When Postmates launched in 2011, it faced an uphill battle: few believed consumers would pay strangers to fetch food or groceries. Fast-forward to today — the company redefined the way cities move things. From a small San Francisco startup, Postmates grew into a $2.65 billion acquisition by Uber in 2020, and remains a cornerstone of the U.S. delivery ecosystem in 2025.
Its evolution wasn’t just about fast delivery — it was about building a logistics network that behaves like an API for urban movement. Postmates connected merchants, couriers, and customers in real-time, democratizing local delivery the same way Uber democratized transportation.
In a world where convenience drives loyalty and time is the new currency, understanding business model of Postmates’ reveals key insights for entrepreneurs building their own on-demand or logistics-based apps
Why Studying Postmates’ Model Matters in 2025
- The on-demand delivery market is expected to cross $350 billion globally by 2025, with hybrid logistics platforms leading the charge.
- Consumer expectations have shifted permanently toward instant gratification — 30-minute deliveries are now standard.
- Postmates’ model blends gig workforce efficiency, merchant partnerships, and tech-powered optimization, offering a replicable framework for founders entering local commerce, quick logistics, or multi-service app markets.
Read more : What is Postmates and How Does It Work? Complete 2025 Guide
How the Postmates Business Model Works
Postmates operates as a three-sided on-demand marketplace connecting customers, couriers (Postmates Fleet), and local merchants — all powered by advanced logistics algorithms and location-based automation.
At its core, it bridges immediacy and availability, giving users access to anything within their city in under an hour — from food and groceries to electronics and flowers.
Business Model Type
- Model: Hybrid (Marketplace + On-Demand Logistics + Subscription)
- Core Components:
- Marketplace: Customers order from partnered or unpartnered merchants.
- Delivery Network: Freelance couriers (Fleet members) fulfill orders via real-time dispatching.
- Subscription Tier: “Postmates Unlimited” — a premium membership offering free delivery on eligible orders.
- Marketplace: Customers order from partnered or unpartnered merchants.
This hybrid model allows Postmates to generate revenue from both sides of the market — users and merchants — while minimizing inventory and infrastructure costs.
Value Proposition by Stakeholder
| Stakeholder | Value Delivered |
| Customers | Instant access to local stores and restaurants, real-time tracking, flexible payment, and subscription benefits. |
| Merchants | Expanded delivery capabilities without owning logistics infrastructure, increased sales reach, and analytics insights. |
| Couriers (Fleet) | Flexible earning opportunities, optimized delivery routes, and instant payouts. |
| Partners (Tech, Payment, API) | Integration into a growing on-demand ecosystem that handles millions of micro-transactions daily. |
Evolution of the Model
- 2011–2015: Built core logistics engine and expanded across major U.S. metros.
- 2016–2019: Introduced Postmates Unlimited (subscription), Party Orders (grouped deliveries), and Postmates API for third-party integrations.
- 2020–2023: Acquired by Uber — integration into Uber Eats logistics backbone improved delivery times and reduced costs.
- 2024–2025: Postmates is positioned as Uber’s urban logistics brand, powering instant delivery for local merchants beyond food (retail, pharmacy, and B2B micro logistics).
Why the Model Still Works in 2025
- Rising consumer demand for hyperlocal and same-hour delivery.
- Merchant reliance on third-party platforms to maintain competitiveness.
- Efficient gig workforce economics integrated with AI dispatch and route optimization.
- Postmates’ brand strength in urban convenience and tech-driven operations.
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Postmates’ success lies in its ability to identify, segment, and continuously adapt to evolving consumer behavior across urban centers.
Its user base isn’t just “people who order food” — it’s urban professionals, convenience-driven millennials, and digitally native consumers who prioritize time over cost.
Primary & Secondary Customer Segments
| Segment | Demographics & Behavior | Why They Use Postmates |
| Urban Millennials (Age 24–40) | Tech-savvy, busy professionals, often single or dual-income households. | Convenience and time-saving for meals, groceries, and essentials. |
| Students & Young Adults | Price-sensitive, social media-active, spontaneous orderers. | Late-night food, snacks, and quick impulse purchases. |
| Remote Workers & Freelancers | Home-based professionals valuing productivity. | Regular meal and grocery deliveries to save time. |
| Small Merchants & Restaurants | Local businesses lacking in-house delivery infrastructure. | Increased reach and operational support. |
| Corporate Clients (B2B Deliveries) | Offices and co-working spaces needing bulk or repeated orders. | Reliable, scheduled deliveries integrated into business workflows. |
Customer Journey Mapping
1. Discovery:
Social media, influencer campaigns, app store optimization, and referral programs drive initial installs.
(Example: “Get $10 off your first delivery” campaign helped boost first-time conversions by 22%.)
2. Conversion:
Smooth onboarding, instant order access, and visible ETAs improve trust.
Users are prompted with cross-category offers — e.g., “Order dinner and get grocery delivery discount.”
3. Retention:
Postmates uses personalized push notifications, AI-driven recommendations, and Unlimited memberships to build loyalty.
In-app gamification (delivery streaks, badges) reinforces engagement.
4. Advocacy:
Satisfied users and couriers promote Postmates on social platforms, boosting word-of-mouth virality and reducing paid CAC (customer acquisition cost).
Market Positioning & Differentiation
- Brand Voice: Urban, energetic, and hyperlocal — positioned as “the app that gets you anything.”
- Competitive Edge: Unlike pure food delivery apps, Postmates caters to all categories — groceries, retail, alcohol, and convenience items.
- Market Share (2025): ~14% of the U.S. urban delivery market (food + retail combined), trailing DoorDash and Uber Eats but leading niche convenience players like GoPuff.
- Geographic Focus: Major metropolitan regions — LA, NYC, Miami, Austin, Seattle — with suburban expansion via Uber’s shared infrastructure.
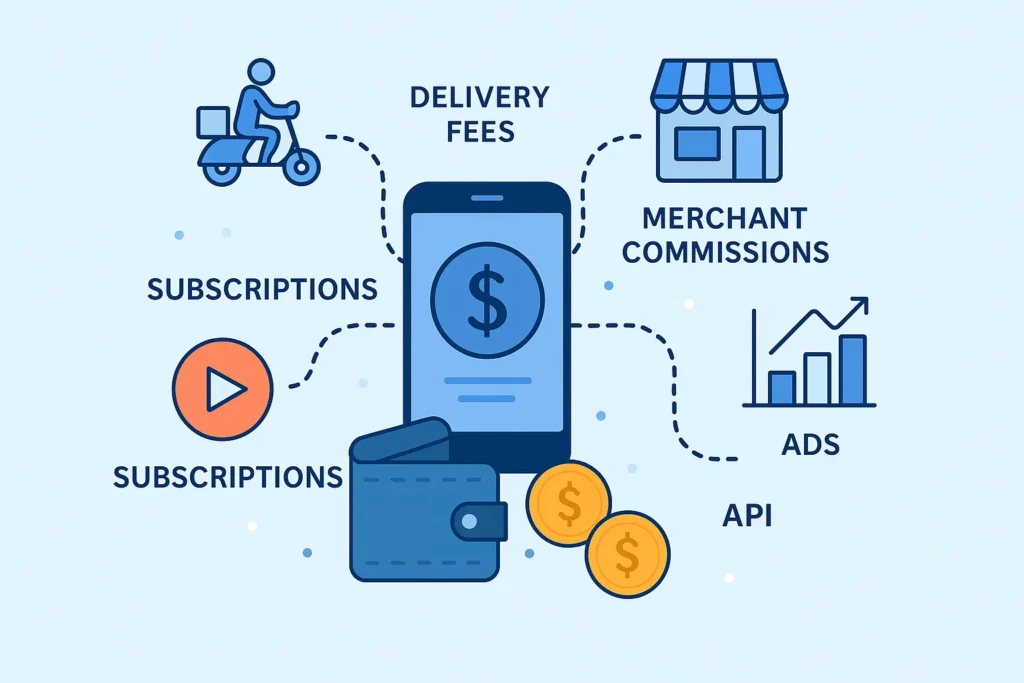
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Postmates operates on a multi-stream monetization framework, strategically balancing user payments, merchant commissions, and subscription revenue.
Its model is designed not just for profit — but for ecosystem growth, ensuring value creation for all stakeholders involved.
Primary Revenue Stream: Delivery Commissions
- Mechanism: A percentage-based commission (typically 15–30%) charged to merchants per order.
- Pricing Model: Dynamic, based on category (food, retail, grocery) and delivery demand in that area.
- Contribution: Around 60% of total revenue in 2025.
- Growth Driver: Integration with Uber Eats’ logistics infrastructure reduced costs and increased volume efficiency.
Secondary Revenue Streams
- Customer Delivery Fees
- Users pay variable delivery charges ($0.99–$9.99) depending on distance, item type, and surge demand.
- Smart pricing algorithms adjust rates dynamically to balance supply and demand.
- Accounts for ~25% of overall revenue.
- Users pay variable delivery charges ($0.99–$9.99) depending on distance, item type, and surge demand.
- Postmates Unlimited (Subscription Model)
- $9.99/month plan offering free deliveries on orders above a threshold ($12).
- Drives recurring monthly revenue and increases average user retention by 38%.
- In 2025, Postmates Unlimited contributes an estimated 10% of total earnings, while reducing churn among power users.
- $9.99/month plan offering free deliveries on orders above a threshold ($12).
- Advertising & Featured Listings
- Merchants pay for boosted visibility within the app.
- Sponsored placements and homepage banners enhance discoverability.
- Contributes ~3–5% of revenue and rising with AI-driven recommendation ads.
- Merchants pay for boosted visibility within the app.
- API & B2B Logistics Services
- Postmates’ “Delivery-as-a-Service” (DaaS) API enables third-party businesses to use its courier network.
- Retailers and grocery chains integrate the API to offer same-hour delivery without building internal fleets.
- Growing enterprise vertical contributing ~5% to total revenue.
- Postmates’ “Delivery-as-a-Service” (DaaS) API enables third-party businesses to use its courier network.
Overall Monetization Strategy
Postmates’ revenue architecture emphasizes diversified streams with compounding effects:
- Cross-Selling: Encouraging food users to order from retail or grocery partners through bundled offers.
- Upselling: Promoting Unlimited membership after 2–3 successful orders.
- Retention Flywheel: Subscription → Free delivery → More orders → Higher merchant commissions → Ad revenue growth.
Psychologically, the pricing design plays on perceived savings — making users feel they’re “saving more” through subscriptions or multi-order deals, even as lifetime spend increases.
Read more : Postmates Clone: Step-by-Step Guide to Building a Multi-Service Delivery App
Operational Model & Key Activities
Behind every “delivered in 30 minutes” promise lies a powerful operational backbone.
Postmates’ operational model integrates technology, logistics, workforce optimization, and merchant coordination — functioning as a real-time urban supply chain engine rather than a simple delivery service.
Core Operations
- Real-Time Order Management System
- Processes millions of concurrent transactions.
- Uses AI-based dispatching to match couriers with optimal delivery routes and order clusters.
- Machine learning predicts delivery ETAs with 95% accuracy using variables like traffic, weather, and order volume.
- Processes millions of concurrent transactions.
- Fleet Management & Courier Optimization
- The “Postmates Fleet” comprises independent gig workers using bikes, scooters, or cars.
- Fleet members receive real-time demand alerts through the courier app.
- Incentives like “Blitz Pricing” encourage availability during surge hours.
- The “Postmates Fleet” comprises independent gig workers using bikes, scooters, or cars.
- Merchant Integration & Support
- Postmates offers merchant dashboards to manage menus, track sales, and adjust promotions.
- Merchants get performance insights (conversion, delivery time, customer rating) through a unified analytics interface.
- Supports over 400,000+ active merchants across the U.S. (2025 data).
- Postmates offers merchant dashboards to manage menus, track sales, and adjust promotions.
- Customer Experience Management
- 24/7 in-app support with chatbot + human escalation.
- Order tracking with live courier location builds transparency and trust.
- Refund automation for service failures strengthens customer retention.
- 24/7 in-app support with chatbot + human escalation.
Resource Allocation (2025 Estimates)
| Category | Approx. Allocation | Focus Area |
| Technology & R&D | 35% | AI dispatch, automation, predictive analytics, user personalization |
| Marketing & Brand | 25% | Paid ads, influencer partnerships, referral campaigns |
| Operations & Support | 20% | Courier onboarding, merchant relations, logistics management |
| HR & Training | 10% | Fleet training, compliance, safety programs |
| Expansion & Partnerships | 10% | Regional scaling, enterprise delivery integrations |
Tech Infrastructure Highlights
- Postmates Dispatch Engine (PDE): Proprietary algorithm that dynamically routes deliveries in under 2 seconds.
- Cloud Infrastructure: Uses distributed AWS architecture for scalability and data reliability.
- Data Security: Encrypted customer and merchant data compliant with GDPR, CCPA, and ISO 27001 standards (post-Uber integration).
- AI & Predictive Analytics: Demand forecasting, price optimization, and churn prevention tools.
Operational Edge
Postmates’ operational strength lies in decentralized logistics — leveraging independent couriers instead of fixed fleets.
This elasticity allows rapid scaling in peak hours while keeping overhead low.
Its machine-learning optimization loop continually refines delivery speed, cost, and satisfaction metrics.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Postmates’ ecosystem has always thrived on collaboration over competition.
From early-stage integrations with payment providers to enterprise-level alliances post-Uber acquisition, partnerships became a strategic lever for growth, efficiency, and long-term defensibility.
Key Partnership Types
- Technology & API Partners
- Cloud & Infrastructure: AWS, Google Cloud — ensuring scalability and uptime reliability.
- Data & AI Integration: Partnerships with analytics firms like Tableau and Snowflake for data visualization and forecasting.
- Platform Integrations: Shopify, Square, and Wix — enabling merchants to activate same-day delivery through Postmates’ API.
- Cloud & Infrastructure: AWS, Google Cloud — ensuring scalability and uptime reliability.
- Payment & Logistics Alliances
- Payments: Stripe, PayPal, and Apple Pay ensure seamless multi-channel checkout experiences.
- Fleet Support: Partnerships with vehicle and e-bike companies for courier benefits (maintenance, financing, insurance).
- Logistics Expansion: Collaborations with regional courier firms for suburban and small-town coverage.
- Payments: Stripe, PayPal, and Apple Pay ensure seamless multi-channel checkout experiences.
- Marketing & Distribution Partnerships
- Cross-promotional deals with brands like Starbucks, Chipotle, and Walmart during launch campaigns.
- “Get Anything Delivered” branding collaborations amplified reach through national advertising.
- Influencer tie-ups on TikTok and Instagram fostered urban lifestyle alignment with young audiences.
- Cross-promotional deals with brands like Starbucks, Chipotle, and Walmart during launch campaigns.
Ecosystem Strategy: Building the Network Effect
- Network Effects: Each new merchant or courier increases platform liquidity, reducing delivery times and improving user satisfaction.
- Partner Value Creation: Merchants get marketing visibility and infrastructure-free logistics. Couriers get steady income streams.
- Ecosystem Monetization: Co-branded campaigns, merchant APIs, and featured listings generate layered revenue.
Competitive Moats: Deep local partnerships and Uber’s shared data ecosystem create high entry barriers for new players.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Postmates’ growth story is a masterclass in iterative scaling — expanding from one city to nationwide coverage while staying nimble in a hyper-competitive space.
Its approach combined organic virality, aggressive market entry, and continuous innovation under a single operational umbrella.
Growth Engines
- Organic Virality & Word of Mouth
- Early adopters became advocates through referral credits (“Give $10, Get $10”) — fueling exponential early growth.
- Social media buzz around the “Get Anything Delivered” slogan turned Postmates into a lifestyle utility, not just a food app.
- In 2025, over 40% of new users still come from referrals — a testament to brand loyalty.
- Early adopters became advocates through referral credits (“Give $10, Get $10”) — fueling exponential early growth.
- Paid Marketing & Acquisition Strategies
- Geo-targeted ad campaigns focused on urban hotspots.
- Co-marketing with restaurants and retailers amplified local traction.
- Influencer campaigns helped Postmates maintain cultural relevance in cities like LA and NYC.
- Post-Uber acquisition, cross-promotion with Uber Eats and Uber Rides reduced CAC by nearly 18%.
- Geo-targeted ad campaigns focused on urban hotspots.
- Product Line Diversification
- Expanded from food delivery to groceries, alcohol, and retail essentials — increasing average order value (AOV) by 32%.
- Launch of Postmates Party (group order discounts) boosted evening and weekend traffic.
- API and B2B logistics services opened enterprise revenue channels for eCommerce brands.
- Expanded from food delivery to groceries, alcohol, and retail essentials — increasing average order value (AOV) by 32%.
Scaling Challenges & Solutions
| Challenge | Impact | Solution Implemented |
| High Delivery Costs | Reduced profit margins | Integration with Uber’s routing algorithms reduced average cost by 15–20%. |
| Courier Retention & Availability | Unpredictable supply | Introduced incentive programs, insurance plans, and instant payouts. |
| Merchant Onboarding | Slowed scaling pace | API-based self-onboarding system and automated POS integration. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Legal hurdles in multiple states | Policy partnerships with city regulators and flexible labor models. |
| Competitive Pressure (DoorDash, Uber Eats) | Market share erosion | Differentiation through “anything delivery” and localized campaigns. |
Sustainable Growth Levers
- Data-Driven Scaling: Predictive analytics identify emerging high-demand neighborhoods before competitors.
- Operational Synergy with Uber: Shared infrastructure, unified data systems, and co-branded campaigns accelerate scalability.
- Sustainability Focus: Investment in EV fleets and carbon-offset programs aligns with modern ESG expectations.
- Product-Led Expansion: AI recommendations and contextual offers increase average order frequency by 21%.
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Postmates competes in one of the most fiercely contested spaces in tech — on-demand delivery, where giants like DoorDash, Uber Eats, and Instacart dominate.
Its survival and continued relevance in 2025 stem from a strategic mix of differentiation, brand positioning, and operational innovation.
Core Competitive Advantages
- Network Effects & Switching Barriers
- Every new courier, merchant, or customer strengthens the network’s density and speed.
- Users develop habitual reliance — Postmates becomes their “go-to” for impulse convenience.
- Merchants gain analytics, repeat business, and in-app visibility — making it costly to switch platforms.
- Every new courier, merchant, or customer strengthens the network’s density and speed.
- Brand Equity & Customer Trust
- Postmates is known for its “get anything, anytime” promise — a brand narrative that transcends food delivery.
- High customer retention from Postmates Unlimited and Party Orders builds predictable recurring revenue.
- Transparent delivery tracking and reliable service have sustained trust in saturated markets.
- Postmates is known for its “get anything, anytime” promise — a brand narrative that transcends food delivery.
- Innovation in Technology
- Proprietary Postmates Dispatch Engine (PDE) enables sub-minute courier assignment and smart route bundling.
- Integration with Uber’s AI infrastructure improves ETAs, pricing algorithms, and demand forecasting accuracy.
- Predictive delivery models now serve 10–15% of orders before they’re even placed, anticipating recurring habits (e.g., morning coffee runs).
- Proprietary Postmates Dispatch Engine (PDE) enables sub-minute courier assignment and smart route bundling.
Market Defense Tactics
| Tactic | Purpose | Example |
| Feature Timing & Differentiation | Stay ahead of competition by leading new formats | “Postmates Party” launched before DoorDash group orders. |
| Pricing Strategy | Compete dynamically without eroding margins | Adaptive surge pricing synced with Uber Eats’ data. |
| Strategic Acquisitions | Expand ecosystem reach | Integration of small courier startups for suburban coverage. |
| Merchant Loyalty Programs | Lock-in partnerships | Tiered commission rebates for long-term merchant retention. |
| Brand Positioning | Maintain unique identity under Uber | Continued independent branding as “Postmates — Beyond Delivery.” |
Long-Term Market Defense Vision (2025 & Beyond)
- Leveraging Uber’s ecosystem for scale while preserving Postmates’ urban premium identity.
- Expanding delivery categories (pharma, retail, home essentials) to diversify dependency on food.
- Building AI-first logistics capabilities for predictive fulfillment and “zero-wait” deliveries.
- Positioning Postmates as the logistics layer for city commerce — a platform every local business can plug into.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
The Postmates journey is more than a success story — it’s a blueprint for how technology, timing, and trust can converge to disrupt a traditional industry.
For entrepreneurs aiming to replicate or adapt the Postmates model, several key lessons emerge from its decade-long evolution.
Key Success Factors
- Start with a Focused Use Case
Postmates began with local restaurant deliveries in San Francisco — proving reliability and scalability before expanding to “deliver anything.”
→ Lesson: Validate a single vertical first (e.g., groceries, pharmacy, or essentials) before diversifying. - Build for Flexibility, Not Control
By adopting a decentralized courier model, Postmates scaled faster and cheaper than competitors relying on fixed fleets.
→ Lesson: Flexibility in operations reduces CAPEX and enables faster market adaptation. - Leverage Behavioral Data Early
From personalized offers to predictive deliveries, Postmates turned user behavior into actionable insights.
→ Lesson: Implement data analytics from day one — even basic insights (peak times, favorite items) fuel retention. - Differentiate Beyond Core Service
While competitors focused solely on food, Postmates built a lifestyle utility around convenience.
→ Lesson: Find your “emotional differentiator” — what does your brand mean beyond its function? - Partnerships > Isolation
API and payment integrations accelerated Postmates’ expansion and reduced development friction.
→ Lesson: Strategic alliances can help startups scale faster than pure funding alone.
Replicable Principles for Startups
| Principle | Execution Tactic | Expected Outcome |
| Lean Launch | Launch MVP in one city with narrow focus | Validate demand before scaling |
| Scalable Tech Stack | Use modular APIs for delivery, payments, analytics | Faster iteration and partner onboarding |
| Subscription Model Early | Introduce loyalty or free-delivery tiers | Increases retention and LTV |
| Data-Driven Marketing | Retarget based on time, category, and behavior | Improves engagement ROI |
| Community-Driven Branding | Encourage user-generated stories and reviews | Builds trust and virality |
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-expanding too quickly without logistics maturity.
- Ignoring courier satisfaction — a key part of the delivery loop.
- Underestimating data infrastructure needs.
- Treating marketing as a one-time launch event instead of an ongoing feedback loop.
Implementation Timeline (Example for New Entrepreneurs)
| Phase | Duration | Focus Area |
| Phase 1 (0–3 months) | Prototype & MVP | App launch in one metro area |
| Phase 2 (3–6 months) | Merchant Onboarding | Build partnerships with local stores |
| Phase 3 (6–12 months) | Growth Loop | Add referral programs, paid ads, and delivery API |
| Phase 4 (12–18 months) | Monetization | Introduce subscription tiers and merchant advertising |
| Phase 5 (18–24 months) | Scale | Expand to new geographies and diversify product lines |
Miracuves Implementation Advantage
At Miracuves, we specialize in replicating proven business models like Postmates — with white-label delivery solutions that are scalable, secure, and ready for market within weeks.
We provide everything you need to launch your on-demand ecosystem — from courier apps to merchant dashboards, integrated payments, and AI-based dispatching.
“Ready to implement the Postmates business model for your market?”
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested frameworks and growth mechanics. Launch in 3–9 days with pricing starting at $3,299. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps across food, grocery, retail, and mobility.
Get your free business modelconsultation today
Conclusion
Postmates’ story is a reflection of the modern platform revolution — where speed, simplicity, and scalability define success more than assets or physical presence ever could.
From a single-city experiment to a nationwide logistics powerhouse, Postmates didn’t just deliver food — it delivered a paradigm shift in how we think about access, time, and convenience.
Its model embodies a timeless truth of entrepreneurship:
Innovation attracts users, but execution builds empires.
In 2025 and beyond, as AI, automation, and sustainability reshape the on-demand economy, Postmates remains a blueprint for founders who want to merge operational excellence with user obsession. Entrepreneurs can draw from its playbook — lean scaling, data-driven decisions, subscription retention, and partnership-driven growth — to build not just delivery apps, but self-sustaining digital ecosystems. The future of platform economies lies in adaptable, AI-powered, community-driven solutions — and Postmates has already paved the path.
FAQs
1. What type of business model does Postmates use?
Postmates operates on a hybrid on-demand marketplace model — combining elements of logistics, gig economy, and subscription services.It connects customers, couriers, and merchants through a three-sided platform, earning revenue via delivery commissions, user fees, and merchant partnerships.
2. How does Postmates’ model create value?
Postmates creates value by eliminating delivery friction. Customers gain instant access to goods, merchants expand their reach without hiring delivery staff, and couriers earn flexible income through optimized delivery routes — creating a win-win ecosystem.
3. What are Postmates’ key success factors?
Postmates succeeded through early market entry, strong “anything delivery” branding, and its powerful Dispatch Engine — enhanced by AI personalization, loyalty programs, and seamless integration with Uber’s ecosystem.
4. How scalable is the Postmates business model?
Highly scalable — because it’s asset-light and data-driven.Using a gig workforce and cloud infrastructure, Postmates can expand city-by-city with minimal operational costs while maintaining performance through automation and predictive analytics.
5. What are the biggest challenges Postmates faces?
Intense price competition from DoorDash and Uber Eats .Postmates faces tough competition from DoorDash and Uber Eats, rising delivery costs, and evolving gig worker regulations. Maintaining profitability while balancing customer discounts and merchant satisfaction remains its biggest ongoing challenge.
6. How can entrepreneurs adapt this model to their region?
Start small in high-density cities to validate demand.Entrepreneurs can adapt the Postmates model by starting in high-demand urban areas, partnering with local merchants and couriers, and launching loyalty or subscription tiers early. Using a white-label platform like Miracuves ensures faster, cost-effective deployment with mobile-first design and real-time tracking.
7. What are alternatives to the Postmates model?
Alternatives to the Postmates model include DoorDash for food-focused efficiency, Instacart for grocery logistics, GoPuff with owned inventory, and Uber Eats as an integrated super-app.Each offers adaptable strategies based on market type, audience, and regional delivery needs.
Related Articles: