The rapid growth of on-demand food delivery services has reshaped the food industry, and at the forefront is DoorDash, a food delivery platform that has established itself as a market leader. Founded in 2013, DoorDash has since scaled into a multi-billion-dollar enterprise, connecting restaurants with customers through an intuitive app and efficient delivery logistics. As consumer demand for convenience continues to rise, DoorDash’s innovative business model has enabled it to dominate the competitive food delivery space by offering multiple revenue streams, strategic partnerships, and cutting-edge technology. Checkout our prebuilt doordash clone
This blog explores the DoorDash business model, breaking down its key components, including how the platform operates, its primary revenue streams, and the strategies that have made it successful. By understanding DoorDash’s business model, entrepreneurs and businesses can gain valuable insights into what it takes to thrive in the food tech app market.
The Evolution of the On-Demand Food Delivery Market
The food delivery business has evolved rapidly over the last decade, driven by changing consumer behaviors and advancements in delivery service apps. DoorDash capitalized on these shifts by offering a streamlined solution that allows customers to order from local restaurants through its user-friendly mobile and web platforms. More importantly, it leveraged a gig economy model by employing independent contractors known as “Dashers” to fulfill orders, ensuring rapid delivery times and reducing overhead costs.
The Scope of This Blog
In this blog, we will delve deep into how DoorDash works, covering aspects such as customer experience, restaurant partnerships, and logistics. We’ll also analyze the company’s key revenue streams, including commissions, delivery fees, and premium subscription models like DashPass. Furthermore, we will explore DoorDash’s challenges and opportunities in a highly competitive landscape with DoorDash competitors like UberEats and Grubhub. The blog will close with an examination of the platform’s potential for future growth, focusing on expanding into new verticals and improving its technology infrastructure.
What is DoorDash?
DoorDash is a leading food delivery platform that has revolutionized the way customers interact with restaurants and local eateries. Founded in 2013, DoorDash has rapidly expanded, offering its services across more than 4,000 cities in the U.S. and international markets like Canada and Australia. The platform connects customers to restaurants via a seamless, user-friendly app and website, providing a convenient solution for busy individuals seeking food delivery options from their favorite establishments. Its success stems from its ability to combine cutting-edge technology, strategic restaurant partnerships, and the use of freelance drivers, or “Dashers,” to create an efficient delivery system.
DoorDash’s Core Service Offerings
DoorDash allows users to browse local restaurants, place orders, and have meals delivered directly to their homes or offices within minutes. In addition to food delivery, the company has also expanded its services to include grocery and alcohol deliveries in select markets, further solidifying its presence as an all-encompassing on-demand delivery service.
DoorDash’s Role in the On-Demand Food Delivery Industry
In the ever-growing on-demand food delivery sector, DoorDash stands out by offering a flexible, scalable model that benefits both customers and restaurants. The platform provides smaller local restaurants with the opportunity to reach a wider customer base without the need for their own delivery infrastructure. Meanwhile, customers can enjoy a wide variety of cuisines from different restaurants without stepping out of their homes.
How DoorDash Works
DoorDash operates as a marketplace that connects customers, restaurants, and independent delivery drivers (Dashers) through its app and website. The process begins when a customer places an order via the DoorDash app, selecting a restaurant and menu items. The order is then transmitted to the restaurant, which prepares the food. At the same time, a Dasher is notified and assigned to pick up the order.
Here’s a breakdown of how DoorDash works:
- Customer Experience:
- Placing an Order: Customers browse menus, choose items, and place orders through the DoorDash platform. They can filter by location, cuisine, and other preferences, making it easy to find restaurants that suit their needs.
- Tracking the Order: Once an order is placed, customers can track it in real-time, from preparation to delivery. The app provides ETA updates and the ability to communicate with both the restaurant and the Dasher if needed.
- Restaurant Involvement:
- Receiving Orders: Restaurants receive orders through the DoorDash portal or integrated POS systems. They prepare the meal within a set time frame to ensure the food is fresh when picked up by the Dasher.
- Partnership Models: Restaurants can choose from various partnership models, including commission-based or a flat-fee delivery service, allowing them flexibility in pricing and operations. This model is particularly beneficial for small businesses without their own delivery infrastructure.
- Dasher’s Role:
- Gig Economy Workers: DoorDash employs a network of freelance drivers, called Dashers, who receive notifications of available delivery tasks via the app. Dashers can accept or reject assignments based on location and time preferences.
- Pick-Up and Delivery: Dashers pick up the food from the restaurant and deliver it to the customer. They follow the optimized routes provided by the DoorDash app to ensure timely delivery.
- Earnings: Dashers are paid per delivery, with earnings determined by a base rate, tips, and promotions offered by DoorDash. The flexibility of this model has attracted a large number of drivers, especially in urban areas where demand is high.
- Efficient Delivery Logistics:
- Algorithm-Driven Matching: DoorDash uses advanced algorithms to match orders with the nearest available Dashers. This minimizes delivery time and improves customer satisfaction. The app factors in real-time traffic data, the location of Dashers, and restaurant preparation times to ensure a smooth delivery experience.
- Peak Period Optimization: DoorDash adjusts pricing and delivery fees dynamically during high-demand times (e.g., lunch and dinner rush hours), providing Dashers with additional incentives to work during these periods.
- Payment & Transaction Flow:
- Customer Payments: Customers pay for their order, which includes the meal cost, taxes, delivery fees, and an optional tip for the Dasher. DoorDash accepts a variety of payment methods, including credit cards, digital wallets, and even cash in some markets.
- Restaurant Payments: DoorDash takes a commission from each order, which can vary based on the partnership agreement. The remainder is paid to the restaurant after deducting the delivery costs.
- Dasher Payments: Dashers are compensated based on the distance traveled, delivery time, and tips received. Payments are processed weekly, and Dashers can also withdraw earnings instantly for a small fee.
Core Components of DoorDash’s Business Model
DoorDash operates on a multi-faceted business model that centers around creating value for customers, restaurants, and Dashers, while optimizing its own revenue streams. The DoorDash business model is highly scalable, allowing it to dominate in both dense urban markets and suburban regions. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the core components:
1. Marketplace Model
At its core, DoorDash functions as a two-sided marketplace, connecting customers who want food delivered with restaurants that need delivery services. This marketplace model offers flexibility and scalability, with DoorDash serving as the intermediary between these two groups.
- For Restaurants: By partnering with DoorDash, restaurants can expand their customer base without building their own delivery infrastructure. This is especially beneficial for small and medium-sized restaurants that cannot afford to run their own delivery services.
- For Customers: The marketplace offers customers access to a wide variety of local eateries, ranging from fast food to high-end dining. The ease of use and convenience of browsing menus, placing orders, and having food delivered to their doorsteps make DoorDash an essential service for many.
2. Third-Party Delivery (Gig Economy)
A key innovation in DoorDash’s business model is its reliance on freelance, independent drivers known as Dashers. This gig economy model enables DoorDash to scale quickly without the need for hiring full-time employees. DoorDash relies heavily on gig economy workers, which allows it to scale rapidly without significant overhead costs. For a deeper understanding of how the gig economy operates, read more about the gig economy here.
- Flexibility for Dashers: Dashers can choose when and where they want to work, providing them with flexibility. This has been crucial for attracting a large number of drivers, especially in cities where part-time work is in high demand.
- Low Overhead for DoorDash: By using freelance contractors, DoorDash significantly reduces its overhead costs related to employee benefits, insurance, and wages. This gig economy model allows DoorDash to expand into new markets rapidly, as there is minimal need for fixed investment in delivery infrastructure.
3. Dynamic Pricing and Fee Structures
DoorDash’s pricing model is dynamic, incorporating various fees and surcharges based on delivery distance, restaurant partnerships, and time of day. This flexible pricing helps DoorDash balance its profitability while still providing value to customers.
- Delivery Fees: Customers are charged a delivery fee, which may vary depending on the order size, distance, and the specific market. This fee helps compensate Dashers and ensures the profitability of each order.
- Service Fees: In addition to delivery fees, DoorDash adds a service fee, typically a percentage of the total order cost, to cover operational expenses like payment processing and technology upkeep.
- Commissions: Restaurants pay DoorDash a commission on every order, typically ranging from 15% to 30%. The exact percentage depends on the specific partnership agreement, but this fee represents a significant portion of DoorDash’s revenue.
4. DashPass Subscription Model
DoorDash offers a subscription service called DashPass, which provides customers with free delivery on eligible orders for a fixed monthly fee. This is a crucial part of DoorDash’s strategy to build customer loyalty and generate recurring revenue.
- Customer Benefits: DashPass subscribers enjoy perks like lower service fees and free delivery on orders above a certain threshold. This encourages frequent use of the platform and adds value for power users who order multiple times a week.
- Revenue Growth: For DoorDash, DashPass is a recurring revenue stream that provides financial stability and increases the lifetime value of each customer. Subscriptions also incentivize higher-order frequency, which benefits both DoorDash and the restaurants on its platform.
5. Advertising and Promotions
A significant part of DoorDash’s revenue comes from its advertising and promotions services offered to restaurants. Through this model, restaurants can pay for higher visibility on the platform, promoting their menus and deals to a larger audience.
- Featured Listings: Restaurants can pay to appear at the top of search results or under “featured” categories, making it easier for them to attract more customers, especially during peak times.
- Targeted Promotions: DoorDash enables restaurants to create custom promotions, such as discounts or free delivery offers, which are strategically designed to attract customers and increase order volume.
6. Technology and Data Utilization
At the heart of DoorDash’s operational success is its advanced use of technology and data analytics. The platform leverages data to improve the efficiency of its delivery process, enhance user experience, and optimize its marketplace.
- Optimized Delivery Routes: DoorDash uses algorithms that consider traffic data, order preparation times, and driver availability to optimize delivery routes, ensuring faster delivery times.
- Customer Insights: DoorDash collects and analyzes customer behavior data to improve personalization. This data helps recommend restaurants, curate promotions, and offer a more seamless user experience, driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
| Component | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Marketplace Model | DoorDash connects restaurants and customers through a centralized platform. | Scalability, increased customer reach |
| Third-Party Delivery | Gig workers (Dashers) handle deliveries instead of in-house teams. | Low overhead, flexibility for Dashers |
| Dynamic Pricing and Fees | Delivery and service fees vary based on demand, distance, and time. | Ensures profitability per transaction |
| DashPass Subscription | Monthly subscription providing free delivery and reduced service fees on orders. | Increases customer retention and frequency |
| Advertising and Promotions | Restaurants pay for increased visibility through featured listings and promotions. | Additional revenue stream for DoorDash |
| Data and Technology | DoorDash leverages data to optimize delivery routes and personalize customer experiences. | Improved efficiency, customer satisfaction |
Key Revenue Streams of DoorDash
The DoorDash business model is driven by several robust revenue streams that ensure its profitability while providing value to customers, restaurants, and drivers. Each of these revenue streams is integral to the platform’s ability to scale and sustain operations in a competitive marketplace.
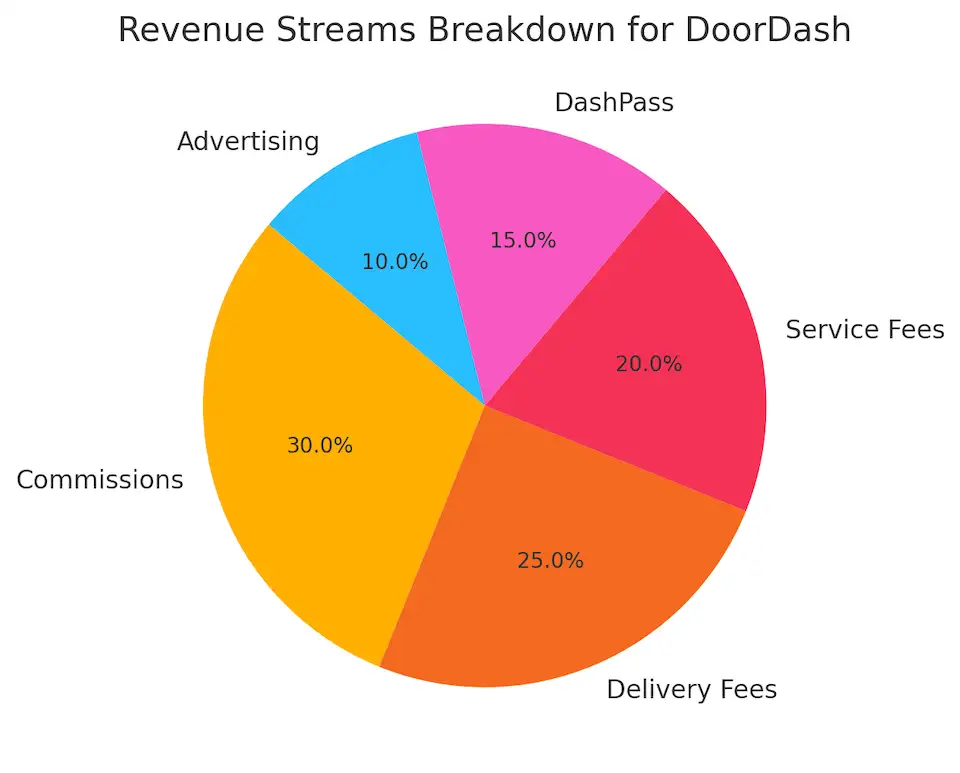
1. Commissions from Restaurants
- Core Revenue Stream: DoorDash charges restaurants a commission fee for every order processed through the platform. These commissions typically range from 15% to 30% of the order value, depending on the partnership agreement.
- Why it Works: This model allows restaurants to reach a larger audience without investing in their own delivery infrastructure, while DoorDash profits from every sale made through its platform.
- Impact: This revenue stream generates significant income for DoorDash, as the volume of orders increases with market penetration. However, it has also led to tensions with some restaurants, who feel burdened by the high fees.
2. Delivery and Service Fees from Customers
- Dynamic Delivery Fees: Customers are charged a delivery fee, which varies based on factors like distance, restaurant location, and demand. These fees are essential for covering the cost of Dashers and maintaining DoorDash’s operational efficiency.
- Service Fees: In addition to delivery fees, customers pay a service fee, usually a percentage of the total order value, which helps DoorDash cover platform costs, payment processing, and app maintenance.
- Impact on Profitability: While these fees increase the cost for the customer, they ensure DoorDash can profit on every transaction, even when offering discounts or promotions.
3. DashPass Subscription Model
- Subscription-Based Revenue: DoorDash’s DashPass subscription service offers customers free delivery and reduced service fees for a flat monthly rate. Priced at around $9.99 per month, this model incentivizes frequent users to order more, while providing DoorDash with a stable, recurring revenue stream.
- Customer Loyalty: DashPass helps retain high-frequency users, ensuring customer loyalty, and increasing the lifetime value of each subscriber.
4. Advertising and Promotions
- Restaurant Promotions: DoorDash offers advertising services to restaurants looking to increase their visibility on the platform. Restaurants can pay to be featured in search results or run promotions that offer free delivery or discounts.
- Revenue Impact: By offering targeted promotions, DoorDash creates another revenue stream while allowing restaurants to reach more customers. This model also helps restaurants stand out during competitive periods, such as holidays or weekends.
5. Peak Pricing and Delivery Surges
- Dynamic Pricing: During periods of high demand, such as lunch and dinner rushes, DoorDash implements surge pricing, charging customers higher delivery fees. This helps manage supply and demand while incentivizing Dashers to work during peak hours.
- Revenue Impact: Surge pricing increases revenue per order and improves delivery efficiency by ensuring a greater number of Dashers are available during high-demand periods.
6. Expansion into New Services
- Grocery and Alcohol Delivery: DoorDash is expanding into verticals beyond restaurant delivery, offering grocery and alcohol delivery in select markets. This diversification opens up new revenue streams while leveraging the existing delivery infrastructure.
- Partnerships with Retailers: By partnering with grocery stores and liquor retailers, DoorDash is able to offer more comprehensive delivery services, further solidifying its presence in the on-demand delivery market.
| Revenue Stream | Description | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Commissions | DoorDash charges restaurants a percentage of each order (15%-30%). | Significant revenue source |
| Delivery Fees | Customers pay a fee for delivery based on distance, demand, and other factors. | Covers operational and driver costs |
| Service Fees | An additional fee paid by customers, typically a percentage of the order value. | Contributes to platform maintenance |
| DashPass Subscriptions | Monthly fee providing customers with free delivery on eligible orders. | Recurring revenue and customer loyalty |
| Advertising | Restaurants pay for increased visibility and promotional placements on the platform. | Increases DoorDash’s marketing revenue |
| Peak Pricing (Surge) | Additional charges during peak times, incentivizing Dashers to work and meet demand. | Boosts revenue during high-demand periods |
Each of these revenue streams plays a crucial role in DoorDash’s business model, ensuring profitability while providing value to restaurants, customers, and Dashers. The combination of commissions, fees, advertising, and expansion into new markets has allowed DoorDash to thrive as a leader in the food delivery business.
Challenges and Opportunities in the DoorDash Business Model
DoorDash’s business model, while highly successful, is not without its challenges. However, with each challenge comes a set of opportunities that, if leveraged properly, can lead to long-term growth and sustainability.
1. High Competition
- Challenge: DoorDash faces stiff competition from UberEats, Grubhub, and other regional food delivery platforms. These competitors vie for market share, often driving up customer acquisition costs.
- Opportunity: DoorDash’s strategy to differentiate through exclusive partnerships, aggressive expansion into smaller markets, and offering diverse services like grocery and alcohol delivery is proving successful in maintaining its competitive edge.
2. Commission Fees & Restaurant Tensions
- Challenge: Restaurants often express dissatisfaction with DoorDash’s commission rates, which can range from 15% to 30% per order. These high fees eat into restaurant profits, especially for smaller establishments, leading to friction between restaurants and the platform.
- Opportunity: To mitigate these tensions, DoorDash could explore more flexible pricing models or tiered commission structures that help small businesses without cutting deeply into their margins. Additionally, creating loyalty programs or exclusive deals for restaurants could foster better relationships.
3. Driver Classification & Legal Issues
- Challenge: As a company deeply rooted in the gig economy, DoorDash faces ongoing legal scrutiny over its classification of Dashers as independent contractors rather than employees. In markets like California, regulatory shifts (like AB5) could force DoorDash to reclassify Dashers as employees, leading to higher costs in terms of benefits, wages, and insurance.
- Opportunity: DoorDash has the opportunity to invest in a hybrid workforce model that balances flexibility for Dashers while providing essential benefits. By being proactive in resolving these legal issues, DoorDash can strengthen its reputation and potentially attract a more stable driver workforce.
4. Profitability and Scaling
- Challenge: DoorDash’s rapid expansion has come with high costs, and despite significant revenues, the company has struggled with consistent profitability. Managing the cost of customer acquisition, driver incentives, and technological investments while still turning a profit remains a significant challenge.
- Opportunity: DoorDash can focus on operational efficiencies, such as optimizing delivery routes through AI and machine learning, reducing customer churn through DashPass, and expanding into higher-margin verticals like grocery delivery. By leveraging data and improving logistics, DoorDash has the potential to reduce operational costs and improve its margins.
5. International Expansion
- Challenge: Although DoorDash is a dominant player in the U.S. market, its presence internationally is still limited. Expanding into international markets introduces unique challenges, including navigating different regulatory environments, cultural preferences, and entrenched local competitors.
- Opportunity: By partnering with international restaurant chains and local grocery stores, DoorDash can enter new regions strategically. Localization of the app’s features, pricing, and services will also allow DoorDash to tailor its offerings to new markets and compete effectively.
6. Technology and Innovation
- Challenge: As technology evolves, customers expect faster and more efficient deliveries, while competitors are also investing in innovations like autonomous deliveries and drones. Staying ahead of technological trends is crucial for DoorDash to maintain its market position.
- Opportunity: DoorDash has the opportunity to invest in cutting-edge technology, such as AI-driven route optimization, drones, and autonomous vehicles for delivery. Leveraging these innovations can reduce reliance on human drivers and cut costs in the long term, giving the company a technological advantage over its competitors.
| Challenge | Description | Opportunity |
|---|---|---|
| High Competition | Competition from UberEats, Grubhub, etc. drives up customer acquisition costs. | Focus on exclusivity, new markets, and services |
| High Commission Fees | Restaurants often complain about DoorDash’s high commission rates. | Offer flexible pricing models or incentives |
| Labor Classification Issues | Legal challenges related to classifying Dashers as independent contractors versus employees. | Explore a hybrid model offering more benefits |
| Profitability Concerns | Difficulty maintaining profitability due to high operational costs and customer acquisition. | Optimize technology and logistics efficiency |
| International Expansion | Regulatory and competitive challenges in international markets. | Partner with local brands and tailor services |
| Environmental Sustainability | Pressure to reduce carbon emissions and packaging waste. | Adopt green delivery methods and eco-friendly practices |
DoorDash’s challenges present unique opportunities for continued growth and success in the on-demand food delivery industry. By addressing legal, operational, and competitive hurdles head-on, DoorDash can continue to refine its business model and expand its influence across the globe.
Want to dominate the food delivery market like DoorDash?
We’ll help you refine your strategy, from
logistics to monetization.
DoorDash’s Impact on Restaurants
The rise of DoorDash and similar food delivery platforms has significantly reshaped the restaurant industry. While these platforms offer numerous benefits to restaurants, they also introduce challenges that can affect profitability and operations. Understanding the impact of DoorDash on restaurants is crucial for restaurant owners considering partnering with such services.
Positive Impacts on Restaurants
1. Expanded Customer Base
- Increased Visibility: Partnering with DoorDash allows restaurants to reach a wider audience beyond their immediate geographic location. Customers who might not have been aware of a restaurant can discover it through the app.
- Access to New Markets: Restaurants can tap into markets without the need to establish physical locations, effectively expanding their reach.
2. Convenience and Operational Efficiency
- No Need for In-House Delivery: Establishing an in-house delivery system requires significant investment in staffing, logistics, and technology. DoorDash provides a ready-made delivery infrastructure, saving restaurants time and resources.
- Focus on Core Competencies: By outsourcing delivery logistics, restaurants can concentrate on food preparation and in-house customer service, enhancing overall quality.
3. Increased Sales Volume
- Higher Order Frequency: The convenience of on-demand food delivery can lead to increased order frequency, especially during off-peak hours or adverse weather conditions when dine-in traffic may be low.
- Promotional Opportunities: Restaurants can leverage DoorDash’s promotional tools to offer discounts and deals, attracting more customers and boosting sales.
4. Data and Insights
- Customer Behavior Analytics: DoorDash provides restaurants with data on customer preferences, peak ordering times, and popular menu items. This information can be valuable for menu planning and marketing strategies.
Negative Impacts on Restaurants
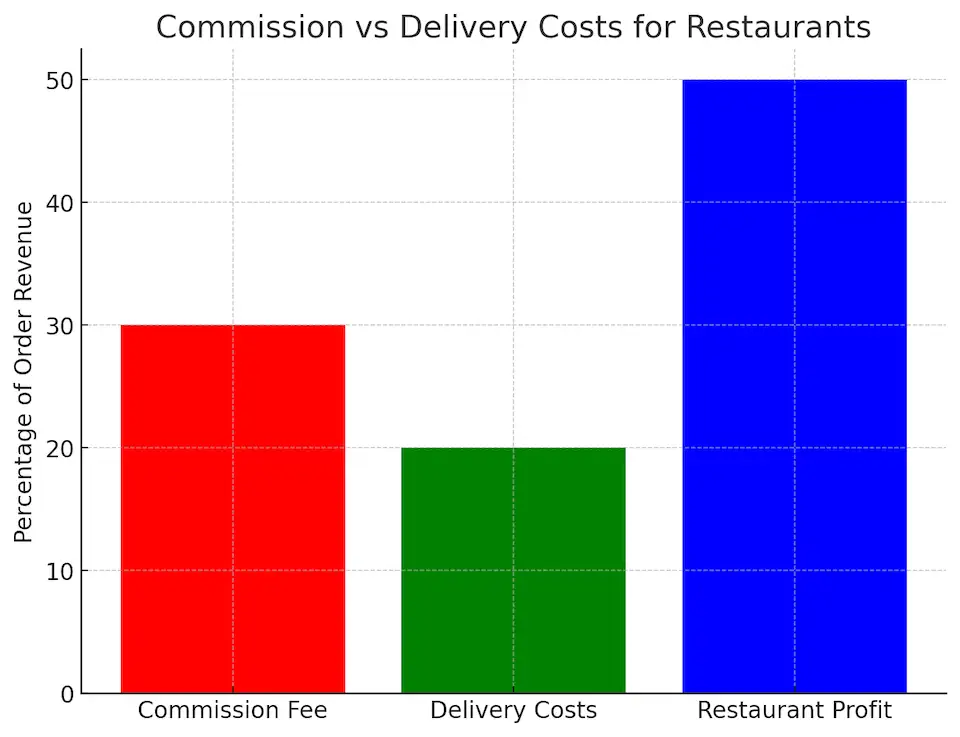
1. High Commission Fees
- Reduced Profit Margins: DoorDash’s commission fees, ranging from 15% to 30% per order, can significantly reduce a restaurant’s profit margins, especially for small businesses with tight budgets.
- Pricing Challenges: To offset commission costs, some restaurants may consider increasing menu prices on the platform, which can deter price-sensitive customers.
2. Dependence on Third-Party Platforms
- Loss of Direct Customer Relationship: When orders come through DoorDash, restaurants may miss opportunities to build direct relationships with customers, affecting brand loyalty.
- Platform Reliance Risks: Heavy dependence on DoorDash can be risky if the platform changes its policies, increases fees, or if technical issues arise.
3. Quality Control Issues
- Delivery Experience: Restaurants have limited control over the delivery process. Poor delivery experiences, such as late arrivals or damaged food, can lead to negative reviews that impact the restaurant’s reputation.
- Consistency Challenges: Ensuring that food quality remains high during delivery is challenging, especially for dishes that are best served fresh and may not travel well.
4. Data Ownership Concerns
- Limited Access to Customer Data: While DoorDash provides some analytics, restaurants may not have full access to customer contact information, limiting their ability to conduct direct marketing campaigns.
Balancing the Pros and Cons
For many restaurants, the decision to partner with DoorDash involves weighing the increased exposure and sales against the costs and potential downsides.
- Strategic Partnerships: Some restaurants negotiate customized agreements with DoorDash to balance commission rates and services provided.
- Hybrid Models: Restaurants may use DoorDash for delivery while encouraging customers to order directly through their own websites by offering incentives.
- Menu Optimization: Adjusting the menu to include items that are delivery-friendly can help maintain food quality and customer satisfaction.
Case Study: A Restaurant’s Journey with DoorDash
“Mama’s Kitchen,” a small family-owned restaurant, partnered with DoorDash to expand its customer base. Initially, they saw a 30% increase in orders. However, the high commission fees began to eat into their profits. To address this, they optimized their menu for delivery, focusing on high-margin items and adjusted pricing strategies. They also encouraged repeat customers to join their loyalty program via inserts in delivery orders, balancing the benefits of DoorDash with their own marketing efforts.
The Future Outlook
As the food delivery industry continues to grow, restaurants must adapt to the changing landscape.
- Negotiation of Terms: Restaurants, especially larger chains, may have the leverage to negotiate better commission rates or terms.
- Investment in Technology: Some restaurants are developing their own apps or partnering with alternative platforms to reduce dependency.
- Community Engagement: Emphasizing local community support and unique dining experiences can help restaurants maintain a loyal customer base outside of delivery platforms.
Read More : HealthifyMe Business Model Explained: How It Works and Generates Revenue
Regulatory and Compliance Considerations
DoorDash, like other gig economy companies, operates in a complex regulatory environment, especially concerning labor laws and food safety regulations. As the company scales, it faces increasing scrutiny from governments and regulatory bodies, which could significantly impact its operations.
1. Labor Classification Issues
- Challenge: One of the most critical regulatory issues DoorDash faces is the classification of its delivery drivers (Dashers) as independent contractors rather than employees. This classification allows DoorDash to avoid providing benefits like healthcare, paid leave, or minimum wage guarantees. However, this model is under growing scrutiny in markets like California, where laws like AB5 seek to reclassify gig workers as employees.
- Potential Impact: If Dashers were to be classified as employees, DoorDash would face a dramatic increase in labor costs, affecting its profitability. The company would need to provide additional benefits, wages, and insurance, significantly changing its business model.
- Opportunity: By offering some form of hybrid workforce model that balances flexibility for Dashers while offering basic protections and benefits, DoorDash could improve its relationship with regulators and workers alike. This could also enhance Dashers’ satisfaction and retention, improving service reliability.
2. Food Safety and Health Regulations
- Challenge: As a food delivery platform, DoorDash must comply with various food safety regulations to ensure that restaurants and drivers handle food according to health standards. This includes maintaining proper temperatures during delivery, hygiene practices, and ensuring the food remains uncontaminated.
- Potential Impact: Non-compliance with these regulations could result in penalties, lawsuits, or reputational damage. DoorDash is required to follow local, state, and federal food safety guidelines, which can vary significantly across regions.
- Opportunity: DoorDash could differentiate itself from competitors by implementing stringent quality control measures and offering transparency around food safety. This could enhance trust with both consumers and restaurants, further solidifying its position in the market.
3. Data Privacy and Security
- Challenge: Handling millions of transactions and customer data daily, DoorDash is subject to data privacy laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe. Protecting customer data, including payment details and personal information, is critical to maintaining consumer trust.
- Potential Impact: Any data breaches or mishandling of sensitive information could lead to fines, lawsuits, and significant reputational damage. The regulatory landscape around data privacy is evolving, and non-compliance could have severe financial consequences.
- Opportunity: Investing in robust cybersecurity measures and transparent privacy policies can help DoorDash not only meet regulatory requirements but also position itself as a trusted and secure platform for customers and restaurants. Enhancing data protection could also attract more users concerned about privacy.
4. Environmental Regulations
- Challenge: With increasing global focus on sustainability, food delivery companies are coming under pressure to reduce their environmental footprint. From vehicle emissions (Dashers’ cars, bikes, and scooters) to packaging waste, DoorDash faces growing expectations to adopt environmentally friendly practices.
- Potential Impact: Governments could impose regulations requiring delivery companies to meet certain environmental standards, particularly in urban areas with pollution concerns. This could lead to increased operational costs, such as adopting electric vehicles or using biodegradable packaging.
- Opportunity: By proactively adopting eco-friendly practices, such as incentivizing Dashers to use low-emission vehicles or encouraging restaurants to use sustainable packaging, DoorDash could enhance its public image and meet emerging environmental regulations ahead of competitors.
5. International Compliance and Market Entry
- Challenge: Expanding into international markets introduces regulatory complexities, including different labor laws, food safety standards, and data protection regulations. Each country has its own set of legal requirements that DoorDash must navigate.
- Potential Impact: Failing to comply with local laws in new markets could result in delayed or blocked entry, fines, and legal challenges, which could hinder DoorDash’s expansion efforts.
- Opportunity: Partnering with local firms to understand and meet regulatory standards can help DoorDash enter international markets more smoothly. Tailoring the platform to local legal and cultural contexts will not only ensure compliance but also foster better customer and restaurant relationships in new regions.
By navigating these regulatory and compliance considerations, DoorDash can protect its reputation and continue to expand its services. Each regulatory challenge also offers an opportunity for innovation and improved operational efficiency, which can further distinguish DoorDash in the competitive on-demand food delivery space.
Future Growth Strategies for DoorDash
As the on-demand delivery market continues to expand, DoorDash is positioning itself for sustained growth by adopting several forward-thinking strategies. These strategies focus on leveraging technology, expanding into new verticals, and tapping into global markets. Here’s how DoorDash plans to scale its operations:
1. Investment in Technology
- AI and Machine Learning: DoorDash is heavily investing in artificial intelligence and machine learning to optimize delivery logistics, improve route planning, and enhance the overall customer experience. By analyzing vast amounts of data on traffic, customer preferences, and delivery patterns, DoorDash can fine-tune its operations for maximum efficiency.
- Autonomous Delivery: The future of delivery logistics is leaning toward automation. DoorDash is actively exploring autonomous delivery methods, including drones and robotic vehicles. These innovations could drastically reduce the reliance on human Dashers, lower operational costs, and improve delivery times, especially in densely populated urban areas. Autonomous delivery is also likely to attract tech-savvy consumers who value speed and innovation. DoorDash is investing in autonomous delivery technology to streamline operations and reduce costs. To learn more about how autonomous delivery is transforming the logistics industry, check out this article on autonomous delivery.
- Customer Insights and Personalization: Data analytics is central to DoorDash’s strategy of improving the customer experience. By leveraging customer behavior insights, DoorDash can personalize the user interface, recommend restaurants or dishes based on past orders, and offer tailored promotions. This not only increases order frequency but also boosts customer satisfaction and retention.
2. Expansion into New Services
- Grocery and Alcohol Delivery: DoorDash has expanded beyond restaurant delivery into grocery delivery and alcohol delivery. By partnering with major grocery chains and local alcohol vendors, DoorDash offers customers more options, broadening its customer base and increasing its revenue streams. These additional services help DoorDash tap into markets that complement its core food delivery business, particularly in suburban and rural areas where demand for grocery delivery is growing.
- Partnerships with Retailers: In addition to food and groceries, DoorDash has begun partnering with retailers to offer same-day delivery of non-food items such as household essentials, health products, and even apparel. These partnerships allow DoorDash to become a one-stop-shop for customers, further increasing order frequency and platform engagement.
3. Geographical Expansion
- Entering New Markets: DoorDash has primarily focused on the U.S., but international expansion is key to its future growth. DoorDash has already entered markets in Canada, Australia, and Japan, and plans to expand into Europe and other parts of Asia. However, each international market comes with its own set of challenges, including navigating local regulations, understanding consumer preferences, and competing with established local delivery platforms.
- Localized Offerings: To succeed in new markets, DoorDash plans to tailor its services to local tastes and cultures. This includes offering local cuisines, adapting the app’s features, and adjusting the pricing model to fit the economic conditions of each region.
4. Enhancing DashPass
- Growing Subscription Revenue: DashPass, DoorDash’s subscription service, is central to its strategy for increasing customer loyalty and boosting recurring revenue. By offering free delivery on eligible orders for a fixed monthly fee, DashPass encourages frequent ordering. DoorDash plans to expand DashPass benefits by adding exclusive restaurant partnerships, priority customer service, and additional perks to differentiate the service from competitors.
- Bundling Services: In the future, DoorDash may bundle DashPass with other services, such as grocery delivery, offering customers greater value while increasing subscription sign-ups.
5. Sustainability and Environmental Initiatives
- Green Delivery Initiatives: With increasing pressure to reduce carbon footprints, DoorDash has committed to adopting more environmentally sustainable practices. The company is exploring the use of electric vehicles, bicycles, and eco-friendly packaging to reduce emissions. It is also working with restaurants to minimize waste and promote the use of biodegradable containers. These initiatives not only reduce operational costs in the long run but also improve DoorDash’s brand image as a responsible corporate entity.
- Carbon Offset Programs: DoorDash is considering introducing carbon offset programs where customers can contribute to environmental causes during checkout. These programs will align DoorDash with growing consumer demand for environmentally responsible companies.
6. Acquisitions and Mergers
- Strategic Acquisitions: DoorDash has been on an acquisition spree, with the purchase of Caviar and Chowbotics being prime examples of its strategy to dominate the market. By acquiring smaller competitors and complementary technology companies, DoorDash can expand its technological capabilities and market reach.
- Consolidating the Market: As competition in the on-demand delivery sector intensifies, DoorDash is likely to engage in more mergers or partnerships with regional players. This will enable the company to quickly gain market share in areas where it currently has a limited presence.
In summary, DoorDash’s future growth strategies focus on scaling its operations through technological innovation, expanding its service offerings, and entering new geographical markets. By staying ahead of industry trends and evolving consumer expectations, DoorDash is positioning itself as a dominant force in the food delivery platform and on-demand delivery sectors. This forward-thinking approach ensures continued success and leadership in the competitive landscape.
Conclusion: DoorDash’s Business Model and Its Future
DoorDash has solidified its position as a leader in the on-demand food delivery industry through its dynamic and scalable business model. By leveraging multiple revenue streams—commissions, delivery fees, subscriptions, and advertising—DoorDash has created a profitable ecosystem that benefits restaurants, customers, and drivers. Despite challenges such as high competition, regulatory pressures, and profitability concerns, the company continues to innovate and expand into new markets and services like grocery and alcohol delivery.
Looking ahead, DoorDash’s growth strategies focus on leveraging technology, expanding internationally, enhancing customer loyalty through DashPass, and adopting sustainable practices. Its investments in AI, automation, and strategic acquisitions also ensure that the company remains at the forefront of the delivery industry.
By staying agile and adaptive, DoorDash is well-positioned to scale further in the food delivery platform space while continuing to meet evolving consumer demands.
Looking to build a cutting-edge on-demand food delivery platform like DoorDash? At Miracuves, we specialize in developing scalable, high-performance apps tailored to your business needs. Whether you’re entering the food delivery market, expanding to new verticals, or optimizing your existing service, we can help you craft a robust, customized solution. Our team combines deep industry expertise with the latest technology to bring your vision to life.
Get in touch today to discuss your project and accelerate your success with Miracuves!
Ready to build your food delivery app with a strong business model?
Build Your Food Delivery Business Today ! Our team will guide you through every step, from app development to creating profitable strategies.
FAQs
1. What is DoorDash’s business model?
DoorDash operates as a two-sided marketplace, connecting customers with local restaurants through an on-demand delivery platform. It generates revenue through commissions, delivery fees, DashPass subscriptions, and advertising. DoorDash leverages gig economy workers (Dashers) to fulfill deliveries, allowing it to scale quickly and efficiently.
2. How does DoorDash make money?
DoorDash’s revenue comes from multiple sources: commissions from restaurants (15%-30% per order), delivery and service fees from customers, DashPass subscriptions, and advertising paid by restaurants for increased visibility on the platform.
3. What are the key challenges in DoorDash’s business model?
DoorDash faces challenges such as high competition from UberEats and Grubhub, legal issues regarding Dasher classification, restaurant dissatisfaction with commission fees, and achieving consistent profitability. These challenges create opportunities for innovation and cost optimization.
4. How does DashPass work for DoorDash?
DashPass is a subscription service where customers pay a monthly fee (around $9.99) for free deliveries and reduced service fees on eligible orders. This subscription increases customer loyalty, retention, and order frequency, contributing to DoorDash’s recurring revenue.
5. What are DoorDash’s future growth strategies?
DoorDash plans to grow by investing in AI and machine learning for optimized deliveries, expanding into grocery and retail delivery, international expansion, enhancing DashPass offerings, and adopting sustainable practices like electric vehicles and eco-friendly packaging.
6. How does DoorDash impact restaurants?
DoorDash helps restaurants reach a wider customer base and increase sales without the need for in-house delivery. However, high commission fees (15%-30%) can impact profitability for smaller restaurants.








