ASOS didn’t just sell clothes online—it redefined how an entire generation shops for fashion.
Founded in the UK in 2000, ASOS scaled from a niche online retailer into a multi-billion-dollar global fashion platform, serving over 20+ million active customers across 200+ markets by 2025.
What makes the Business Model of ASOS worth studying isn’t just its scale—but how its business model blends retail, private labels, marketplace dynamics, data-driven merchandising, and logistics intelligence into one tightly integrated system.For modern founders exploring D2C commerce, marketplace platforms, vertical integration, and data-led product strategies, ASOS offers a proven blueprint for building scalable, profitable digital fashion ecosystems.
ASOS offers a blueprint on how to balance control and scale while navigating thin margins, fast trends, and global competition.
At Miracuves, we closely analyze models like ASOS because they demonstrate how platform architecture, monetization layers, and operational discipline must work together to build profitable digital ecosystems—not just high-traffic apps.
How the ASOS Business Model Works
ASOS operates on a hybrid digital commerce business model—combining first-party retail, private-label brands, and a curated marketplace inside a single fashion ecosystem.
At its core, ASOS is not just an online store. It is a vertically controlled fashion platform where ASOS manages demand, pricing, inventory strategy, and customer experience end-to-end, while selectively allowing third-party brands to scale within its infrastructure.
1. Type of Business Model
ASOS uses a Hybrid Fashion Platform Model, consisting of:
- First-Party (1P) Retail Model
ASOS buys inventory directly from brands or produces in-house labels and sells to consumers. - Private-Label / Owned Brands Model
ASOS Design and exclusive labels generate higher margins and differentiation. - Marketplace Model (ASOS Marketplace)
Independent brands and boutiques sell via ASOS’s platform under controlled guidelines.
This hybrid structure allows ASOS to balance margin control with assortment scale.
2. Value Proposition by User Segment
For Consumers
- Trend-responsive fashion with frequent new drops
- Wide assortment across price points and styles
- Seamless mobile-first shopping experience
- Fast delivery, easy returns, and personalized discovery
For Brands & Sellers
- Access to a global, Gen-Z and millennial audience
- Logistics, payments, and customer acquisition handled by ASOS
- Data insights on demand trends and performance
For ASOS (Platform Owner)
- Full control over merchandising and pricing
- Higher margins through private labels
- Marketplace scale without full inventory risk
- Rich behavioral data to optimize conversion and retention
3. Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
- Consumers – Drive demand and trend velocity
- In-house design & sourcing teams – Control private-label creation
- Third-party brands & boutiques – Expand catalog depth
- Logistics & fulfillment partners – Enable global delivery
- Technology & data teams – Power personalization, forecasting, and UX
Each stakeholder strengthens the ecosystem while keeping ASOS at the center of value capture.
4. Evolution of the ASOS Model
ASOS did not start as a marketplace.
- Early Phase: Pure online fashion retailer
- Growth Phase: Expansion into private labels for margin and brand control
- Platform Phase: Introduction of ASOS Marketplace to scale variety
- Optimization Phase (2023–2025):
- Inventory rationalization
- Data-driven buying
- Margin discipline
- Focus on profitable growth over raw expansion
This evolution reflects a shift from growth-at-all-costs to sustainable platform economics.
5. Why the Model Works in 2025
ASOS’s model aligns strongly with 2025 consumer behavior:
- Mobile-first, discovery-driven shopping
- Fast fashion cycles powered by data
- Demand for affordable but expressive fashion
- Willingness to buy private labels if brand trust exists
- Global reach without physical retail overhead
In an era where traditional retailers struggle with inventory and rent, ASOS’s digital-native operating leverage remains its biggest advantage.
Read more : What is ASOS and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
ASOS didn’t grow by trying to serve “everyone.” Its success comes from deep focus on a clearly defined, digitally native fashion audience, then expanding intelligently within that core.
1. Primary & Secondary Customer Segments
Primary Segment: Digital-Native Fashion Shoppers
- Age group: 18–34
- Highly mobile-first, social-media influenced
- Shops frequently, but with value sensitivity
- Looks for trend relevance over long-term ownership
- Comfortable with private labels and online-only brands
Secondary Segments
- Fashion-conscious professionals seeking affordable style updates
- Global customers in Europe, North America, Australia, and emerging markets
- Independent fashion enthusiasts shopping via ASOS Marketplace
This segmentation allows ASOS to maintain high repeat purchase frequency rather than relying on big-ticket orders.
2. Customer Journey: Discovery → Conversion → Retention
Discovery
- Social platforms (Instagram, TikTok, YouTube)
- Influencer and creator-led fashion content
- App store discovery and word-of-mouth
- Seasonal campaigns and trend drops
Conversion
- Personalized product feeds powered by browsing behavior
- Dynamic pricing and frequent promotions
- Trust signals: free/fast returns, global shipping
- Mobile-optimized checkout
Retention
- App notifications and email personalization
- Style-based recommendations and saved preferences
- Consistent private-label sizing and fit familiarity
- High cadence of new arrivals to create habit loops
ASOS optimizes lifetime value over single-order margins
3. Acquisition Channels by Segment
- Gen Z users: Social-first discovery, creator content, short-form video
- Repeat buyers: Email, app push, personalization engines
- Marketplace buyers: Search-driven and niche fashion interest groups
- International customers: Localized pricing, delivery options, and UX
Each channel is tuned to behavioral intent, not just demographics.
4. Market Positioning & Competitive Edge
ASOS positions itself as:
- Trend-forward but affordable
- Digital-native and culture-aware
- More expressive than Amazon
- More accessible than luxury fashion platforms
Key Differentiators
- Strong private-label dominance
- High-speed trend response
- Global reach without physical stores
- Deep personalization driven by data
Rather than competing purely on price, ASOS competes on style relevance, assortment breadth, and digital experience.
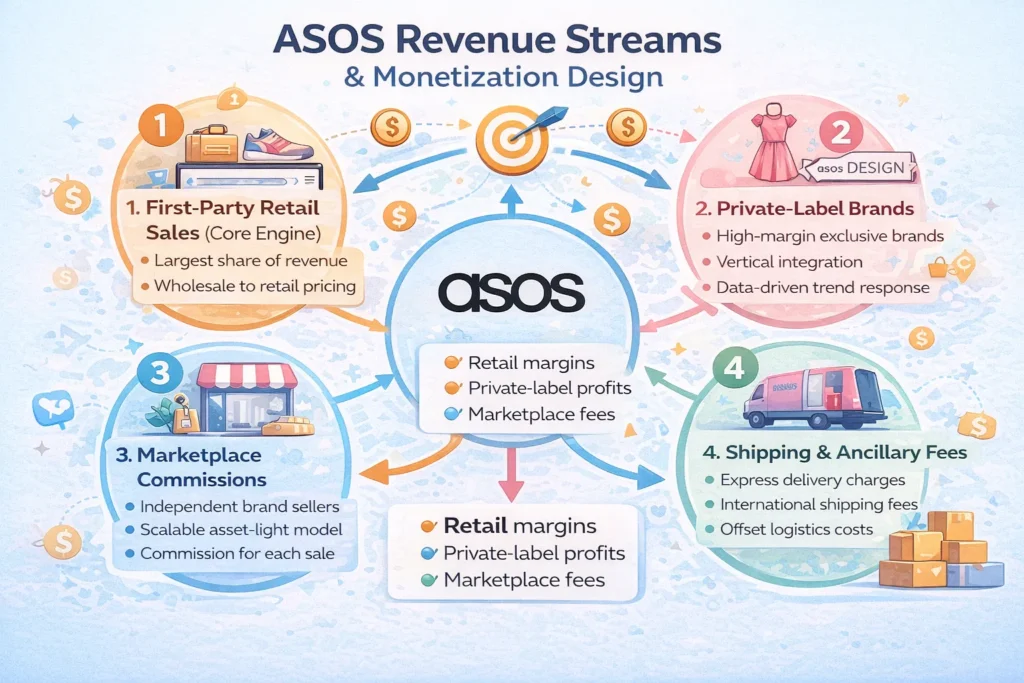
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Once ASOS mastered customer retention and high-frequency shopping behavior, its business model unlocked a layered monetization architecture. Rather than depending on a single income source, ASOS blends retail margins, private-label economics, and marketplace fees to stabilize revenue in a low-margin industry.
Primary Revenue Stream 1: First-Party Retail Sales (Core Engine)
Mechanism
ASOS purchases inventory directly from global brands and sells products to consumers through its app and website.
Pricing Model
- Wholesale procurement → retail markup
- Dynamic pricing based on demand and seasonality
- Heavy use of promotions and flash sales
Revenue Contribution
- Largest share of total revenue
- Lower margins compared to digital-only services
- High volume compensates for thinner margins
Growth Trajectory
- Rationalized SKU count to improve sell-through
- Focus on faster inventory turnover
- Reduction in markdown dependency
This stream provides control over customer experience and assortment
Primary Revenue Stream 2: Private-Label & Owned Brands (Margin Multiplier)
Mechanism
ASOS designs, sources, and sells its own brands such as ASOS DESIGN exclusively on the platform.
Why It Matters
- Higher gross margins than third-party brands
- Full control over pricing, trends, and supply chain
- Strong brand recognition among Gen Z shoppers
Revenue Contribution
- Smaller volume than 1P retail
- Disproportionately higher profit contribution
Growth Trajectory
- Data-driven trend forecasting
- Faster design-to-shelf cycles
- Expansion into category-specific labels
Private labels are ASOS’s profit stabilizer.
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: ASOS Marketplace Commissions
Mechanism
Independent brands and boutiques sell via ASOS Marketplace and pay commissions per transaction.
Pricing Model
- Commission-based fees
- Seller-funded promotions
- Optional value-added services
Revenue Contribution
- Asset-light and scalable
- Expands assortment without inventory risk
- Lower operational overhead
Growth Trajectory
- Curated seller onboarding
- Focus on brand quality over volume
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Shipping, Returns & Ancillary Fees
- Express delivery fees
- International shipping surcharges
- Membership-style delivery programs in select regions
These fees help offset logistics-heavy costs.
Overall Monetization Strategy
ASOS’s monetization design is intentionally balanced:
- Retail volume drives scale
- Private labels drive profitability
- Marketplace drives expansion without capital risk
Psychologically, ASOS uses:
- Frequent discounts to trigger impulse buying
- Tiered pricing to serve budget and premium shoppers
- Personalization to increase basket size
Each revenue stream reinforces the others—creating a resilient, interconnected revenue system.
Read more : ASOS Revenue Model: How ASOS Makes Money in 2025
Operational Model & Key Activities
Behind ASOS’s sleek shopping experience is a highly optimized operational engine built to handle massive SKU volumes, rapid trend cycles, and global fulfillment—all without physical stores.
1. Core Operational Activities
Platform & Technology Management
- Mobile-first app and web platform optimization
- Personalization algorithms for product discovery
- Real-time pricing and inventory visibility
- A/B testing across UX, checkout, and promotions
Merchandising & Inventory Control
- Demand forecasting using historical and behavioral data
- Short buying cycles to reduce overstock risk
- SKU rationalization to improve sell-through
- Markdown optimization rather than blanket discounting
Supply Chain & Fulfillment
- Centralized distribution centers
- Regional delivery optimization for speed and cost
- Reverse logistics systems for high-volume returns
- Tight coordination with third-party logistics partners
Customer Support & Experience
- Multi-channel customer service (chat, email, in-app)
- Automated returns and refunds
- Proactive communication on delivery and delays
2. Resource Allocation Strategy (2025 Lens)
ASOS allocates resources based on digital leverage rather than physical expansion:
- Technology & Data: Significant ongoing investment in AI, forecasting, and personalization
- Logistics & Operations: Major cost center due to global shipping and returns
- Marketing: Performance-driven spend across social, influencers, and paid channels
- Human Capital: Strong focus on data science, supply chain, and product teams
- R&D: Continuous testing of new formats, features, and shopping experiences
3. Regional Expansion Operations
- Localized websites and pricing
- Region-specific delivery options
- Compliance with tax, customs, and return regulations
- Selective market exits to protect profitability
ASOS’s operational discipline reflects a shift from growth-first to margin-aware scaling.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
ASOS understands that scaling a fashion platform globally is not a solo effort. Its ecosystem strategy is built around strategic alliances that reduce complexity, accelerate reach, and strengthen competitive moats.
1. Partnership Philosophy
ASOS partners where ownership is inefficient and collaborates where speed, scale, or expertise matter more than control. The goal is to stay asset-light while maintaining experience quality.
2. Key Partnership Categories
Technology & Platform Partners
- Cloud infrastructure and data analytics providers
- AI and personalization technology vendors
- Fraud detection and payment security platforms
These partnerships help ASOS maintain platform reliability and personalization at scale.
Payment & Financial Partners
- Global payment gateways supporting multi-currency transactions
- Buy-now-pay-later providers appealing to Gen Z shoppers
- Regional payment methods for market localization
Payments partnerships directly improve conversion rates and checkout success.
Logistics & Fulfillment Alliances
- Third-party logistics providers for international shipping
- Last-mile delivery partners in key regions
- Returns management and reverse logistics specialists
These alliances reduce capital intensity while enabling fast, flexible delivery.
Brand & Seller Partnerships
- Global fashion brands supplying inventory
- Independent designers and boutiques via ASOS Marketplace
- Exclusive collaborations to drive demand spikes
Brand partnerships expand assortment while preserving ASOS’s merchandising control.
Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Customs, tax, and compliance partners
- Local market advisors during geographic expansion
- Sustainability and ethical sourcing collaborators
3. Ecosystem Strategy & Competitive Moat
ASOS’s ecosystem creates:
- Network effects: More brands → more shoppers → more data
- Partner lock-in through access to demand and infrastructure
- Monetization leverage via commissions, exclusivity, and scale
By embedding partners deeply into its platform, ASOS turns collaboration into a defensive advantage.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
ASOS’s growth has never relied on a single lever. Instead, it engineered multiple, reinforcing growth engines—balancing brand, data, and infrastructure to scale globally.
1. Core Growth Engines
Organic Virality & Brand-Led Growth
- Social-first brand presence on Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube
- Influencer collaborations and creator-led styling content
- User-generated content driving fashion discovery
- Seasonal trend campaigns that create urgency
Fashion is inherently social—and ASOS embeds itself inside that loop.
Performance Marketing & Paid Acquisition
- Search and social advertising optimized by SKU-level performance
- Retargeting based on browsing and cart behavior
- Region-specific paid strategies tied to demand elasticity
ASOS treats marketing as a data feedback loop, not a spend-only function.
Product & Experience Expansion
- Expansion of private-label categories
- Improved personalization and recommendation engines
- Faster delivery options and localized experiences
- Mobile app feature enhancements
Geographic Expansion Strategy
- Entry into digitally mature markets first
- Localization of pricing, sizing, and payments
- Strategic exits from low-margin regions to protect profitability
2. Scaling Challenges & How ASOS Responded
Challenge: Inventory Risk & Margin Pressure
- Solution: SKU rationalization and demand forecasting
Challenge: High Returns in Online Fashion
- Solution: Fit data, sizing consistency, and return optimization
Challenge: Rising Customer Acquisition Costs
- Solution: Focus on retention, app engagement, and owned channels
Challenge: Operational Complexity at Scale
- Solution: Automation, regional partnerships, and platform modularity
ASOS’s evolution shows a shift from expansion-first to efficiency-led scaling.
Read more : Best ASOS Clone Script 2025 – Launch Your Fashion Marketplace in Days
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
ASOS operates in one of the most competitive digital markets—online fashion. Its survival and leadership depend on defensive depth, not just aggressive growth.
1. Core Competitive Advantages
Network Effects
- More shoppers attract more brands
- More brands expand assortment and data
- More data improves personalization and conversion
This loop strengthens ASOS’s position with every transaction.
Brand Equity & Trust
- Two decades of digital-first credibility
- Strong emotional connection with Gen Z and millennials
- Reliability in delivery, returns, and service
Trust reduces switching even when competitors offer discounts.
Private-Label Differentiation
- Exclusive designs unavailable elsewhere
- Faster trend response than third-party brands
- Better margin control during pricing pressure
Data-Driven Personalization
- AI-led recommendations
- Dynamic pricing and merchandising
- Predictive demand planning
Data allows ASOS to compete on relevance, not just price.
2. Market Defense Tactics
Against New Entrants
- Faster product iteration
- Deeper personalization
- Scale-driven logistics advantages
Against Price Wars
- Private labels protect margin
- Targeted promotions instead of blanket discounts
- Loyalty-driven retention rather than one-time offers
Against Platform Giants
- Focus on fashion identity rather than general commerce
- Curated experience instead of infinite catalogs
- Community and culture, not just transactions
Strategic Acquisitions & Partnerships
- Selective acquisitions to expand capabilities
- Partnerships to neutralize threats without heavy capex
ASOS defends its market by making itself harder to replace, not by racing to the bottom on price.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
This is where ASOS’s story becomes most valuable for founders. Its success wasn’t driven by a single innovation—but by disciplined execution across model design, operations, and data.
1. Key Factors Behind ASOS’s Success
- Digital-first from day one
No legacy stores, no offline baggage—everything optimized for online behavior. - Control before scale
ASOS focused on owning inventory logic, pricing, and UX before opening up to marketplace sellers. - Private labels as a margin engine
Owned brands stabilized profits in a low-margin industry. - Data as a strategic asset
Demand forecasting, personalization, and inventory planning all flow from customer data. - Operational realism
ASOS adjusted markets, SKUs, and costs instead of chasing vanity growth.
2. Replicable Principles for Startups
Entrepreneurs can adapt ASOS’s model by focusing on:
- Start with one core audience, not everyone
- Build supply-side control before adding scale layers
- Use private labels or exclusivity to protect margins
- Treat logistics and returns as product features
- Optimize for lifetime value, not first-order profit
You don’t need ASOS’s scale—you need its sequencing.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Scaling SKUs too fast without demand data
- Relying only on discounts to drive growth
- Ignoring return economics
- Expanding internationally before operational readiness
- Treating tech as a cost center instead of a growth lever
4. Adapting the Model for Local or Niche Markets
ASOS’s framework works well when adapted to:
- Regional fashion marketplaces
- Niche verticals (streetwear, modest fashion, sustainable fashion)
- D2C brands adding a marketplace layer
- Influencer-led or community-driven commerce apps
Local adaptation should focus on cultural relevance and logistics feasibility.
5. Implementation Timeline & Investment Priorities
A realistic rollout inspired by ASOS:
- Phase 1: Core D2C platform + inventory logic
- Phase 2: Data-driven personalization & retention
- Phase 3: Private-label or exclusive supply
- Phase 4: Marketplace expansion
- Phase 5: Geographic scaling
Investment should prioritize technology, data, and operations before aggressive marketing.
Ready to implement ASOS’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable commerce and marketplace platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps and digital platforms.
Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion :
ASOS’s journey proves a critical truth about modern digital businesses: technology alone doesn’t create dominance—business model discipline does.
In an industry known for thin margins, volatile demand, and brutal competition, ASOS survived and scaled by combining data-led decision-making, controlled expansion, private-label economics, and platform thinking. Its evolution from a pure retailer to a hybrid fashion ecosystem shows how founders must continuously refine—not rigidly defend—their original model.
FAQs :
What type of business model does ASOS use?
ASOS operates a hybrid business model combining first-party retail, private-label brands, and a curated marketplace within a single digital fashion platform.
How does ASOS’s business model create value?
ASOS creates value by offering trend-led fashion at scale, personalized discovery, fast delivery, and global reach—while giving brands access to a high-intent audience.
What are ASOS’s key success factors?
Digital-first operations, strong private labels, data-driven merchandising, efficient logistics, and high customer retention.
How scalable is the ASOS business model?
Highly scalable. ASOS expands without physical stores, using centralized logistics, digital distribution, and marketplace partners to grow internationally.
What are the biggest challenges ASOS faces?
Inventory risk, high return rates, margin pressure, and rising customer acquisition costs.
How can entrepreneurs adapt the ASOS model to their region?
By starting with a focused niche, controlling supply, using local logistics partners, and scaling marketplace features gradually.
What are alternatives to the ASOS model?
Pure D2C brands, influencer-led commerce platforms, vertical marketplaces, or subscription-based fashion models.
How has the ASOS business model evolved over time?
It evolved from online retail to a hybrid ecosystem emphasizing profitability, data intelligence, and controlled marketplace expansion.
Related Article :








