Zoom grew from a niche video conferencing tool valued at $1 million in 2013 to a $17+ billion enterprise by 2025, redefining how the world connects remotely.
What started as a simple, reliable video meeting solution became one of the fastest-scaling SaaS stories in history. Zoom didn’t just enable meetings — it revolutionized communication for individuals, enterprises, schools, and governments worldwide. By offering simplicity, scalability, and superior performance, Zoom captured massive global market share even as competitors like Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Cisco Webex fought fiercely.
In 2025, as hybrid work becomes the default and virtual collaboration extends beyond meetings — to webinars, events, AI note-taking, and digital offices — business model of Zoom continues to evolve. For entrepreneurs and app founders, understanding how Zoom built a profitable, sticky ecosystem around remote productivity offers invaluable lessons in platform design, subscription monetization, and user retention.
How the Zoom Business Model Works
Zoom operates on a Freemium-to-Enterprise Subscription Model, built to scale across individuals, SMBs, and Fortune 500 companies alike. Its genius lies in balancing mass accessibility (free tier) with deep enterprise value (premium features, integrations, and reliability).
1. Type of Model
Zoom follows a Hybrid SaaS Model, combining:
- Freemium access to attract and onboard users easily.
- Subscription tiers for revenue — monthly/annual payments for premium usage.
- Enterprise licensing for large-scale deployments.
- Platform ecosystem revenue via Zoom Apps and Zoom SDK for developers.
2. Value Proposition
Zoom delivers uninterrupted, high-quality communication experiences with minimal setup friction.
- For Users: Instant, HD-quality meetings and calls across any device.
- For Businesses: Secure collaboration, administrative control, and analytics.
- For Developers: APIs and SDKs to embed video communication into other apps.
- For Partners: Ecosystem integrations that drive additional adoption.
Its focus on low latency, high stability, and ease of use creates a trust-based moat competitors struggle to replicate.
3. Stakeholders
Zoom’s ecosystem thrives through:
- End Users: Individuals, educators, remote workers.
- Business Clients: Enterprises, SMBs, universities, governments.
- Developers: Building apps or embedding Zoom features.
- Partners: Hardware, telecom, and enterprise integration providers.
Each plays a key role in sustaining engagement, data feedback loops, and recurring revenue.
4. Evolution Over Time
- 2013–2017: Focused on product perfection and free virality.
- 2018–2020: Enterprise expansion and IPO success.
- 2020–2022: Pandemic-driven hypergrowth and infrastructure scaling.
- 2023–2025: Platform transformation — Zoom evolving into a “Unified Communications Hub” with products like Zoom Phone, Zoom Events, AI Companion, and Workspaces.
5. Why It Works in 2025
- The hybrid work culture remains permanent across industries.
- Enterprises seek AI-driven collaboration tools — a Zoom strength.
- Zoom’s ecosystem diversification (Meetings, Chat, Events, Phone, Contact Center) creates multiple engagement touchpoints.
- 2025 integrations with tools like Slack, Asana, and Salesforce make Zoom an embedded productivity layer.
| Key Partners | Key Activities | Value Proposition | Customer Relationships | Customer Segments |
| API partners, cloud providers, enterprise IT | Product development, infrastructure scaling, support | Reliable, scalable video & collaboration tools | Self-service, enterprise account management | Individuals, SMBs, Enterprises, Developers |
Read more : What is Zoom App and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Zoom’s growth is anchored in its ability to serve diverse customer segments—from individual users hosting free video calls to multinational corporations deploying unified communication systems across continents. Its segmentation strategy is data-driven, designed to convert mass adoption into recurring enterprise revenue.
1. Primary Customer Segments
a. Individual & Small Teams (Freemium Users)
- Profile: Freelancers, students, remote workers, early adopters.
- Need: Quick, reliable communication tools without friction.
- Behavior: Start free → upgrade when usage limits are hit (e.g., 40-min meeting cap).
- Conversion Driver: Ease of onboarding + “viral meeting links.”
b. Business & Enterprise Clients
- Profile: SMBs, enterprises, schools, healthcare, governments.
- Need: Secure, scalable collaboration and administrative control.
- Behavior: Multi-license purchases, annual contracts, SLAs, integration needs.
- Conversion Driver: Reliability, compliance (HIPAA, SOC 2, GDPR), and AI-powered features.
c. Developers & Platform Integrators
- Profile: SaaS developers, EdTech, Telehealth, and event platforms.
- Need: Embeddable video capabilities.
- Behavior: Integrate Zoom APIs and SDKs for video infrastructure.
- Conversion Driver: Developer-friendly APIs and global reliability.
2. Customer Journey (Discovery → Conversion → Retention)
- Discovery: Viral growth through link-sharing, word-of-mouth, and corporate mandates.
- Conversion: Automated onboarding via the free plan; upselling through time or participant limits.
- Retention: AI features (Zoom IQ), seamless cross-device experience, and enterprise dashboards create high stickiness.
- Expansion: Upgrades to paid tiers and add-ons like Zoom Phone, Events, and Contact Center.
3. Acquisition Channels
- Organic: Word-of-mouth, referrals, and brand equity from the pandemic era.
- Paid Marketing: Search ads, enterprise lead nurturing, event sponsorships.
- Partnership Channels: Hardware and software bundling (e.g., Logitech, Poly, Microsoft integrations).
- Developer Ecosystem: Zoom Apps Marketplace drives recurring visibility.
4. Market Positioning
Zoom’s brand stands for simplicity, stability, and trust.
Even with rivals like Google Meet and Microsoft Teams offering free bundling, Zoom’s best-in-class user experience and independent platform flexibility allow it to dominate paid professional and event-based segments.
Market Snapshot 2025:
- Over 350 million daily meeting participants.
- More than 220,000 enterprise customers.
- Average revenue per user (ARPU) rising through AI-driven premium offerings
| Segment | Needs | Monetization Trigger | Retention Driver |
| Individuals | Easy video calls | 40-min cap, meeting limits | Habitual use, brand trust |
| SMBs | Affordable, secure collaboration | Custom branding, admin tools | Productivity gains |
| Enterprises | Scalable communication system | Integration, SLA | Cross-product usage |
| Developers | Embedded video APIs | API calls & licensing | SDK performance |
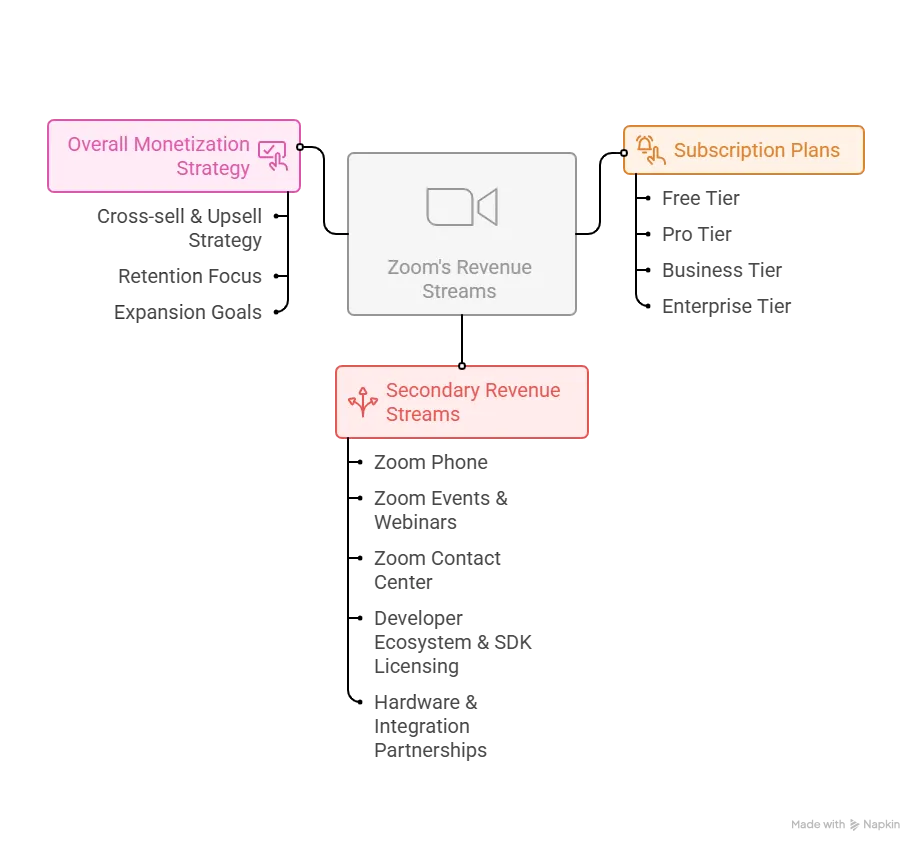
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Zoom’s revenue design is a masterclass in SaaS-based recurring monetization — combining predictable subscription income with diversified upsell and ecosystem-driven streams. Its model converts user trust into long-term revenue through tiered pricing, enterprise contracts, and platform extensions.
1. Primary Revenue Stream: Subscription Plans (≈ 80% of total revenue)
Mechanism:
Zoom operates on a tiered subscription model — monthly or annual billing for added features, capacity, and support.
Tiers (2025):
- Free: Basic meetings, 40-minute limit, up to 100 participants.
- Pro: ~$15.99/user/month — unlimited meetings, 5GB cloud recording.
- Business: ~$19.99/user/month — branding, reporting, and SSO integration.
- Enterprise: Custom pricing — advanced admin, compliance, and analytics.
Growth Trajectory (2025):
- Revenue up 9% YoY, reaching ~$4.8 billion.
- Enterprise customers contribute over 55% of total income.
- Increasing ARPU via bundled services (Zoom Phone, AI Companion).
2. Secondary Revenue Streams
a. Zoom Phone (Cloud Telephony)
- Unified voice calling solution integrated with meetings and chat.
- Generates recurring SaaS revenue via per-line licenses.
- 7M+ paid seats globally as of 2025.
b. Zoom Events & Webinars
- Monetizes virtual events, conferences, and hybrid experiences.
- Pricing based on attendee scale — $79–$999 per event.
- Used by enterprises, universities, and large-scale event hosts.
c. Zoom Contact Center
- Omnichannel customer engagement solution for enterprises.
- Subscription-based pricing per agent/month.
- Adds cross-selling synergy with existing enterprise accounts.
d. Developer Ecosystem & SDK Licensing
- Monetization via API usage fees and Zoom Apps Marketplace commissions.
- Generates indirect network value — partners drive traffic and new B2B revenue.
e. Hardware & Integration Partnerships
- Certified hardware devices and meeting room bundles (Zoom Rooms).
- Revenue through B2B partnerships with Logitech, Poly, DTEN, and Neat.
3. Overall Monetization Strategy
Zoom’s revenue engine revolves around retention and expansion, not just acquisition.
- Cross-sell & Upsell Strategy:
Encourage movement across verticals — e.g., Meetings → Phone → Events → Contact Center. - Psychology Behind Pricing:
Free plan hooks users; premium tiers introduce critical collaboration tools (cloud storage, AI summaries). - Ecosystem Economics:
Every added product (Chat, Whiteboard, AI Companion) strengthens the value stack — reducing churn and increasing customer lifetime value (CLV). - Enterprise Elasticity:
Multi-product bundles enable Zoom to withstand price competition while maintaining profitability.
| Stream | Model Type | Share (Approx.) | Growth Potential 2025 | Notes |
| Subscriptions | Recurring SaaS | 80% | Stable, steady | Core foundation |
| Zoom Phone | SaaS / Usage | 10% | Rising rapidly | High retention |
| Events & Webinars | One-time + SaaS | 5% | Seasonal growth | Expanding hybrid use |
| Contact Center | Enterprise SaaS | 3% | High margin | Enterprise contracts |
| SDKs & Marketplace | Platform revenue | 2% | Expanding | Developer adoption |
Operational Model & Key Activities
Zoom’s operational excellence is the invisible engine behind its massive scale. Unlike many SaaS peers that rely on aggressive expansion, Zoom’s strength lies in disciplined operations, robust infrastructure, and lean efficiency — enabling it to deliver billions of meeting minutes daily with minimal latency and near-zero downtime.
1. Core Operations
Zoom’s daily operations revolve around five high-performance pillars:
- Platform Reliability & Infrastructure:
Zoom runs on a hybrid cloud setup combining AWS, Oracle Cloud, and its own data centers — ensuring uptime of 99.99% across 190+ countries. - Product Innovation & Engineering:
A continuous cycle of feature rollouts (Zoom AI Companion, Workspaces, Team Chat, and Intelligent Meeting Summaries).
Regular updates keep UX friction low and engagement high. - Customer Support & Success:
24/7 multi-tiered support across regions; dedicated enterprise success managers.
Self-service knowledge base supports over 30 languages. - Marketing & Brand Building:
Thought leadership content, enterprise webinars, and integrated campaigns focused on “Work Transformation.”
Brand trust remains a major acquisition lever even in saturated markets. - Security & Compliance Operations:
Ongoing investment in encryption, compliance (ISO 27001, SOC 2, HIPAA), and incident response automation.
A strong differentiator after earlier privacy controversies.
2. Resource Allocation (2025 Estimates)
| Function | Approx. Budget Share | Key Focus Area |
| Technology & Infrastructure | 45% | Cloud optimization, AI R&D, latency reduction |
| Marketing & Customer Success | 25% | Brand reinforcement, enterprise retention |
| Human Resources & Training | 15% | Global hiring, remote work optimization |
| R&D and Product Development | 10% | Zoom AI Companion, Workspaces, Contact Center |
| Regulatory & Compliance | 5% | Regional compliance, data localization |
3. Regional Expansion Strategy
Zoom follows a “glocal” operational model — maintaining a global platform standard but tailoring support and compliance per region.
- Asia-Pacific: Strong presence in India, Japan, and Singapore with local data centers.
- Europe: GDPR-compliant infrastructure and EU-hosted meeting options.
- North America: Enterprise and education markets lead adoption.
- Middle East & Africa: Focus on partnerships with telecom and government sectors.
4. Operational Efficiency & Automation
- AI-driven customer support chatbots handle millions of queries monthly.
- Predictive scaling models optimize cloud usage and cost per meeting.
- Continuous Deployment pipelines enable rapid, low-risk feature updates.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Zoom’s evolution from a standalone video app into a comprehensive communication ecosystem has been powered by one critical factor — strategic partnerships. By creating an open, API-friendly infrastructure, Zoom amplified its reach, diversified its value proposition, and built an ecosystem where every participant — user, developer, or hardware partner — contributes to sustained growth.
1. Collaboration Philosophy
Zoom’s partnership approach is built on co-creation and interoperability. Rather than competing head-on with every platform, Zoom integrates wherever collaboration makes users’ workflows smoother.
- The guiding belief: “Work happens across tools — not within silos.”
- Every partnership enhances user productivity, expands distribution, or adds new monetization streams.
2. Key Partnership Types
a. Technology & API Partners
- Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Oracle Cloud — for global cloud redundancy and performance optimization.
- OpenAI & Anthropic (2024-25) — powering the Zoom AI Companion for note-taking, summarization, and intelligent meetings.
- Salesforce, HubSpot, Asana, Slack, and Notion — deep workflow integrations connecting CRM, productivity, and communications.
b. Payment & Logistics Alliances
- Regional payment gateway partners (Stripe, PayPal, Alipay) enable seamless global billing.
- Data localization and compliance providers (OneTrust, TrustArc) help Zoom meet country-specific legal standards.
c. Hardware & Device Partners
- Logitech, Poly, Neat, DTEN, HP — certified Zoom Rooms and Zoom Phone devices.
- Bundled enterprise packages simplify adoption and enhance video-hardware performance.
d. Marketing & Distribution Partners
- Co-marketing campaigns with Google Workspace and Microsoft Azure Marketplace to reach enterprise decision-makers.
- Telecom carriers (AT&T, BT, Telstra) resell Zoom services to enterprise clients.
e. Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Collaboration with education ministries and health authorities for compliant virtual learning and telehealth operations.
- Regional compliance partners in the EU, India, and the Middle East ensure lawful data handling.
3. Ecosystem Strategy & Impact
Zoom’s partner ecosystem isn’t a side operation — it’s a growth multiplier.
- Network Effects:
Each new integration increases Zoom’s utility, reducing customer churn and driving adoption across new verticals. - Partner Value Creation:
Developers earn revenue through Zoom’s App Marketplace (revenue-sharing model).
Hardware vendors gain recurring software tie-ins. - Monetization Synergy:
Cross-licensed features (e.g., AI Companion in partner apps) generate incremental SaaS revenue. - Competitive Moat:
The combination of platform openness and reliability makes it hard for competitors to dislodge enterprise accounts without replicating years of integrations.
| Partner Type | Examples | Strategic Value |
| Cloud & AI | AWS, Oracle, OpenAI | Performance & AI innovation |
| Software | Salesforce, Asana, Slack | Workflow integration |
| Hardware | Logitech, Poly, Neat | Hardware-software synergy |
| Telecom | AT&T, BT, Telstra | Market expansion |
| Compliance | OneTrust, EU Data Partners | Regional regulation compliance |
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Zoom’s growth playbook is built on scalable simplicity — delivering an exceptional experience first, then layering advanced products and enterprise solutions over time. From 10 million daily users in 2019 to over 350 million participants by 2025, Zoom’s trajectory reveals how deliberate scaling, ecosystem expansion, and strategic pivots can sustain long-term dominance.
1. Core Growth Engines
a. Organic Virality & Network Effects
- Zoom’s “meeting link” is its ultimate viral feature — frictionless sharing drove exponential adoption.
- Word-of-mouth and organic invites replaced traditional advertising during the 2020 boom, a strategy still yielding strong organic retention.
- Integrated referral incentives and workspace integrations amplify daily usage in 2025.
b. Enterprise Acquisition & Account Expansion
- Focused enterprise sales teams targeting verticals like education, healthcare, and finance.
- “Land and expand” model: start with small team subscriptions, then scale across departments or regions.
- Average contract value (ACV) up 15% YoY as multi-product adoption rises.
c. Product Diversification
Zoom strategically evolved from a single-product SaaS to a multi-product communications suite:
- Zoom Phone (Cloud Telephony)
- Zoom Events (Virtual Events Platform)
- Zoom Contact Center (Omnichannel Customer Support)
- Zoom AI Companion & Workspaces (Productivity and collaboration tools)
Each product feeds the others — driving ecosystem retention and ARPU growth.
d. Geographic Expansion
- Deep localization across Asia-Pacific, Europe, and LATAM markets.
- Strategic data centers built in compliance with local privacy laws.
- Multi-language UI and local payment support.
e. AI-Powered Differentiation (2024–2025 Focus)
- AI Companion features embedded in meetings, chats, and summaries.
- Generative AI note-taking and sentiment analysis improve post-meeting productivity.
- AI innovation acts as Zoom’s competitive defense against commoditization
2. Scaling Challenges & Solutions
| Challenge | Description | Zoom’s Solution |
| Infrastructure Strain | Massive surge in global usage | Hybrid cloud + edge data centers |
| Security & Privacy Concerns | Early “Zoom-bombing” incidents | End-to-end encryption, compliance upgrades |
| Competitive Saturation | Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, Slack | Ecosystem diversification & superior UX |
| Retention Fatigue | User burnout post-pandemic | AI-driven engagement and cross-product value |
| Revenue Plateau | SaaS market maturity | Expansion into enterprise telephony & CX |
3. The 2025 Growth Framework
Zoom’s scaling model now focuses on depth over breadth — increasing value per customer rather than chasing raw sign-ups.
Zoom’s Growth Flywheel (2025):
- Attract — Free access and ease of onboarding
- Engage — Seamless performance and features
- Convert — Subscription upgrade incentives
- Expand — Add-on sales (Phone, AI, Events)
- Retain — AI productivity insights and integrations
This feedback loop ensures profitable, self-sustaining growth rather than growth dependent on constant acquisition spend.
Read more : Best Zoom Clone Scripts in 2025: Features & Pricing Compared
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Zoom’s sustained leadership in 2025’s hyper-competitive communication market is a result of strategic agility, deep product focus, and customer trust. While rivals like Microsoft Teams, Google Meet, and Slack benefit from bundled ecosystems, Zoom’s independent status allows it to innovate faster and serve across ecosystems — not within a single walled garden.
1. Competitive Advantages
a. Network Effects & Switching Barriers
- Every new user adds value through meeting invitations, integrations, and platform familiarity
- Once organizations embed Zoom into workflows (training, sales, webinars, phone systems), switching costs become substantial — both technically and behaviorally.
b. Brand Equity & Reliability
- “Let’s Zoom” remains synonymous with virtual meetings — a linguistic advantage that reinforces brand dominance.
- Unmatched call stability and cross-device compatibility enhance loyalty.
c. Innovation in Technology & AI
- AI Companion (launched 2024) provides real-time meeting summaries, action items, and communication analysis.
- Continuous R&D investment (~10% of revenue) ensures Zoom remains ahead in AI-driven collaboration.
d. Open Ecosystem Advantage
- While Teams and Meet are tied to Microsoft and Google stacks, Zoom integrates with both — offering freedom of choice for enterprise IT departments.
- Developer marketplace adds 2,000+ integrated apps — from CRM to analytics tools.
e. Compliance & Security Strength
- End-to-end encryption, regional data hosting, and compliance certifications make Zoom a trusted enterprise partner.
- Focused risk management after early missteps turned privacy into a strategic asset.
2. Market Defense Tactics
a. Strategic Product Layering
Zoom expands horizontally (new products) and vertically (premium add-ons).
Example: “Zoom One” bundles Meetings, Phone, Chat, Whiteboard, and AI — locking in multi-feature contracts.
b. Pricing & Value Strategy
- Maintains affordable base tiers while upselling enterprise-grade functionality.
- AI features and automation justify premium pricing, avoiding direct price wars.
c. Timed Feature Rollouts
- Staggered releases of AI and productivity features maintain market buzz.
- Agile rollouts ensure rapid response to competitor innovations.
d. Acquisition & Talent Moves
- Acquisitions of AI startups and real-time analytics companies (e.g., Workvivo, 2023) strengthen core product value.
- Strategic hiring from AWS, Cisco, and Microsoft bolsters product leadership.
e. Community & Brand-Led Loyalty
- Continuous thought leadership via Zoomtopia events and enterprise roundtables.
- Building emotional trust through transparency and product-led storytelling.
3. Market Landscape Snapshot (2025)
| Competitor | Core Strength | Zoom’s Defensive Edge |
| Microsoft Teams | Office 365 integration | Platform independence & UX simplicity |
| Google Meet | Free bundling | Superior quality & enterprise security |
| Slack (Salesforce) | Team messaging | Zoom Phone + Chat ecosystem |
| Cisco Webex | Enterprise legacy | Better UX, lower friction |
| RingCentral | Telephony expertise | Unified platform advantage |
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Zoom’s journey offers an invaluable blueprint for founders who want to build scalable, resilient, and profitable digital platforms. Its business model combines precision, patience, and user obsession — principles that any startup can adapt to thrive in 2025’s competitive app economy.
1. Key Factors Behind Zoom’s Success
a. Solve One Problem Perfectly Before Scaling
Zoom didn’t start as an all-in-one platform. It focused entirely on one pain point — reliable video calls that just work.
Entrepreneurs often spread too thin too early; Zoom’s early discipline created the foundation for its later expansion.
b. Design for Frictionless Adoption
The magic link, one-click join, and zero-download onboarding flow made Zoom’s growth self-propelling.
Lesson: Every extra step in your funnel kills 10% of potential users. Reduce friction at all costs.
c. Freemium Done Right
Zoom’s free tier wasn’t charity — it was a lead-generation engine.
By allowing full functionality with strategic limits (40-minute cap), Zoom ensured users experienced full value before converting.
d. Product-Led Growth > Marketing-Led Growth
Instead of heavy advertising, Zoom relied on performance and word-of-mouth.
When your product genuinely solves pain, users become your marketers.
e. Evolve With Context
From pandemic dependence to AI innovation, Zoom continually reinvented itself.
Lesson: Don’t defend your old model — iterate before the market forces you to.
2. Replicable Principles for Startups
- Start Narrow, Scale Broad: Launch with one use case, then layer products.
- Invest in UX & Trust: Simplicity beats feature overload.
- Use Data Intelligently: Every user action should improve your app.
- Build Ecosystems, Not Silos: Open APIs drive long-term value.
- Monetize Through Value, Not Restriction: Price tiers should feel empowering, not punishing.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Launching multiple half-baked features instead of perfecting one core function.
- Ignoring customer feedback loops.
- Underinvesting in backend stability.
- Treating free users as freeloaders instead of future customers.
- Neglecting compliance and data protection (a trust-killer in 2025).
4. Adaptation Strategies for Local or Niche Markets
- Localize aggressively — from languages to payment methods.
- Simplify onboarding for low-tech demographics.
- Explore white-label or B2B2C models for faster regional expansion.
- Offer industry-specific versions (e.g., Zoom for Education, Zoom for Healthcare).
5. Implementation Timeline & Investment Priorities
| Phase | Focus Area | Key Deliverables | Approx. Duration |
| Phase 1 | MVP Development | Core functionality, UX testing | 3–4 months |
| Phase 2 | Monetization & Scaling | Pricing tiers, analytics, freemium funnel | 2 months |
| Phase 3 | Ecosystem Integration | APIs, payment gateways, localization | 3 months |
| Phase 4 | Growth Optimization | AI features, user retention, automation | Ongoing |
6. Founder Takeaway: Build Like Zoom
To replicate Zoom’s trajectory, founders should focus on platform depth, operational discipline, and seamless scalability.
The app’s success isn’t luck — it’s architecture.
Ready to implement Zoom’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable SaaS platforms modeled on real-world success stories.
We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable video conferencing, marketplace, and service platforms.
Get your free business model consultation today and start turning ideas into global-ready apps — fast.
Conclusion :
Zoom’s story isn’t just about video calls — it’s about clarity of vision and disciplined execution.
In an era of distractions, pivots, and rapid churn, Zoom proved that simplicity can scale faster than complexity. Its founders understood that real innovation doesn’t always mean reinventing the wheel — sometimes, it means making it roll smoother, faster, and further than anyone else.
From startup to global infrastructure provider, Zoom embodies the core principle of the platform economy: create undeniable value, make it effortless to use, and design your business model to grow as your users grow.
As we move deeper into 2025, the next frontier of digital platforms lies in AI-powered collaboration and connected ecosystems — a space Zoom already dominates. But for entrepreneurs, the lesson is timeless:
FAQs :
1. What type of business model does Zoom use?
Zoom operates on a Freemium Subscription SaaS model, where users can access basic video conferencing for free and upgrade to paid plans for advanced features. It also earns from enterprise contracts, developer APIs, and premium add-ons like Zoom Phone and Zoom Events.
2. How does Zoom’s model create value?
Zoom creates value by providing reliable, easy-to-use, and secure communication for individuals, businesses, and institutions. Its AI-driven platform saves time, enhances collaboration, and reduces operational costs for remote and hybrid workforces.
3. What are Zoom’s key success factors?
Zoom’s success comes from its reliable performance, seamless multi-device experience, smart freemium strategy, and continuous AI-driven innovation. Its strong brand trust and enterprise-grade compliance sustain long-term loyalty.
4. How scalable is Zoom’s business model?
Zoom’s cloud-based architecture lets it support billions of meeting minutes daily with minimal extra cost. Its API ecosystem and global partners ensure sustainable, efficient scalability.
5. What are the biggest challenges Zoom faces?
Zoom faces fierce competition from bundled tools like Teams and Meet, plus market saturation and regulatory hurdles. Maintaining growth beyond pandemic demand is its ongoing challenge
6. How can entrepreneurs adapt Zoom’s model to their region?
Focus on niche uses like telehealth or online education, and localize pricing and compliance. Miracuves’ white-label video app helps replicate this proven model in just 3–9 days.
7. What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a Zoom-like platform?
With Miracuves, you can launch in 3–9 days instead of 12–18 months. The investment starts at $2,499, covering hosting, AI tools, payments, and compliance essentials.
8. What are alternatives to Zoom’s business model?
Alternatives include freemium ad-based models like Google Meet, bundled SaaS (Microsoft Teams), vertical SaaS (Telehealth/EdTech), and open-source options like Jitsi.
9. How has Zoom’s business model evolved over time?
From 2013–2018, Zoom grew through freemium onboarding; 2020 brought global explosion, and by 2025 it evolved into an AI-powered collaboration and communication ecosystem.
Related Article :








