In 2007, Glassdoor began with a radical idea — what if job seekers could see inside a company before they applied? Founded by Robert Hohman, Rich Barton, and Tim Besse, the platform turned anonymous employee reviews into one of the world’s most powerful talent intelligence engines.
Fast forward to 2025, and the business model of Glassdoor has evolved far beyond a review site. With 60M+ monthly users, 2.5M+ employers, and integration with Indeed under the Recruit Holdings umbrella, it has become a cornerstone of the global hiring ecosystem. Its hybrid model — combining user-generated transparency with enterprise recruiting tools — reshaped how professionals choose where to work.
For entrepreneurs and founders, the Glassdoor business model offers a fascinating study in network-driven platform design, data-driven monetization, and trust-based branding. In a world where reputation defines recruitment, Glassdoor’s model proves that transparency can, in fact, be monetized.
How the Glassdoor Business Model Works
Glassdoor operates on a hybrid platform model, blending crowdsourced content, data analytics, and employer branding solutions. Its structure creates a two-sided ecosystem — where job seekers access free insights and employers pay to manage, promote, and optimize their brand presence.
1. Type of Model
Hybrid Marketplace & Freemium SaaS
Glassdoor combines:
- Marketplace Dynamics: Matching job seekers and employers.
- Freemium Content Model: Free access for users; monetized services for businesses.
- Data-as-a-Service (DaaS): Proprietary data licensing and analytics partnerships.
2. Core Value Proposition
| User Segment | Value Proposition |
| Job Seekers | Access transparent company reviews, salary insights, interview experiences, and job listings — all in one place. |
| Employers | Build trust through verified branding pages, respond to reviews, attract top talent, and run targeted recruitment ads. |
| Advertisers & Partners | Reach a professional audience with high intent and demographic precision. |
Glassdoor’s “give-to-get” principle — users must share their own review or salary info to access deeper data — fuels continuous engagement and content authenticity.
3. Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
- Users / Employees – Provide ratings, salaries, and workplace feedback.
- Employers – Pay to manage profiles and recruit candidates.
- Recruit Holdings (Parent Company) – Integrates Glassdoor with Indeed for data, traffic, and ad network synergies.
- Partners – API integrations for HR software, applicant tracking systems (ATS), and compensation analytics.
This interconnected network ensures each stakeholder contributes to — and benefits from — the platform’s trust-driven loop.
4. Evolution of the Model
- 2008–2015: Focused on user growth via anonymous reviews and transparency.
- 2016–2019: Introduced employer branding subscriptions and job listings.
- 2020–2023: Integrated with Indeed under Recruit Holdings, building a shared data and ad marketplace.
- 2024–2025: Evolved into a Career Intelligence Platform — leveraging AI to personalize job matches and sentiment insights.
5. Why It Works in 2025
- Shift toward authenticity: Job seekers demand transparency over perks.
- Data-driven hiring: Employers value analytics on candidate perception.
- AI integration: Predictive job matching and review sentiment analysis enhance UX.
- Trust moat: Decade-long reputation for credible data builds defensibility.
Read more : What is Glassdoor App and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Glassdoor’s success lies in its ability to serve multiple audiences — job seekers, employers, and data partners — while maintaining alignment between transparency, credibility, and recruitment ROI. Its segmentation approach ensures content supply (reviews) and demand (jobs) remain in constant balance.
1. Primary Customer Segments
| Segment | Profile | Motivation |
| Job Seekers & Employees | Professionals aged 21–45 seeking new opportunities or company insights. | Gain transparent knowledge on salaries, reviews, and culture before applying. |
| Employers / Recruiters | Mid to large enterprises (100–10,000+ employees) investing in employer branding and hiring. | Attract top talent, enhance company reputation, and optimize recruitment funnel. |
| Enterprise Partners & Agencies | HR tech firms, analytics platforms, and workforce consultants. | Access aggregated market data and trends for benchmarking and insights. |
2. Secondary Segments
- Students and Graduates: Use Glassdoor for internship reviews and entry-level salaries.
- SMBs: Seek cost-effective visibility among competitors.
- Advertisers: Target professionals with niche or B2B offerings.
By 2025, Glassdoor’s segmentation has evolved into an intent-based user graph — connecting users’ search behavior, job interests, and feedback patterns to personalize recommendations.
3. Customer Journey Mapping
Discovery → Contribution → Exploration → Application → Retention
- Discovery: Organic search (Google Jobs, LinkedIn, SEO).
- Contribution: Users leave a review or salary report to unlock deeper access.
- Exploration: Personalized company pages, salary comparisons, and interview prep tools.
- Application: Redirection to Glassdoor or Indeed listings.
- Retention: Alerts, AI-driven job recommendations, and career progress tracking.
Each journey loop enriches Glassdoor’s data ecosystem, fueling both relevance and engagement.
4. Market Positioning
Glassdoor positions itself as a career intelligence brand, not just a job portal.
- Tagline essence: “Know your worth. Find your fit.”
- Competitive Edge: User-generated authenticity, integrated recruiting suite, and sentiment analytics.
- Market Share: Holds ~20–25% of U.S. job search traffic alongside Indeed and LinkedIn.
Differentiation: Transparency-first approach vs. transaction-first rivals.
Read more : Best Glassdoor Clone Scripts 2025: Launch Your Job-Market Platform
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Glassdoor’s monetization architecture reflects a data-enriched recruitment economy — where transparency, trust, and engagement are converted into predictable B2B revenue.
By 2025, the company’s estimated annual revenue exceeds $320–350 million, fueled by a diversified mix of employer subscriptions, advertising, and analytics products.
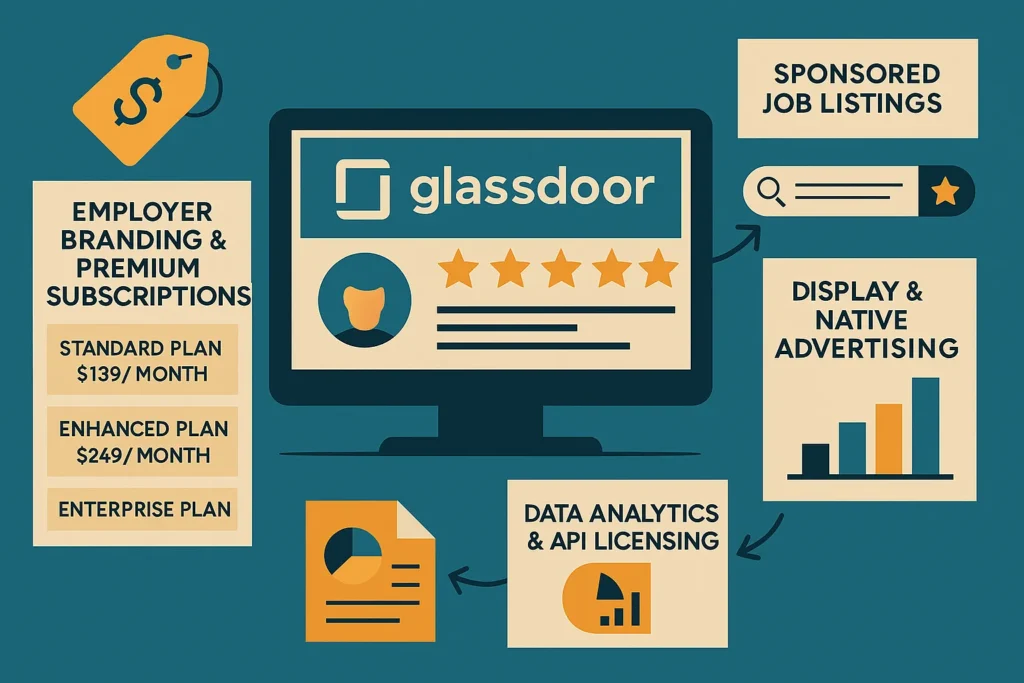
1. Primary Revenue Stream — Employer Branding & Premium Subscriptions (~65–70% of Total Revenue)
Mechanism:
Employers subscribe to Glassdoor for Employers, gaining access to branded profile pages, advanced analytics, and ad-free review management.
Pricing Tiers (2025):
- Standard Plan: $139/month — Basic analytics, logo, and responses to reviews.
- Enhanced Plan: $249/month — Competitor benchmarking, targeted job promotions, custom media.
- Enterprise Plan: Custom — Multi-location management, sentiment analysis, and ATS integration.
Growth Trajectory:
Employer renewals average 80% annually, driven by long-term partnerships and measurable hiring ROI.
2. Secondary Revenue Stream 1 — Sponsored Job Listings (~15–20%)
Mechanism:
Employers pay to feature their listings at the top of search results or in recommended feeds.
CPC Range: $0.25–$1.20 depending on role type and region.
Synergy: Integrated with Indeed’s ad marketplace, maximizing visibility across both platforms.
3. Secondary Revenue Stream 2 — Display & Native Advertising (~8–10%)
Mechanism:
B2B and B2C brands (software, education, upskilling, finance) advertise to professionals on Glassdoor.
Formats: Homepage banners, sponsored insights, salary comparison pages.
Value Proposition: High-intent audience, professional demographic targeting.
4. Secondary Revenue Stream 3 — Data Analytics & API Licensing (~5%)
Mechanism:
Glassdoor licenses aggregated salary, review, and workplace trend data to:
- Consulting firms
- HR tech platforms
- Market research companies
Example: Partnerships with LinkedIn Talent Insights, Payscale, and Statista for real-time compensation intelligence.
5. Monetization Strategy Summary
Glassdoor’s monetization engine thrives on interconnected streams:
- Employer branding drives recurring revenue.
- Sponsored jobs boost transactional revenue.
- Data licensing and ads expand scalability.
Its psychological edge lies in credibility — employers invest not to hide flaws but to demonstrate transparency, which in turn attracts better talent.
Operational Model & Key Activities
Glassdoor’s operational backbone is designed around trust, data accuracy, and platform scalability. Every daily process — from content moderation to AI-based insights — reinforces its position as the go-to career transparency platform.
1. Core Operations
| Function | Description |
| Content Moderation & Verification | Human-AI hybrid moderation ensures authentic, policy-compliant reviews. Roughly 10–15% of submissions are flagged for accuracy each day. |
| Platform Development | Continuous improvements to UX, personalization, and API integrations. Heavy investment in data science and AI-driven sentiment modeling. |
| Data Integrity & Compliance | Strict adherence to GDPR, CCPA, and ISO 27001 standards for anonymized user data. |
| Sales & Customer Success | Dedicated B2B sales teams for enterprise accounts; onboarding specialists help optimize branding pages. |
| Marketing & Growth | SEO, social media, and brand storytelling campaigns targeting job seekers and HR decision-makers. |
2. Resource Allocation (2025 Estimates)
- Technology & Infrastructure: ~40% of total budget — covers AI tools, cloud hosting, and data pipelines.
- Marketing & Growth: ~25% — performance marketing, content outreach, and employer education programs.
- HR & Talent: ~15% — employee well-being and training (Glassdoor maintains strong internal culture credibility).
- R&D & Product Innovation: ~10% — experimentation with predictive analytics and review authentication models.
- Operations & Administration: ~10% — partnerships, finance, and compliance.
3. Daily Operational Cycle
- User Data Flow: New reviews and salary inputs feed into moderation systems.
- Validation Layer: AI checks for anomalies; human moderators verify flagged entries.
- Content Refresh: Verified insights update company pages and salary benchmarks.
- Employer Interaction: Businesses log in to manage responses, view analytics, and promote listings.
- Feedback Loop: Insights from both sides inform feature updates and pricing refinements.
This cyclical operational rhythm sustains engagement, data reliability, and customer retention simultaneously.
4. Infrastructure & Tech Stack Overview
- Cloud Hosting: AWS multi-region deployment for global uptime.
- AI & ML Tools: NLP models for sentiment analysis, anomaly detection, and salary prediction.
- APIs: Integrations with Indeed, ATS platforms (Workday, Lever, Greenhouse), and analytics tools.
- Data Security: ISO 27001 + SOC 2 Type II compliance to maintain user trust and partner confidence.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Glassdoor’s ecosystem thrives through strategic alliances that expand its reach, enhance data accuracy, and strengthen monetization channels. The platform has evolved into a career data and hiring intelligence network, sustained by a web of partnerships spanning technology, recruitment, and compliance.
1. Collaboration Philosophy
Glassdoor doesn’t operate in isolation — it scales through ecosystem integration. Its partnerships are built on a “shared value of transparency and access” principle: every partner adds to the depth, credibility, or distribution of career-related data.
2. Key Partnership Types
a. Technology & API Partners
- Indeed (Core Integration): Seamless job posting and traffic exchange within the Recruit Holdings ecosystem.
- HR Software Platforms: Integrations with Workday, Greenhouse, Lever, and BambooHR for synchronized employer profiles and review insights.
- AI/Analytics Providers: Collaboration with data firms for salary modeling and job-market forecasting.
b. Payment & Monetization Alliances
- Partnerships with payment gateways (Stripe, Adyen) streamline global employer billing and subscription management.
- API-linked ad inventory through Recruit’s ad network, allowing advertisers to target both Glassdoor and Indeed audiences simultaneously.
c. Marketing & Distribution Partners
- Joint campaigns with LinkedIn Learning, Coursera, and Harvard Business Review to promote workplace transparency thought-leadership.
- Affiliate traffic partnerships with job aggregators and career blogs to grow user inflow.
d. Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Cooperation with EU data protection agencies and U.S. Department of Labor on wage transparency initiatives
- Partnerships with diversity and inclusion organizations to align content with fair workplace representation standards.
3. Ecosystem Impact
These partnerships create a multi-layered value chain:
- Shared data pipelines increase market intelligence accuracy.
- Cross-platform visibility enhances employer ROI.
- Network effects — the more partners Glassdoor integrates, the more valuable its data becomes for everyone involved.
By 2025, Glassdoor’s ecosystem model positions it not just as a review portal but as a Career Intelligence Hub — merging data, reputation, and recruitment in one scalable network.
Read more : Glassdoor App Marketing Strategy That Gets Users Talking (and Trusting)
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Glassdoor’s growth is anchored in a flywheel model — where user-generated content attracts traffic, traffic attracts employers, and employer activity generates monetizable data that fuels further growth. Between 2020 and 2025, the company shifted from expansion-led growth to ecosystem-driven scalability, leveraging AI, integrations, and personalization.
1. Growth Engines
a. Organic Virality & Referral Loops
- Every company review and salary entry boosts SEO visibility (over 85% of traffic originates from organic search).
- “Give-to-get” mechanics encourage user participation — post a review or salary to access more insights.
- Positive network loops: more data → better insights → higher trust → more users.
b. Paid Acquisition & Marketing
- Targeted campaigns on LinkedIn, YouTube, and Google Ads highlight employer brand pages and salary tools.
- B2B retargeting funnels for HR managers and recruiters drive premium subscription upsells.
- 2025 focus: localized campaigns in EMEA and APAC, especially India, Germany, and Japan.
c. Product-Led Growth
- AI-powered “Know Your Worth” salary tool and personalized Job Match AI keep users returning.
- The Glassdoor Mobile App, redesigned in 2024, increased engagement by 22% YoY.
- Integration with Indeed Apply streamlines job applications, boosting conversion by 18%.
d. Geographic Expansion
- Over 45 localized versions of Glassdoor now exist.
- Expansion prioritizes markets with rising employer branding demand, such as Southeast Asia and Latin America.
- Localized salary benchmarking tools enhance trust and regional usability.
2. Scaling Challenges (and How They Were Solved)
| Challenge | Solution |
| Review Authenticity & Spam | AI-based anomaly detection and “verified employment” features. |
| Data Privacy Regulations | GDPR, CCPA, and SOC 2 compliance frameworks embedded across infrastructure. |
| Competition from LinkedIn & Indeed | Focused on differentiation through trust, sentiment analytics, and transparency-first branding. |
| Monetization Plateau (2021–2022) | Introduced integrated advertising suite and salary data APIs. |
3. Strategic Growth Levers (2025–2027 Outlook)
- AI Career Coach: Predictive career guidance using user history.
- Employer Trust Index: Data-driven scoring of employer credibility.
- Global Insights Portal: Industry benchmarking dashboards for enterprises.
Glassdoor’s future growth relies on becoming not just a platform for job search — but a decision engine for every career choice, powered by trusted data.
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Glassdoor competes in one of the most contested digital spaces — online recruitment and employer branding — dominated by giants like LinkedIn, Indeed, and ZipRecruiter. Yet, its transparency-first positioning and data credibility keep it resilient. Glassdoor’s strategy focuses on defending its niche while expanding its influence through AI-driven insights and ecosystem integration.
1. Competitive Advantages
a. Trust and Authenticity
- User-generated credibility remains its strongest moat.
- 100M+ verified reviews and salary reports make it a data-rich trust brand, hard to replicate by competitors.
b. Network Effects
- The more users contribute, the richer and more accurate the insights become.
- This self-reinforcing cycle raises switching barriers for both users and employers.
c. Integration with Indeed
- As part of Recruit Holdings, Glassdoor leverages Indeed’s traffic (over 600M monthly visits) for cross-platform visibility and ad monetization.
- Shared datasets enhance job matching precision and advertiser ROI.
d. Technological Edge
- Advanced AI sentiment analysis translates millions of reviews into actionable workplace insights.
- Predictive analytics identify employer perception shifts before they impact hiring pipelines.
e. Brand Positioning
- Glassdoor owns the “career transparency” narrative, while competitors focus on networking (LinkedIn) or listing volume (Indeed).
- Its ethical stance resonates with Gen Z and millennial job seekers, strengthening long-term loyalty.
2. Market Defense Tactics
| Threat | Glassdoor’s Response |
| New Entrants / Review Clones | Uses proprietary moderation algorithms and review-verification technology to maintain credibility. |
| Price Competition (LinkedIn / ZipRecruiter) | Emphasizes data-driven hiring quality over volume-based pricing. |
| Platform Fatigue | Bundles insights, job search, and reviews into a unified experience. |
| Shifts in User Behavior | Introduced AI-driven Career Path Predictions to evolve beyond reviews. |
| Regulatory Scrutiny | Proactively complies with global data privacy standards, positioning itself as a responsible data guardian. |
3. Strategic Differentiation
- Transparency as Core IP: Competitors can copy job boards, not trust networks.
- Employer Sentiment Index (ESI): Proprietary metric that quantifies workplace satisfaction.
- AI-Powered Benchmarking: Offers real-time insights on hiring trends by industry and region.
- Integrated Employer Ecosystem: Through Indeed, Glassdoor enables end-to-end recruitment visibility — from brand perception to job conversion.
4. Future Defense Outlook (2025–2030)
Glassdoor’s continued defense will hinge on:
- Predictive HR Intelligence: Turning insights into proactive hiring strategies.
- Partnership Expansion: Deeper integration with HR suites and DEI analytics providers.
- Reputation Capitalization: Monetizing workplace culture insights for consulting and compliance use cases.
In essence, while competitors chase scale, Glassdoor defends its leadership through trust, data sophistication, and transparency economics — a trifecta few can replicate.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Glassdoor’s journey from a simple review portal to a global career intelligence ecosystem holds deep lessons for entrepreneurs building modern digital platforms — especially those pursuing trust-based marketplaces, review-driven apps, or freemium SaaS models.
1. Key Factors Behind Glassdoor’s Success
a. Trust as a Currency
Glassdoor monetized credibility — not content. By maintaining transparent, user-verified data, it converted community trust into sustainable B2B revenue.
b. Network Effects Done Right
It turned user participation (reviews, salaries, interviews) into a self-growing ecosystem. Each new data point improved the experience for everyone else.
c. Freemium + Ecosystem Monetization
Instead of paywalls, Glassdoor offered free access to users while charging employers for visibility, analytics, and branding — ensuring growth without alienating the base.
d. Integration over Isolation
By merging with Indeed, Glassdoor tapped into shared infrastructure, audience, and ad tech — proving that strategic mergers can amplify platform scale.
2. Replicable Principles for Startups
- User Contribution Loop: Encourage users to exchange data for access (reviews, uploads, participation).
- Dual Value Proposition: Balance user benefit and partner monetization.
- Transparency Branding: Make honesty your competitive advantage.
- Data Monetization: Turn aggregated insights into new B2B products.
- Continuous Moderation: Protect credibility with automated + human checks.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-focusing on monetization before achieving data depth.
- Ignoring community moderation — fake content destroys platform trust fast.
- Neglecting UI simplicity — Glassdoor’s clean UX drives retention.
- Failing to evolve from product to ecosystem — integration creates defensibility.
4. Adaptation for Local or Niche Markets
For entrepreneurs building regional review or job platforms, Glassdoor’s framework can be localized:
- Focus on trust and privacy compliance first.
- Localize salary data and job categories.
- Build partnerships with HR software vendors early.
- Start with SMB onboarding before scaling to enterprise.
- Use AI to personalize results and improve data quality.
5. Implementation Timeline & Investment Priorities
| Phase | Duration | Core Focus | Budget Weight |
| Phase 1: MVP Launch | 0–3 months | Basic review + job matching engine | 25% |
| Phase 2: Trust Layer | 3–6 months | Review verification, moderation tools | 20% |
| Phase 3: Monetization | 6–9 months | Employer subscriptions + analytics dashboard | 30% |
| Phase 4: Scaling | 9–18 months | Regional expansion, mobile app, ad modules | 25% |
Ready to implement Glassdoor’s proven business model in your market?
Miracuves specializes in building scalable, white-label job, review, and marketplace platforms — powered by real-time analytics, AI moderation, and secure multi-role architectures.
We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable, trust-based apps in less than 30 days.
Get your free business model consultation today at Miracuves
Conclusion :
Glassdoor’s business model demonstrates a rare truth in the digital age — trust scales faster than technology. What began as a disruptive idea in workplace transparency evolved into a billion-dollar ecosystem by aligning the interests of employees, employers, and data partners around one universal need: honesty.
Its model thrives because it blends purpose with profitability — empowering individuals to make informed career decisions while giving organizations the data to improve themselves. In doing so, Glassdoor turned human experiences into measurable business intelligence, proving that ethical transparency can coexist with commercial success.
As we move deeper into 2025 and beyond, the platform economy is entering a new phase — one defined not just by speed and scalability, but by authenticity, accountability, and insight. Entrepreneurs who can engineer trust into their platforms — the way Glassdoor did — will lead the next generation of sustainable digital businesses.
FAQs :
1. What type of business model does Glassdoor use?
Glassdoor operates on a hybrid business model combining a freemium content platform and B2B SaaS monetization. It’s both a career marketplace and a data-driven analytics service — offering free access for job seekers and paid plans for employers.
2. How does Glassdoor’s model create value?
Value is created through transparency and trust. Job seekers gain honest workplace insights, while employers use the platform to manage their brand image, attract talent, and access analytics on employee sentiment and recruitment performance.
3. What are Glassdoor’s key success factors?
Its massive user-generated data, verified content, and integration with Indeed give it scale and credibility. Ethical branding and clear employer ROI ensure lasting success.
4. How scalable is Glassdoor’s model?
Highly scalable — data and reviews compound exponentially. Once the trust infrastructure and moderation systems are built, adding new regions, languages, or employers incurs minimal marginal cost.
5. What are the biggest challenges in this model?
Balancing privacy with openness, ensuring authenticity at scale, meeting compliance (GDPR/CCPA), and staying ahead of strong competition.
6. How can entrepreneurs adapt Glassdoor’s model to their region?
Focus on localized salary data, partnerships with regional HR tools, verified users to prevent spam, and cultural transparency norms.
7. What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a similar platform?
A well-defined MVP can be launched within 3–9 days with Miracuves’ pre-built job and review platform frameworks. Budget typically ranges from ( Starts at $2,899 ) cost depending on features like review moderation, salary analytics, and AI integration.
8. What are the alternatives to this model?
LinkedIn, Monster, Blind, and Comparably — each offers jobs or reviews, but none integrate transparency, analytics, and branding like Glassdoor.
9. How has the model evolved over time?
From 2008–2025, Glassdoor moved from anonymous reviews to AI-driven career intelligence — adding branding tools, Indeed integration, and sentiment dashboards.
10. How can Miracuves help entrepreneurs build a similar platform?
Miracuves delivers ready-to-launch, white-label job and review platforms modeled on Glassdoor’s proven architecture — complete with AI moderation, employer dashboards, and data analytics. Entrepreneurs can launch their own career intelligence startup in 3-9 days guaranteed delivery with full scalability and compliance assurance.
Related Article :








