Booking.com has established itself as one of the most influential online travel agencies (OTAs) globally, reshaping how travelers book accommodations, flights, and experiences. By leveraging a robust business model, the platform has not only transformed the travel booking experience for millions of users but has also generated significant revenue for its partners across the travel and hospitality sectors. Understanding Booking.com business model offers valuable insights into the intricate mechanisms that drive the success of modern travel aggregators and tech platforms in the competitive OTA space.
What Makes Booking.com Unique?
Booking.com operates as both a travel aggregator and marketplace, allowing consumers to access a wide range of services, including hotel accommodations, flights, car rentals, and travel experiences. However, its real strength lies in its commission-based revenue model, which ensures a consistent revenue stream while incentivizing service providers to join the platform.
Why Study Booking.coms Business Model?
The continuous innovation behind Booking.com’s operations is a key learning point for businesses, especially those in tech and travel. Entrepreneurs and developers in these industries can extract critical insights on customer acquisition, user retention, and partnerships by analyzing Booking.com’s approach. Its adaptability to global markets, use of cutting-edge technology, and ability to scale while maintaining user satisfaction make it a perfect case study in successful platform growth.
Checkout our Readymade travel Booking app script
What is Booking.com and How It Works
Booking.com is a global leader in the travel aggregator space, allowing travelers to book a variety of services like accommodations, flights, car rentals, and travel experiences from one platform. It functions as an intermediary between service providers (hotels, airlines, etc.) and customers, offering both convenience and flexibility.
Travel Aggregator Functionality
At its core, Booking.com serves as a travel aggregator app, pulling together offerings from various providers and presenting them to users in a streamlined manner. Whether booking a luxury hotel or a budget-friendly stay, customers can browse options, compare prices, and make informed choices. The platform’s sophisticated search engine filters results based on user preferences, such as location, amenities, and price range.
Booking.com’s Multi-Service Approach
Booking.com isn’t limited to just hotel bookings. It extends its services to cover various aspects of a traveler’s journey, including flights, car rentals, and local experiences. This multi-service model allows travelers to plan their entire trip in one place, reducing friction and making the travel planning process seamless.
How Booking.com Generates Trust
An essential part of Booking.com’s success lies in its user-generated content. Customer reviews and ratings provide valuable feedback, enabling users to make informed decisions based on the experiences of others. This reliance on reviews helps build trust and transparency, which are critical in the travel booking process.
Core Elements of Booking.com Business Model
Booking.com business model is built on simplicity, scalability, and profitability. Its success lies in its ability to generate revenue while offering a seamless experience for both travelers and service providers. The key components of this model can be categorized into three main elements: the commission-based structure, the merchant vs. agency model, and its advertising revenue stream. Each of these plays a crucial role in ensuring the platform’s dominance in the online travel industry.
| Feature | Merchant Model | Agency Model |
|---|---|---|
| Inventory Ownership | Booking.com buys inventory in bulk | Booking.com acts as a middleman |
| Risk | Assumes financial risk for unsold inventory | No financial risk; commission-based |
| Pricing Control | Booking.com controls pricing | Hotels control pricing |
| Payment Structure | Upfront payment by Booking.com | Hotels pay a commission on completed bookings |
Commission-Based Model
At the heart of Booking.com’s revenue engine is its commission-based model, which accounts for the bulk of the company’s earnings. Booking.com earns a commission from hotels, accommodations, and other service providers for each booking made through its platform. These commissions typically range from 10% to 30%, depending on the region, type of accommodation, and the level of services provided by Booking.com.
This commission-based structure benefits both parties:
- For Booking.com: It provides a steady revenue stream with minimal overhead, as it does not own the properties but facilitates the connection between service providers and travelers.
- For Partners: Hotels and accommodation providers gain access to a global audience, increasing their occupancy rates and visibility without significant upfront costs.
The commission model is particularly advantageous for service providers because they only pay Booking.com after a successful booking, which reduces the financial risk for them. This success-fee arrangement encourages businesses to list their services on the platform, contributing to Booking.com’s vast inventory.
Merchant vs. Agency Model
Booking.com operates two distinct revenue-generating models: the merchant model and the agency model.
- Merchant Model: In this arrangement, Booking.com buys inventory (such as hotel rooms) in bulk at a discounted rate and then sells it to customers at a markup. The platform assumes the risk, as it has to pay for the inventory upfront, but it also controls the pricing, allowing for potential higher margins. This model is more commonly used for last-minute deals or discounted offers where Booking.com can influence pricing strategies to fill vacancies quickly.
- Agency Model: In contrast, the agency model works by simply facilitating transactions between travelers and service providers. Booking.com acts as a middleman and earns a commission on every booking without taking ownership of the inventory. This is the more common model used on the platform, as it eliminates financial risk for Booking.com while providing flexibility for hotels and travelers. Under this model, service providers are responsible for managing their pricing, availability, and customer service, while Booking.com handles the marketing, booking process, and customer acquisition.
Advertising Revenue
Beyond commissions, Booking.com generates additional income through advertising. As a platform with millions of daily visitors, it offers hotels and other service providers the opportunity to advertise their listings more prominently on the site. These sponsored listings appear at the top of search results, increasing visibility and, consequently, bookings.
- PPC (Pay-Per-Click): Hotels can bid for better visibility, paying Booking.com each time a user clicks on their listing. This creates a competitive marketplace where properties with higher advertising budgets can gain more exposure.
- Display Ads: Booking.com also earns revenue through display advertising, offering brands in the travel industry (such as airlines, car rentals, or travel insurance companies) the chance to advertise on its platform, tapping into its large user base.
The advertising model not only diversifies Booking.com’s revenue streams but also encourages platform loyalty from service providers looking to maximize their bookings.
User-Generated Content and Trust
A vital component of Booking.com’s success is its reliance on user-generated content in the form of reviews and ratings. Travelers place significant trust in reviews from other users, and this feedback helps maintain Booking.com’s credibility. Additionally, the platform’s transparency in showcasing both positive and negative reviews builds consumer trust, leading to higher user engagement and conversions.
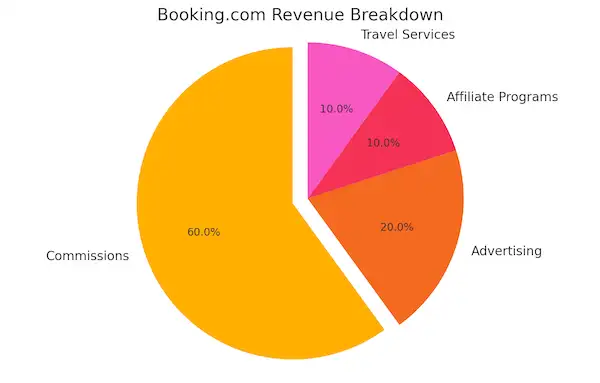
Booking.com’s Revenue Streams
Booking.com has developed a diversified revenue structure that not only relies on its primary commission model but also includes supplementary income streams. By offering various services within the travel ecosystem, Booking.com has created multiple avenues for generating profit. Let’s take a deeper look at the platform’s main revenue drivers, starting with commissions and expanding into its broader financial mechanisms.
| Revenue Stream | Description | Primary/Secondary |
|---|---|---|
| Commissions | Percentage of each booking transaction | Primary |
| Advertising | Sponsored listings and display ads | Secondary |
| Affiliate Programs | Commission through referral links | Secondary |
| Travel Services | Revenue from car rentals, flights, and experiences | Secondary |
Primary Revenue Source – Commissions
Booking.com’s primary revenue source comes from the commission fees it charges hotels, hostels, vacation rentals, and other accommodation providers for each booking made through its platform. The platform typically charges between 10% to 30%, depending on the location, type of property, and services opted for by the property owner.
This commission-based model has allowed Booking.com to remain profitable without owning or managing any accommodations directly. Instead, it acts as an intermediary, providing service providers with access to a vast global audience while collecting a percentage of the booking value. This model creates a low-cost, scalable business that thrives as more users and providers join the platform.
How the Commission Structure Works
- Tiered Commission Rates: Booking.com offers service providers the flexibility to choose different levels of commission rates. Higher commissions often lead to better visibility on the platform, while lower commissions may restrict a listing’s exposure to potential customers.
- Customer Payments: Under the agency model, customers usually pay directly to the hotel or service provider upon check-in or check-out, with Booking.com handling only the booking process. For its role in facilitating the booking, Booking.com earns a commission, paid by the service provider.
This straightforward structure encourages hotels and other accommodation providers to work with Booking.com, as they don’t have to pay unless a booking is successfully completed.
Additional Revenue Streams
While commissions remain the core of Booking.com’s revenue, the company has also developed additional streams to diversify its income and capture more value from the travel ecosystem.
Advertising Revenue
As a highly trafficked platform, Booking.com generates significant revenue from advertising. The site allows hotels, airlines, and other travel-related services to promote their offerings through sponsored listings, which appear at the top of search results. This pay-per-click (PPC) advertising model enables service providers to gain more visibility on the platform by paying for each click on their promoted listing.
Additionally, display ads are also a key part of the monetization strategy, where non-travel companies can advertise on the platform to reach a wide, engaged audience of travelers. These ads can be customized based on user location, travel interests, and preferences, increasing their relevance and effectiveness.
Affiliate Programs
Booking.com extends its reach and revenue potential through affiliate marketing. It partners with other websites, blogs, and travel agencies by offering them a commission for referring users to Booking.com. Affiliates place Booking.com’s links or widgets on their websites, and when visitors click through and complete a booking, the affiliate earns a percentage of the commission, further extending Booking.com’s digital presence and increasing bookings.
Travel Services Expansion
In recent years, Booking.com has expanded beyond accommodations to include services such as car rentals, flight bookings, and travel experiences. By offering a broader range of services, the platform captures more of the travel journey, maximizing revenue opportunities. For example:
- Car Rentals: Partnering with car rental services like Hertz or Avis allows Booking.com to offer customers the option to rent vehicles, earning commission on every booking.
- Flights: Booking.com now also operates in the flight booking space, allowing users to purchase flights directly through the platform, which adds another source of commission-based revenue.
- Travel Experiences: From guided tours to local attractions, Booking.com has ventured into offering curated travel experiences, further enhancing the user experience while generating additional income.
Subscription and Service Fees
While most of the revenue from Booking.com comes from commissions and advertising, service fees for certain types of accommodations or features have been added to diversify its income. For instance, some property owners may opt to pay for premium services that give them more control over their listings, or higher visibility through Boost programs and advanced management tools.
Packaging Deals for Added Value
Booking.com also bundles services together, offering packaged deals for accommodations and flights or car rentals. This bundling strategy not only enhances user convenience but also drives more revenue by encouraging travelers to book multiple services through one platform.
Global Reach and Dynamic Pricing
Booking.com’s global footprint allows it to take advantage of dynamic pricing strategies, adjusting rates and fees based on demand, seasonal trends, and geographic location. This dynamic approach maximizes revenue during peak travel seasons and keeps the platform competitive by offering more attractive rates during off-peak periods.
Competitive Landscape
Booking.com operates in a fiercely competitive market, dominated by other online travel agencies (OTAs) and travel aggregators. Understanding how Booking.com navigates this competitive landscape sheds light on its strategies for maintaining market leadership and continued growth.
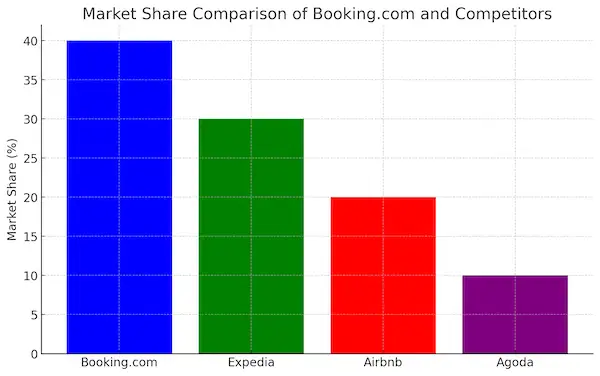
Key Competitors of Booking.com
- Expedia: As one of Booking.com’s primary rivals, Expedia offers a broad range of travel services, including hotels, flights, and car rentals. Expedia’s diversified portfolio includes other platforms such as Hotels.com, Orbitz, and Vrbo, which expand its reach across different segments of the market. However, Booking.com surpasses Expedia in market share, primarily due to its focus on the European and global accommodation market.
- Airbnb: While not a direct competitor in terms of traditional hotel bookings, Airbnb poses a significant threat by offering short-term vacation rentals, a growing sector in the travel industry. Airbnb’s unique value proposition, which centers around offering local, immersive experiences, appeals to a distinct demographic. However, Booking.com has responded by incorporating vacation rentals into its offerings to compete with Airbnb.
- Agoda: Particularly strong in the Asian travel market, Agoda is a subsidiary of Booking Holdings, the parent company of Booking.com. Although they operate independently, Agoda’s growth in the Asia-Pacific region offers additional competition to Booking.com’s global expansion efforts, especially in the budget travel and hotel segments.
- TripAdvisor: Known for its user-generated content and reviews, TripAdvisor also serves as a travel booking platform, although its primary strength lies in its recommendation engine. Booking.com competes with TripAdvisor by emphasizing its own review system and offering additional travel services like car rentals and flights that TripAdvisor doesn’t fully integrate.
- Other Players: Several regional competitors, such as MakeMyTrip in India and Ctrip (now Trip.com Group) in China, offer significant competition within their local markets. These companies are formidable in their respective regions but have limited global impact compared to Booking.com’s international reach.
| Competitor | Market Focus | Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Expedia | Full-service OTA | Strong in North America, comprehensive services | Less focus on accommodations outside the U.S. |
| Airbnb | Vacation rentals | Immersive, unique stays | Limited in traditional hotel bookings |
| Agoda | Budget hotels in Asia | Strong presence in Asia | Lesser known in Western markets |
Read Also “How Airbnb Makes Money: The Complete Business Model Behind the Short-Term Rental Giant“
How Booking.com Stands Out
Despite intense competition, Booking.com differentiates itself through several strategies:
- Focus on Accommodations: Booking.com’s largest strength lies in its sheer volume of available properties. By focusing heavily on hotel bookings and expanding into vacation rentals, Booking.com offers a more comprehensive selection than many of its competitors.
- Global Reach: Booking.com’s global presence, particularly in Europe, allows it to compete effectively with platforms that have more regional influence, such as Agoda in Asia or Expedia in North America.
- User Experience and Trust: With millions of customer reviews, user-generated content is at the core of Booking.com’s appeal. Travelers trust the platform because of its transparency and ease of use, both of which are key differentiators in the OTA market.
Challenges from Competitors
While Booking.com has solidified its position as a leader in the travel industry, it faces several ongoing challenges:
- Airbnb’s Growth: As more travelers seek authentic and local experiences, Airbnb’s growing market share in vacation rentals presents a significant threat. Booking.com has responded by increasing its inventory of vacation homes, but Airbnb remains a formidable competitor in this niche.
- New Entrants: The rise of smaller, niche travel platforms that cater to specific needs, such as eco-friendly travel or last-minute deals, could chip away at Booking.com’s market share in certain sectors.
- Regulatory Scrutiny: Like other OTAs, Booking.com faces ongoing scrutiny regarding its pricing practices, such as offering the best available rates (often referred to as price parity agreements). This has led to regulatory pressure, particularly in Europe, where competition laws have required Booking.com to change certain practices.
Want to build the next Booking.com?
Create a high-revenue booking platform with dynamic pricing,
global partnerships, and seamless user experience.
Customer Acquisition and Retention Strategies
Booking.com’s dominance in the OTA market is due to its highly effective customer acquisition and retention strategies. By leveraging a combination of SEO, paid marketing, and user-centric features, the platform not only attracts new customers but also ensures they keep coming back.
SEO and Paid Marketing
Booking.com invests heavily in search engine optimization (SEO) and paid search advertising to maintain visibility. Its SEO strategy focuses on ranking for high-intent keywords related to travel, accommodation, and booking services, while its paid search campaigns (Google Ads, for example) target specific keywords to drive immediate traffic to the platform.
SEO Strategy
The platform utilizes content optimization for keywords like “hotel booking,” “travel aggregator,” and region-specific searches. By creating dedicated landing pages optimized for these queries, Booking.com attracts organic traffic from travelers looking for accommodations in specific cities or countries.
Paid Advertising
On the paid marketing front, Booking.com spends significantly on Google Ads and Bing Ads, ensuring it appears at the top of search results for high-value travel-related queries. This aggressive paid advertising strategy is designed to capture potential customers before they land on competitor sites, such as Expedia or Airbnb. Additionally, Booking.com runs display ads and remarketing campaigns to keep its brand in front of customers who have previously visited the platform, enticing them to return and complete their bookings.
User Experience and Loyalty Programs
Booking.com’s user experience is a key factor in retaining customers. The platform is known for its intuitive interface, ease of booking, and comprehensive search filters, which allow travelers to customize their search based on preferences like price, location, and amenities.
Personalization and Recommendations
Booking.com excels at using personalization to enhance the user experience. Once a user makes a booking, the platform leverages data analytics to offer personalized suggestions for future trips, such as destinations or hotels similar to the user’s past bookings. This level of customization makes travelers feel understood and valued, increasing their likelihood of returning.
Loyalty Programs
To further encourage repeat bookings, Booking.com offers its Genius Loyalty Program. Through this program, frequent users unlock discounts, free upgrades, and priority customer service. The Genius program is tiered, so the more a customer books, the greater their benefits. This loyalty system not only increases retention but also incentivizes users to book more frequently through Booking.com rather than exploring other OTAs.
Partner Relations
Booking.com’s success isn’t just due to its customer-facing strategies; its relationships with hotels, property owners, and other service providers are just as important. The platform offers flexible commission structures and helps partners increase their visibility through tools like Boost campaigns, which allow properties to appear higher in search results for a fee.
Partner Support and Tools
For partners, Booking.com offers a range of support tools to manage listings, track bookings, and improve performance. These tools include performance analytics, market insights, and competitive pricing tools, which help property owners maximize their revenue. By providing valuable data and insights, Booking.com fosters strong, long-lasting relationships with its partners, ensuring that they remain loyal to the platform.
Partnerships and Integrations
Booking.com has built a strong ecosystem by forming strategic partnerships and integrating with various travel-related services, enhancing the customer experience and creating additional revenue streams. By expanding its platform to include airlines, car rentals, and travel insurance providers, Booking.com offers a seamless experience for travelers looking to manage their entire trip in one place.
Strategic Partnerships
Booking.com collaborates with airlines, car rental companies, and tour providers to offer bundled services, providing customers with added convenience. For example, through partnerships with major airlines, customers can book both their flights and accommodations in one transaction. This strategy not only makes Booking.com a one-stop solution for travel planning but also boosts its revenue by cross-selling different travel services.
Additionally, the company has partnerships with local experience providers such as tour companies, enhancing its offering beyond traditional accommodations. This integration into the experiential travel sector allows Booking.com to cater to the rising demand for immersive travel experiences.
API Integrations for Better User Experience
Booking.com leverages API integrations to ensure real-time availability and pricing updates for its services. For example, hotels can manage their bookings through a centralized system that automatically updates availability across multiple OTAs, including Booking.com. These integrations allow for a smoother booking process for both service providers and travelers, reducing the risk of overbooking or price discrepancies.
Value of Partnerships to Booking.com’s Growth
These strategic alliances have enabled Booking.com to expand its offerings and increase its market share, solidifying its position as a leading player in the online travel agency space. By partnering with a wide array of travel service providers, Booking.com ensures that customers can plan every aspect of their trip through its platform, thus increasing customer retention and loyalty.
Global Expansion Strategy
Booking.com’s global expansion strategy has played a pivotal role in its dominance in the online travel industry. By entering new international markets, the platform has successfully adapted to regional differences, legal requirements, and traveler preferences.
Entering New Markets
Booking.com’s global reach spans over 220 countries, with a strong presence in regions like Europe, Asia-Pacific, and North America. Its expansion strategy includes understanding local markets, partnering with region-specific travel service providers, and adjusting its platform to meet local consumer needs.
For example, in regions where cultural differences or regulatory barriers are significant, Booking.com tailors its marketing strategies and offers services in local languages, making it easier for travelers and service providers to engage with the platform. This localized approach allows Booking.com to scale without losing relevance in new markets.
Localization and Legal Compliance
A major component of Booking.com’s success abroad is its ability to localize content and comply with the legal and regulatory frameworks of each country. This includes offering customer service in multiple languages, complying with tax regulations, and adhering to local laws regarding online transactions, data privacy, and consumer protection.
To build trust with users, Booking.com also integrates local payment methods in regions where credit card usage might not be the norm, making transactions smoother and more accessible for customers.
Competitive Advantage Through Early Market Entry
Booking.com’s strategy of being an early entrant into emerging markets has given it a significant edge over regional competitors. By establishing its presence in markets where demand for online travel bookings is growing, the company was able to build strong brand recognition and user loyalty before local OTAs gained traction.
Adaptability to Market Dynamics
Booking.com constantly evolves to meet market dynamics and traveler behavior in different regions. For example, in areas with high mobile internet usage, the platform prioritizes mobile app optimization and marketing to capture a growing base of mobile travelers.
Data-Driven Decision Making
Booking.com’s success is deeply rooted in its ability to harness data analytics and artificial intelligence (AI) to optimize both user experience and operational efficiency. Through data-driven insights, the platform continuously improves its offerings, helping users find the most relevant travel options while maximizing partner revenue.
How Data Powers Personalization
Booking.com collects massive amounts of data from user interactions, including search behavior, booking history, and preferences. This data is fed into sophisticated AI algorithms to create personalized recommendations for users. Whether it’s suggesting hotels based on previous stays or recommending destinations aligned with the user’s interests, this tailored approach enhances the customer experience and increases booking conversions.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
By using predictive analytics, Booking.com can anticipate travel trends, demand fluctuations, and pricing shifts. This allows the platform to optimize its pricing strategies and adjust hotel availability in real-time, ensuring users get the best deals while helping service providers maximize occupancy.
Forecasting tools also aid hotel partners by offering insights into upcoming peak travel periods, allowing them to adjust pricing or manage inventory more effectively.
A/B Testing for Continuous Improvement
Booking.com constantly runs A/B tests to optimize everything from user interface design to marketing campaigns. These tests allow the platform to make data-driven decisions on which features work best for user engagement and conversion rates. Whether it’s tweaking a call-to-action button or testing new layouts, this iterative process ensures Booking.com remains responsive to user preferences.
Fraud Detection and Security
Data analytics also play a vital role in fraud detection and ensuring platform security. By analyzing transaction patterns, Booking.com can quickly identify suspicious activities and mitigate potential fraud, safeguarding both users and service providers.
Booking.com’s Mobile Strategy
Booking.com’s mobile strategy has been a key driver in its global success, particularly in emerging markets where mobile devices are the primary means of internet access. The platform has optimized its mobile experience to ensure that users can seamlessly search, book, and manage their travel arrangements via their smartphones or tablets.
Mobile App Optimization
Booking.com’s mobile app is designed to provide a user-friendly, fast, and efficient booking experience. It offers intuitive navigation, personalized recommendations, and easy access to reviews and property details. By leveraging features like push notifications, the app keeps users engaged with timely reminders about upcoming bookings, special deals, and last-minute offers.
Mobile-First Design and Features
The platform uses a mobile-first approach for both its website and app, ensuring that mobile users get a smooth, responsive experience. Features such as one-click booking, mobile-only discounts, and seamless integration with payment gateways encourage users to finalize their bookings on the go.
Booking.com also understands the importance of mobile-specific marketing, offering exclusive deals to app users. These incentives not only drive app downloads but also increase engagement and retention among mobile users.
Growth Through Mobile Usage
Booking.com’s focus on mobile technology has allowed it to tap into markets with high smartphone penetration but lower desktop usage, such as Asia and Africa. By offering a robust mobile solution, it has captured a significant share of travelers in these regions, who primarily use their mobile devices to plan and book trips.
Incorporating AI and machine learning into its mobile platform, Booking.com tailors offers and recommendations to individual users, increasing booking conversion rates. For instance, users receive personalized deals based on their search and booking history, as well as local travel trends.
Impact of User-Generated Content
One of Booking.com’s greatest strengths is its reliance on user-generated content, which fosters trust and transparency on the platform. Reviews, ratings, and photos provided by users play a crucial role in shaping customer decisions and influencing bookings.
Building Trust Through Reviews and Ratings
Travelers rely heavily on the millions of reviews left by other users to make informed decisions about accommodations and services. Booking.com prominently displays user feedback on each property’s page, making it easy for potential customers to gauge the quality of a hotel or vacation rental.
These reviews offer detailed insights into the customer experience, covering everything from cleanliness and location to the quality of service and amenities. This transparency helps travelers feel more confident in their choices, as they can see both positive and negative feedback, making the decision-making process more reliable.
Importance of Authenticity
Booking.com ensures authenticity by allowing only verified guests who have completed a booking to leave a review. This approach prevents fake reviews and ensures that the feedback on its platform reflects genuine traveler experiences. Verified reviews help maintain the credibility of the platform, encouraging new users to trust the service.
Leveraging Content for SEO and Engagement
User-generated content also plays a crucial role in SEO. Each new review adds fresh content to Booking.com’s pages, keeping them relevant and engaging. The platform also uses these reviews to tailor its search results, showing users properties that have the best feedback for their specific preferences, further enhancing user engagement and satisfaction.
Visual User-Generated Content
In addition to written reviews, users can also upload their own photos of properties, providing an authentic visual representation of the accommodations. These photos are often more relatable than professional images provided by the hotels, as they show real-life experiences of the property, which can be more appealing to potential customers.
Customer Support and Service Quality
Booking.com’s customer support is a key pillar in its efforts to retain customer loyalty and satisfaction. The platform offers 24/7 customer service in multiple languages, ensuring that users from around the world have access to help when needed. Whether it’s booking issues, cancellations, or disputes, Booking.com’s support team is readily available through phone, email, and live chat.
24/7 Support Availability
Booking.com ensures that customers can access support at any time, regardless of time zones or booking complexities. This round-the-clock availability is crucial, especially for travelers who might encounter problems while on the move, such as issues with check-ins or cancellations.
Dispute Resolution
In situations where travelers encounter disputes with hotels or service providers, Booking.com acts as an intermediary, facilitating quick dispute resolution. The platform’s policies around cancellations and refunds are designed to be user-friendly, allowing travelers to make changes with minimal hassle. This feature helps ensure customer satisfaction, even when things don’t go as planned.
Localized Support
To cater to its global user base, Booking.com offers support in multiple languages, ensuring travelers from different regions can get assistance in their native language. This localized support, along with region-specific payment options, creates a seamless experience for international travelers.
Service Quality for Partners
Booking.com also focuses on providing high-quality support to its partners—hotels, vacation rentals, and other service providers. Property owners have access to dedicated support teams that assist with listing management, pricing strategies, and resolving any customer-related issues. This two-sided support structure helps maintain positive relationships between Booking.com, its partners, and its customers, ensuring smooth operations and sustained loyalty.
Challenges Faced by Booking.com
Despite its global dominance, Booking.com faces significant challenges that could impact its future growth. These challenges range from regulatory scrutiny to market saturation, and the platform must continuously adapt to stay competitive.
Regulatory and Compliance Issues
Booking.com operates across numerous jurisdictions, each with its own regulatory framework. In Europe, for instance, the platform has faced scrutiny over price parity agreements, where hotels are prevented from offering lower prices on competing OTAs or their own websites. Regulatory bodies have increasingly scrutinized these practices, forcing Booking.com to adapt its pricing strategies to comply with local competition laws.
Additionally, Booking.com must navigate data privacy laws, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in the European Union, which imposes strict requirements on how companies collect, store, and process user data. Ensuring compliance across multiple countries is an ongoing challenge that requires significant legal and operational resources.
Market Saturation
As the online travel industry matures, market saturation is becoming a challenge for Booking.com. The rise of alternative OTAs, niche travel platforms, and direct bookings via hotel websites has increased competition. To maintain its market share, Booking.com must continue innovating and providing superior value to both travelers and service providers.
Economic and Travel Disruptions
Global events such as the COVID-19 pandemic have shown how vulnerable the travel industry is to external shocks. Booking.com saw a sharp decline in bookings and revenue as international travel came to a halt during the pandemic. Although the company has recovered, it faces ongoing uncertainty due to changing travel restrictions, economic downturns, and fluctuating consumer confidence.
Booking.com must also account for environmental concerns, as travelers are increasingly seeking sustainable travel options. The platform has started to promote eco-friendly accommodations, but it faces challenges in balancing profitability with the growing demand for sustainability.
Competition from Niche Platforms
While Booking.com competes well with traditional OTAs like Expedia, it faces increasing competition from niche travel platforms that offer specialized services, such as eco-friendly accommodations, adventure travel, or luxury vacation rentals. These platforms cater to specific traveler segments, and although they don’t pose an immediate threat to Booking.com’s broad market, they could slowly erode its market share in certain categories.
Future of Booking.com
Booking.com is constantly evolving to maintain its position in the travel industry, and its future lies in technological advancements, market expansion, and sustainability efforts.
Expansion into New Markets and Services
Booking.com is expanding its reach into new markets and service offerings, such as travel experiences and tours. The company is also moving towards a more holistic approach by offering end-to-end travel solutions, covering accommodations, flights, car rentals, and local activities. This expansion will allow it to capture more of the travel journey, creating a one-stop shop for travelers.
Technology and Innovation
Booking.com is at the forefront of travel technology innovation, investing heavily in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to improve personalization and customer service. By leveraging these technologies, the platform can provide more tailored recommendations, enhance the search experience, and streamline customer support.
Voice search and chatbot assistance are also expected to become more prevalent, allowing users to book travel simply by speaking to a virtual assistant. These innovations not only improve the user experience but also allow Booking.com to stay ahead of competitors in the travel tech space.
Focus on Sustainability
As the travel industry increasingly prioritizes sustainability, Booking.com is making strides to promote eco-friendly accommodations and reduce the environmental impact of travel. The platform has introduced sustainability certifications for properties, helping users make more informed choices when booking eco-conscious stays. This aligns with the growing demand from travelers for sustainable travel options and supports Booking.com’s long-term commitment to reducing its carbon footprint.
Adapting to Future Travel Trends
Booking.com is well-positioned to adapt to future travel trends, such as the rise of remote work and digital nomadism. As more people combine work and travel, the platform will likely expand its offerings to cater to long-term stays, coworking-friendly accommodations, and flexible booking options.
Diversification of Services
Beyond just accommodations, Booking.com is also looking to diversify its services further by integrating travel insurance, transportation services, and local experiences into its platform. This diversification allows it to offer a complete travel solution, increasing customer retention and generating new revenue streams.
Conclusion
Booking.com’s business model is a masterclass in scalability, innovation, and customer-centric strategies. By leveraging a robust commission-based model, investing in cutting-edge technologies like AI and machine learning, and focusing on global expansion, the company has become a leader in the online travel industry. Its ability to navigate challenges, from regulatory pressures to increased competition, while continuously expanding its services—such as integrating eco-friendly travel options—demonstrates its agility and forward-thinking approach.
For businesses looking to learn from a travel tech giant, Booking.com serves as a prime example of how to build a sustainable, diversified revenue engine that thrives on customer trust and data-driven decisions. Its future, driven by technological advancements and a strong commitment to sustainability, promises continued growth and market leadership.
Ready to build your own scalable, tech-driven travel platform like Booking.com? Miracuves offers custom online travel agency solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you’re aiming to create a marketplace for accommodations, flights, or full-service travel packages, our expert team can help you develop a cutting-edge platform with seamless booking experiences, personalized recommendations, and robust revenue models.
Start your journey today with Miracuves and launch a travel platform designed to compete with the best. Contact us for a consultation and let’s turn your vision into reality!
Visit Miracuves to learn more.
Optimize Your Booking Business Strategy?
Optimize your booking platform with a proven business model that drives customer engagement, increases bookings, and boosts profits. Need a solution?
FAQs
1. How does Booking.com make money?
Booking.com generates revenue primarily through a commission-based model, earning between 10-30% of the booking value from hotels and service providers. The platform also earns revenue from advertising, affiliate partnerships, and additional services like flights, car rentals, and travel experiences.
2. What is the difference between Booking.com’s merchant and agency models?
In the merchant model, Booking.com buys hotel inventory upfront and resells it, assuming financial risk. In the agency model, Booking.com acts as a middleman, facilitating bookings and earning commissions without owning inventory or pricing control.
3. What are Booking.com’s key competitors?
Booking.com competes with major players like Expedia, Airbnb, and Agoda. While Expedia offers full-service travel solutions, Airbnb focuses on vacation rentals, and Agoda has a strong presence in the Asian market.
4. How does Booking.com use data for personalization?
Booking.com leverages data analytics and AI to offer personalized recommendations based on user behavior, past bookings, and search patterns, improving the user experience and boosting conversion rates.
5. How does Booking.com manage customer reviews?
Booking.com only allows verified users who have completed a stay to leave reviews, ensuring authenticity and trust. These reviews are prominently displayed to help users make informed decisions about accommodations.
6. What challenges does Booking.com face in the travel industry?
Booking.com faces challenges such as regulatory scrutiny over pricing practices, competition from niche platforms like Airbnb, and economic disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic, which impact global travel demand.
Explore the world effortlessly with Miracuves – built for smooth bookings, unique stays, and reliable navigation:
- Travel Booking Like Service – A streamlined travel service that makes it easy to book flights, hotels, and manage itineraries in one place.
- Expedia Like Service – Smart travel services offering seamless booking for flights, hotels, and holiday packages.
- Yatra Like Service – Reliable travel services for flights, trains, hotels, and complete holiday planning.







