GrabMart is Grab’s on-demand grocery delivery platform across Southeast Asia, connecting local stores, dark warehouses, and delivery partners through a single ecosystem focused on speed and convenience.
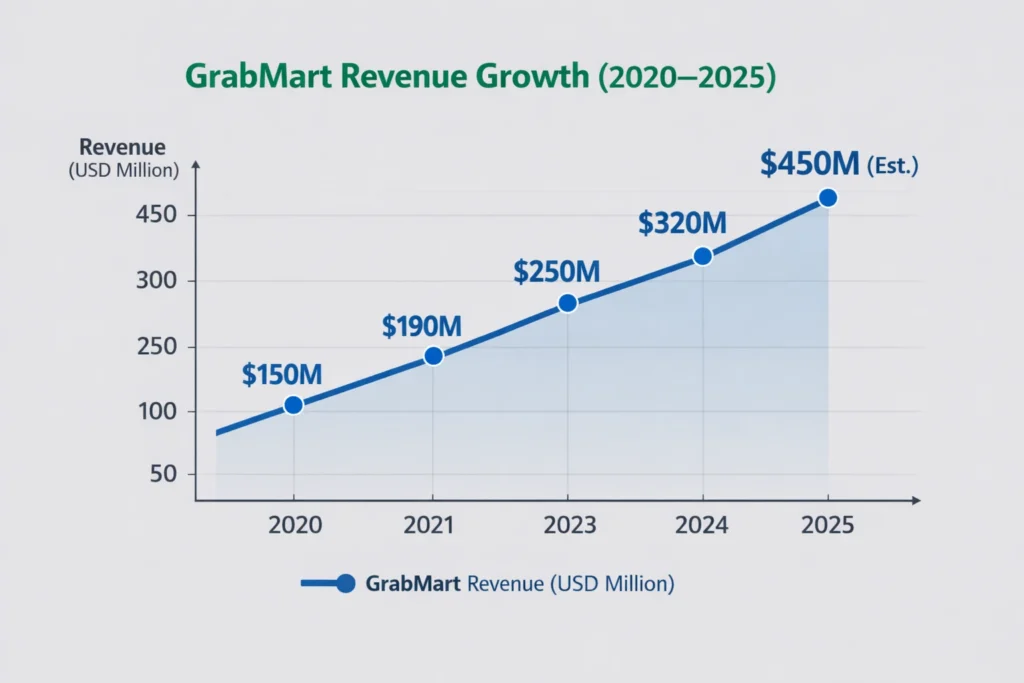
By 2025, grocery has become one of Grab’s fastest-growing verticals as consumers shift from occasional food orders to frequent purchases of daily essentials, driving higher order frequency and repeat usage.
For founders building hyperlocal or instant-commerce platforms, GrabMart’s revenue model offers practical insights into monetizing frequency, optimizing logistics, and scaling profitably across dense urban markets.
GrabMart Revenue Overview – The Big Picture
GrabMart operates under Grab Holdings Ltd, whose Deliveries segment (food + grocery) is the company’s largest revenue contributor.
2025 Key Metrics (Estimated):
- 2025 GMV (GrabMart only): ~$1.4–1.6 billion
- 2025 Net Revenue Contribution: ~$380–450 million
- Grab Holdings Valuation: ~$18–20 billion
- YoY Growth (GrabMart): ~25–30%
- Primary Markets: Singapore, Indonesia, Malaysia, Vietnam, Thailand, Philippines
- Average Order Value: $18–25
- Profit Margin (mature cities): 8–12%
- Main Competitors: GoMart, ShopeeMart, Lazada, Amazon Fresh (select markets)
Read More: What is GrabMart and How Does It Work?
Primary Revenue Streams Deep Dive
Revenue Stream #1: Merchant Commission Fees
GrabMart earns a commission from grocery stores, supermarkets, and dark stores.
- Commission Range: 10–25% per order
- Revenue Share: ~45%
- Pricing Logic: Higher commission for high-demand or fast-delivery merchants
Revenue Stream #2: Delivery & Service Fees
Paid by customers per order.
- Delivery Fee: $1–4 (dynamic)
- Platform Fee: $0.50–1.50
- Revenue Share: ~25%
Revenue Stream #3: GrabUnlimited Subscriptions
Subscription model driving retention and frequency.
- Monthly Price: ~$3–5
- Benefits: Free deliveries, discounts
- Revenue Share: ~10%
Revenue Stream #4: Sponsored Listings & Ads
Merchants pay to boost visibility inside the app.
- CPC / CPA based ads
- Revenue Share: ~12%
- High-margin revenue
Revenue Stream #5: Data & Partner Promotions
Brand promotions, FMCG partnerships, analytics insights.
- Revenue Share: ~8%
Revenue streams percentage breakdown
| Revenue Stream | Description | % of Total Revenue (2025) |
|---|---|---|
| Merchant Commission Fees | Percentage charged to grocery stores & dark stores | 45% |
| Delivery & Service Fees | Customer-paid delivery, platform, and small-order fees | 25% |
| Subscriptions (GrabUnlimited) | Monthly plans offering free deliveries & discounts | 10% |
| Sponsored Listings & In-App Ads | Paid merchant promotions and featured placements | 12% |
| Data Partnerships & Brand Deals | FMCG promotions, analytics, co-marketing campaigns | 8% |
| Total | 100% |
The Fee Structure Explained
User-Side Fees
- Delivery fee
- Small basket fee
- Surge pricing during peak hours
- Subscription upsell
Provider-Side Fees
- Commission on orders
- Sponsored placement fees
- Promotional campaign fees
Hidden Revenue Layers
- Supplier-funded discounts
- Margin on private-label products
Regional Pricing Variation
Urban markets see higher AOV and lower delivery fees; tier-2 cities rely more on commissions.
Complete fee structure by user type
| User Type | Fee Category | What It Covers | Typical Pricing (2025) | When It Applies |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Customer (Buyer) | Delivery Fee | Last-mile delivery cost (distance/time based) | $1.00–$4.00 per order | Every order; varies by distance, demand, weather |
| Customer (Buyer) | Platform / Service Fee | App convenience + operations support | $0.50–$1.50 per order | Most orders (can vary by market/promotions) |
| Customer (Buyer) | Small Basket Fee | Extra charge for low AOV orders to protect margins | $0.50–$2.00 | If cart value is below a threshold (e.g., <$10–$15) |
| Customer (Buyer) | Surge / Peak Pricing | Dynamic uplift to manage demand & rider supply | +10%–40% on delivery fee | Peak hours, heavy rain, holidays, shortages |
| Customer (Buyer) | Priority / Express Add-On | Faster delivery slot / instant dispatch | $0.50–$2.50 | Optional upgrade (availability varies) |
| Customer (Buyer) | Tip (Optional) | Customer-paid gratuity to delivery partner | 100% optional | Optional; passed to rider/driver (platform may not take a cut) |
| Customer (Buyer) | Subscription (GrabUnlimited) | Free/discounted deliveries + exclusive deals | $3–$5/month | Optional; reduces per-order fees for frequent users |
| Customer (Buyer) | Cancellation / No-Show Fee | Compensation for wasted rider time/merchant prep | $1–$5 | If late cancellation after dispatch or no-show cases |
How GrabMart Maximizes Revenue Per User
GrabMart focuses heavily on frequency-based monetization.
- Smart customer segmentation
- Subscription-driven upselling
- Cross-selling food + grocery orders
- AI-based dynamic pricing
- Reorder reminders & cart nudges
- Retention rewards via GrabRewards
- Optimized LTV through weekly usage
Example:
A subscribed household ordering twice weekly generates 3× more lifetime revenue than a casual user.
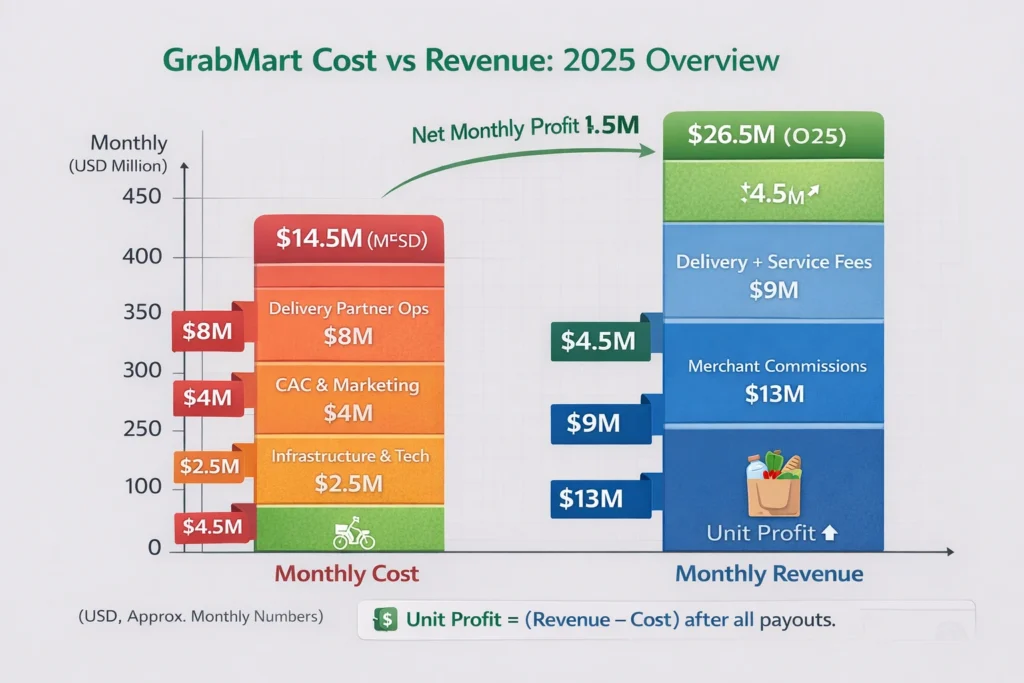
Cost Structure & Profit Margins
Major Costs
- Delivery partner incentives
- Cloud infrastructure & mapping APIs
- Customer acquisition (discounts, vouchers)
- Operations & merchant onboarding
- Product & AI development
Unit Economics
- Contribution margin positive in core cities
- Break-even achieved after ~15–18 orders per user
Profitability Path
- Higher subscription penetration
- Reduced incentives
- Private-label expansion
Future Revenue Opportunities & Innovations
New Revenue Streams
- Private-label groceries
- B2B bulk grocery delivery
- Dark store franchising
AI/ML Monetization
- Predictive demand pricing
- Smart inventory partnerships
Market Expansion
- Tier-2 cities
- Rural fulfillment hubs
Risks & Threats
- Thin margins
- High logistics costs
- Regulatory pressure
Founder Opportunities
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Your Opportunity
What Works:
- Commission + fee hybrid model
- Subscription-led retention
- Merchant advertising monetization
What to Replicate:
- Hyperlocal logistics
- Data-driven pricing
- Frequency-first design
Market Gaps:
- Regional grocery brands
- Faster rural fulfillment
- B2B grocery supply
Founder Improvements:
- Lower-cost delivery models
- Community-driven sourcing
Want to build a platform with GrabMart’s proven revenue model? Miracuves helps entrepreneurs launch revenue-generating platforms with built-in monetization systems. Our GrabMart-style grocery delivery scripts come with flexible revenue models you can customize. In fact, some clients see revenue within 30 days of launch, and if you want it, we may arrange and deliver it in 30–90 days.
If you want advanced language-level scripts or enhanced versions, Miracuves provides those too.
Final Thought
GrabMart demonstrates that grocery delivery can evolve into a scalable, profitable business when built around daily-use behavior.
Its success comes from high-order frequency, data-led pricing, and strong merchant monetization—not one-off transactions.
For founders, the key takeaway is simple: repeat usage, tight unit economics, and subscriptions drive sustainable growth.
FAQs
1. How much does GrabMart make per transaction?
Typically $2–5 per order after commissions and fees.
2. What’s GrabMart’s most profitable revenue stream?
Merchant commissions and sponsored listings.
3. How does GrabMart’s pricing compare to competitors?
Mid-range pricing with stronger subscription value.
4. What percentage does GrabMart take from providers?
Around 10–25% depending on merchant category.
5. How has GrabMart’s revenue model evolved?
Shifted from discounts to subscriptions and ads.
6. Can small platforms use similar models?
Yes, at a regional or city scale.
7. What’s the minimum scale for profitability?
Roughly 10,000+ monthly active users per city.
8. How to implement similar revenue models?
Combine commissions, delivery fees, and ads.
9. What are alternatives to GrabMart’s model?
Inventory-led or B2B grocery platforms.
10. How quickly can similar platforms monetize?
Within weeks of launch if merchant supply is strong.








