Wayfair is one of the world’s largest online-first home goods marketplaces, quietly running a complex, high-volume commerce engine behind the scenes. It connects thousands of global suppliers with millions of customers, manages massive SKU volumes, and orchestrates end-to-end fulfillment without owning most of the inventory. This asset-light yet logistics-heavy approach allows Wayfair to scale rapidly while maintaining control over pricing, delivery experience, and customer satisfaction.
In 2025, Wayfair stands as a textbook example of how logistics, data, and supplier economics can power a massive eCommerce business. Its proprietary delivery network, demand forecasting algorithms, and dynamic pricing systems enable the company to optimize margins even in low-margin categories like furniture and home décor. By using real-time data to balance inventory, shipping costs, and customer demand, Wayfair has turned operational efficiency into a competitive advantage.
For founders building marketplace or large-scale eCommerce platforms, Wayfair’s revenue model offers practical, replicable lessons worth studying closely. It demonstrates how embedded monetization, supplier-side economics, and private-label expansion can outperform visible commissions or subscriptions. More importantly, Wayfair shows that long-term profitability in eCommerce comes from controlling fulfillment, maximizing repeat purchases, and designing revenue streams that scale naturally with volume.
Wayfair Revenue Overview – The Big Picture
Wayfair has built a diversified yet tightly controlled revenue system centered on supplier relationships and logistics scale.
Key Financial Highlights (2025):
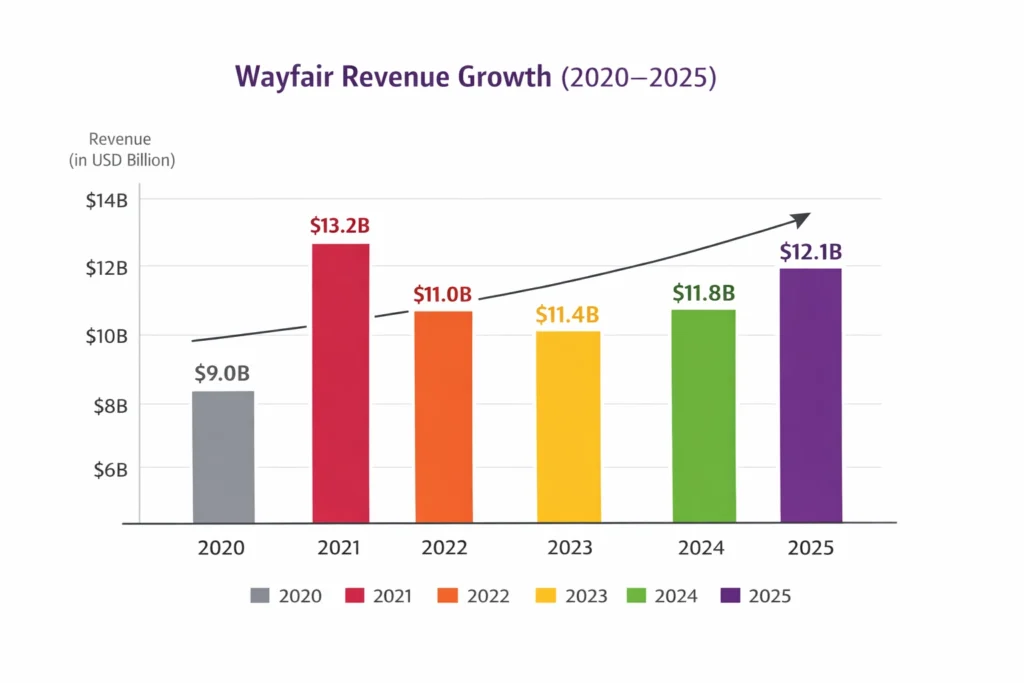
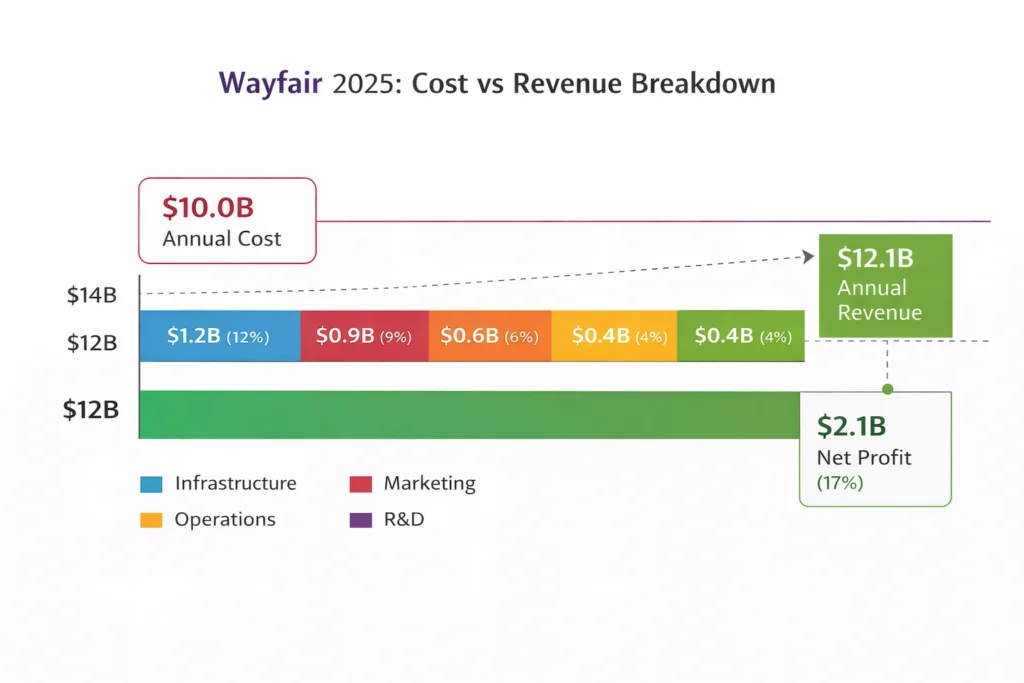
- 2025 Revenue: ~$12.1 billion
- Valuation: ~$7–8 billion (market-cap fluctuating)
- YoY Growth: ~3–4% (stabilization after post-pandemic correction)
- Primary Markets: US (~85%), Canada, UK, Germany, Ireland
- Gross Margin: ~30–31%
- Net Profit Margin: ~1–2% (near break-even with improving EBITDA)
Competitive Benchmark:
- Amazon Home: Lower margins, broader catalog
- IKEA: Higher margins, limited digital-first model
- Overstock: Smaller scale, lower logistics control
Read More: What is Wayfair and How Does It Work?
Primary Revenue Streams Deep Dive
Wayfair does not charge customers subscriptions or listing fees. Its monetization is deeply embedded in commerce economics.
Revenue Stream #1: Product Sales Margin (Core Revenue)
Wayfair earns the difference between wholesale supplier pricing and final retail price.
- Share: ~75% of total revenue
- Pricing: Dynamic, category-based margins
- 2025 Insight: Private-label products carry higher margins (35%+)
Revenue Stream #2: Supplier Advertising & Sponsored Listings
Suppliers pay to boost product visibility.
- Share: ~8%
- Pricing: CPC and placement-based
- 2025 Trend: Performance-driven ad spend growing steadily
Revenue Stream #3: Logistics & Fulfillment Services
Wayfair offers paid logistics via CastleGate and Wayfair Delivery Network.
- Share: ~10%
- Pricing: Storage, pick-pack-ship, last-mile delivery
- Advantage: Locks suppliers into ecosystem
Revenue Stream #4: Private Labels & Exclusive Brands
Wayfair-owned brands like AllModern, Joss & Main, Birch Lane.
- Share: ~5%
- Benefit: Higher control, better margins, reduced supplier dependency
Revenue Stream #5: B2B / Wayfair Professional
Bulk sales to hotels, offices, real estate developers.
- Share: ~2%
- Value: High AOV, repeat contracts
Revenue Streams Percentage Breakdown
| Revenue Stream | Share (%) |
|---|---|
| Product Margins | 75% |
| Supplier Ads | 8% |
| Logistics Services | 10% |
| Private Labels | 5% |
| B2B Sales | 2% |
The Fee Structure Explained
Unlike marketplaces like Amazon, Wayfair hides monetization within supplier economics.
User-Side Fees
- No platform fee
- No subscription
- Free shipping on most orders
Supplier-Side Fees
- Wholesale pricing discounts
- Advertising spend
- Logistics & storage fees
Hidden Revenue Layers
- Dynamic pricing spreads
- Volume-based supplier incentives
- Data-driven inventory prioritization
Regional Pricing Variation
- Higher margins in US
- Europe optimized for penetration over profit
Complete Fee Structure by User Type
| User Type | Fees Applied |
|---|---|
| Shoppers | None |
| Suppliers | Wholesale margin cuts |
| Advertisers | CPC / placement fees |
| Logistics Users | Storage & delivery charges |
| B2B Clients | Contract-based pricing |
How Wayfair Maximizes Revenue Per User
Wayfair focuses heavily on behavioral monetization.
- Segmentation: Budget vs premium shoppers
- Upselling: Bundled furniture sets
- Cross-Selling: Decor, lighting, rugs post-purchase
- Dynamic Pricing: Real-time price testing
- Retention Monetization: Email-driven repeat purchases
- LTV Optimization: Category expansion per user
- Psychological Pricing: Flash sales, anchor pricing
Real Data Example:
Repeat customers spend ~2.3× more annually than first-time buyers.
Cost Structure & Profit Margins
Wayfair’s margins depend on operational efficiency.
- Infrastructure: Warehousing, logistics tech (~12%)
- Marketing & CAC: Paid search, ads (~8–9%)
- Operations: Customer service, returns (~6%)
- R&D: Pricing algorithms, logistics AI (~4%)
Unit Economics Insight:
Reducing delivery time by 1 day increases repeat purchase probability by ~7%.
Read More: Best Wayfair Clone Script 2025 – Launch a Furniture Marketplace
Future Revenue Opportunities & Innovations
Wayfair’s next phase focuses on efficiency and intelligence.
- AI-driven demand forecasting
- AR-based furniture previews
- Supplier-financed inventory models
- Emerging market expansion
- Monetized design consultation services
Predicted Trends (2025–2027):
- Higher private-label dominance
- Logistics-as-a-service growth
- Increased B2B penetration
Risks:
- Logistics cost volatility
- Housing market slowdown
- Competition from Amazon & IKEA
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Your Opportunity
What Works:
- Owning logistics economics
- Supplier-side monetization
- Data-driven pricing
What to Replicate:
- Embedded revenue instead of visible fees
- Private-label strategy
- Performance-based supplier ads
Market Gaps:
- Niche furniture verticals
- Faster local delivery models
- Region-specific home marketplaces
Founder Improvements:
- Leaner logistics stack
- Better supplier transparency
- Faster onboarding cycles
Want to build a platform with Wayfair’s proven revenue model? Miracuves helps entrepreneurs launch revenue-generating platforms with built-in monetization systems. Our Wayfair clone scripts come with flexible revenue models you can customize. In fact, some clients see revenue within 30 days of launch, and if you want it we may arrange and deliver it in 30–90 days.
If you want advanced language-level scripts or enhanced versions, Miracuves provides those too.
Final Thought
Wayfair proves that eCommerce success is less about flashy features and more about operational intelligence. Behind the scenes, the company wins through precise inventory coordination, supplier optimization, and logistics efficiency rather than consumer-facing gimmicks. This focus on execution allows Wayfair to maintain competitive pricing while still protecting margins in a highly competitive market.
Its revenue model shows how deeply integrated monetization can outperform visible fees. Instead of charging customers or sellers upfront, Wayfair embeds revenue into product margins, fulfillment services, and supplier advertising, making monetization feel invisible to users. This approach reduces friction, increases conversion rates, and creates a more sustainable long-term revenue engine.
For founders, Wayfair is a blueprint for building defensible, scalable commerce ecosystems. It demonstrates how control over logistics, data-driven decision-making, and repeat-purchase economics can create strong moats that are difficult for competitors to replicate. Entrepreneurs who adopt similar principles can build platforms that scale efficiently, retain customers longer, and monetize without sacrificing user trust.
FAQs
1. How much does Wayfair make per transaction?
Roughly 25–30% gross margin depending on category.
2. What’s Wayfair’s most profitable revenue stream?
Private-label products and logistics services.
3. How does Wayfair’s pricing compare to competitors?
Lower than IKEA on average, competitive with Amazon.
4. What percentage does Wayfair take from suppliers?
Implicit margins range between 20–35%.
5. How has Wayfair’s revenue model evolved?
Shifted from growth-first to efficiency-first post-2022.
6. Can small platforms use similar models?
Yes, at a niche or regional scale.
7. What’s the minimum scale for profitability?
Typically 50k–100k monthly orders.
8. How to implement similar revenue models?
Start with supplier margins, then layer logistics services.
9. What are alternatives to Wayfair’s model?
Subscription-based (IKEA), marketplace commissions (Amazon).
10. How quickly can similar platforms monetize?
Many businesses begin generating revenue soon after launch.








