects
3) Paid Marketing + Trust-Based Branding
eToro uses aggressive paid acquisition — but with a very specific style:
- sponsorships
- brand-safe influencer marketing
- “financial empowerment” positioning
- high trust, mainstream visibility
Unlike crypto exchanges that leaned into hype, eToro often markets itself as:
- stable
- regulated
- community-driven
- multi-asset (not “just crypto”)
4) Product Expansion = LTV Expansion
eToro grows by increasing what users can do inside the platform.
This includes:
- more asset classes
- fractional investing
- thematic portfolios
- crypto + stocks in one environment
- tiered membership and benefits
This strategy increases LTV because users don’t churn to other apps when their needs evolve.
5) Geographic Scaling Strategy
eToro’s global growth has been structured around:
- expanding into regions where retail investing is rising
- targeting markets where mobile-first fintech adoption is strong
- prioritizing jurisdictions with clearer regulatory pathways
This is a classic “regulated platform expansion” model:
Enter where regulation is manageable, then deepen product complexity later.
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
By 2026, eToro isn’t competing in a single market.
It’s competing in multiple overlapping arenas at once:
- against retail brokerages (Robinhood-style)
- against crypto exchanges (Coinbase-style)
- against traditional investing platforms (banks + legacy brokers)
- against new fintech apps that try to clone features fast
So eToro’s real competitive strength isn’t “better trading.”
It’s how it defends a multi-layered ecosystem.
Core Competitive Advantages
1) Network Effects + Social Switching Costs
eToro’s biggest moat is its social layer.
Because users:
- follow traders
- build portfolios around copied strategies
- interact with the community
- track performance over time
…switching to another broker is not just moving money.
It’s abandoning:
- their copied investors
- their strategy history
- their social credibility and learning environment
That creates social switching costs, which are far stickier than price.
2) Brand Trust in a High-Fear Category
In finance, trust is currency.
eToro has positioned itself as:
- global
- regulated
- stable
- mainstream
That matters because many competitors (especially crypto-first platforms) face trust issues after industry collapses and scandals.
So in 2026, eToro benefits from a powerful advantage:
It feels “safe enough” for beginners — but still exciting enough for traders.
3) Multi-Asset Diversification = Strategic Defense
Many platforms are trapped:
- brokers struggle to win in crypto
- crypto exchanges struggle to win in stocks
- banks struggle to win in UX
eToro sits in a strong middle position:
- stocks + ETFs
- crypto
- forex/commodities (region dependent)
- portfolios + social investing
This gives it resilience:
When one market slows (e.g., crypto winter), another can keep activity alive.
4) Product Innovation Through “Community Intelligence”
eToro’s social feed isn’t just engagement.
It’s also:
- behavioral data
- trend detection
- investor sentiment signals
This becomes an advantage in:
- product design
- portfolio creation
- personalization
- feature prioritization
Essentially, eToro can see what retail investors want before competitors do.
5) Regulatory Compliance as a Competitive Moat
Most startups treat regulation as a cost.
eToro turns it into a barrier for others.
Because once you build:
- licensing frameworks
- AML systems
- KYC pipelines
- audit-ready reporting
…it becomes extremely hard for new entrants to match quickly.
Read more : Best eToro Clone Scripts 2026: Build a Social Trading Platform That Scales Globally
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Alright — here’s where we turn eToro from a case study into a playbook.
Because the real value in studying eToro isn’t admiring the scale.
It’s understanding the repeatable principles behind how it built a defensible platform in one of the hardest categories on earth: money + trust + regulation.
What Made eToro Successful (The Real Drivers)
1) It Didn’t Sell Trading — It Sold Confidence
Most brokerages sell tools.
eToro sold something emotionally stronger:
- “You can invest even if you’re new.”
- “You can learn by watching others.”
- “You can copy proven strategies.”
That reduced the #1 barrier to entry in finance: fear.
2) It Turned Investing Into a Marketplace
eToro isn’t just a platform where people trade.
It’s a marketplace where:
- strategies are the product
- top traders are the supply-side
- beginners are the demand-side
3) It Used Network Effects Where Competitors Couldn’t
Traditional brokers can’t easily add social features because:
- it’s culturally “not them”
- it adds moderation risk
- it changes the product identity
eToro built social-first early — and that became a moat.
4) It Monetized Invisibly (Without Feeling Like It)
eToro’s revenue streams are mostly embedded:
- spreads
- conversion fees
- withdrawal fees
- premium tiers
This makes the monetization feel “natural,” not aggressive.
5) It Built Trust Like a Tech Company, Not a Bank
eToro invested in:
- UI clarity
- transparency
- performance stats
- regulated legitimacy
- mainstream sponsorship trust
This combination is rare — and very hard to replicate quickly.
Implementation + Investment Priorities
Here’s a realistic founder timeline if you want to build an eToro-inspired platform:
Phase 1 : MVP Foundation
Priorities:
- onboarding + identity flow
- core transaction layer
- user wallet / portfolio tracking
- basic social feed (optional)
Phase 2 : Marketplace Layer
Priorities:
- expert profiles
- follow + copy mechanics
- transparency dashboards
- ranking + discovery
Phase 3 : Monetization + Retention
Priorities:
- tiered membership
- cross-sell asset categories
- partner integrations
- referral systems
Phase 4 : Scaling + Defense
Priorities:
- compliance automation
- regional expansion
- ecosystem partnerships
- trust + integrity operations
Ready to implement eToro’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps. Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion
eToro’s business model proves a powerful truth about platform economies in 2026:The biggest companies don’t just sell products — they build systems where other people create value.eToro didn’t win by being the cheapest broker or the most advanced trading terminal.
It won by turning investing into a social ecosystem — where trust is built through transparency, strategies become marketplace assets, and learning becomes a retention engine.
Innovation creates attention. Execution creates durability.
eToro had both — and that’s why it survived cycles that wiped out dozens of competitors across fintech and crypto.As we move deeper into 2026 and beyond, platform economies will evolve toward community-powered decisions, creator-style monetization, and trust-first ecosystems — not just feature-driven apps.
FAQs
1) What type of business model does eToro use?
eToro uses a hybrid brokerage + social trading platform model. It combines multi-asset investing with community features like CopyTrading, creating both transactional and network-effect value.
2) How does eToro’s model create value?
It creates value by making investing simpler, social, and trust-driven. Beginners learn faster through CopyTrading, while experienced traders gain visibility and monetization opportunities.
3) What are eToro’s key success factors?
Its biggest success factors are CopyTrading, strong brand trust, multi-asset access, and global scaling through compliance. These combine to create high retention and strong switching costs.
4) How scalable is eToro’s business model?
Highly scalable — because it’s digital, multi-market, and fueled by network effects. As more users and top traders join, the platform becomes more valuable without linear cost growth.
5) What are the biggest challenges in eToro’s model?
The biggest challenges are regulatory complexity, platform trust, fraud prevention, and operational risk. Social trading also adds moderation and integrity issues that most brokerages don’t face.
6) How can entrepreneurs adapt eToro’s model to their region?
Founders can localize it by focusing on 1–2 assets first, integrating local payment rails, and building trust via verified expert profiles. The “copy” concept works best when paired with local credibility.
7) What are alternatives to eToro’s business model?
Alternatives include pure brokerage models (Robinhood-style), crypto exchange models (Coinbase-style), or subscription-based investing apps. Each is simpler, but lacks eToro’s social-network moat.
8) How has eToro’s business model evolved over time?
It evolved from a standard trading platform into a global multi-asset ecosystem. Over time, it strengthened CopyTrading, expanded into crypto and stocks, and built deeper monetization through
Related Article :
- What is Robinhood App and How Does It Work?
- What is SoFi App and How Does It Work?
- Best Remitly Clone Scripts 2025: Launch Your Global Remittance App Faster & Smarter
- Best Stripe Clone Scripts 2025: Build a Scalable Global Payment Infrastructure for Your Startup
- Best N26 Clone Scripts 2026 for Digital Banking Startups








