Founded in Lithuania in 2008 as a simple peer-to-peer clothing exchange, Vinted quietly evolved into Europe’s largest second-hand fashion marketplace, operating across 20+ countries. Vinted reached over 80 million registered users, achieved sustained profitability in core markets, and became a benchmark for circular-economy platforms.
Vinted scaled to a multi-billion-euro valuation by breaking a core marketplace rule, redefining how the business model of Vinted works in practice. Instead of charging sellers commission, the platform lets sellers list freely while buyers pay for protection, convenience, and trust. Logistics and safety systems become revenue engines rather than cost centers, strengthening the overall Vinted revenue model.
For entrepreneurs exploring marketplace, recommerce, or community-driven platforms, Vinted is a masterclass in business model design over brute-force monetization.
At Miracuves, we study platforms like Vinted not just for what they earn—but how architectural decisions create scalable, defensible ecosystems. Vinted’s model shows that when incentives are aligned correctly, growth becomes compounding rather than costly.
How the Vinted Business Model Works
Vinted operates a buyer-funded, trust-led marketplace—a model that deliberately removes friction from the supply side while monetizing value-added services on the demand side.
At its core, Vinted is not just a resale app. It is a behavioral marketplace designed around affordability, trust, and repeat transactions. Every structural decision in the model supports one outcome: high-liquidity, low-friction peer-to-peer trade at scale.
Business Model Overview
Type of Model
- Peer-to-peer Marketplace
- Buyer-service–driven monetization
- Logistics-enabled platform
- Circular economy / recommerce model
Unlike traditional marketplaces (eBay, Depop, Etsy), Vinted does not rely on seller commissions. This single choice reshapes the entire ecosystem.
Value Proposition by User Segment
For Sellers
- Zero selling fees
- Simple listing and pricing
- Large, active buyer base
- Integrated shipping options
- Fast payout after delivery confirmation
Result:
Sellers list more items, price more competitively, and churn less.
For Buyers
- Lower prices due to zero seller commission
- Buyer Protection (refunds, dispute resolution)
- Verified payments and delivery tracking
- Massive supply across fashion categories
Result:
Buyers feel safe transacting with strangers at scale.
For Vinted (Platform)
- Predictable, transaction-linked revenue
- High repeat purchase frequency
- Strong unit economics without inventory risk
- Network effects driven by liquidity, not discounts
Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
- Individual sellers: Supply creation and pricing
- Buyers: Demand and monetization source
- Logistics partners: Shipping, tracking, cost efficiency
- Payment providers: Secure escrow-style transactions
- Trust & moderation teams: Fraud prevention and dispute handling
Vinted’s role is to orchestrate trust, not control inventory.
How the Model Evolved Over Time
Early Phase (2008–2015)
- Community-driven listings
- Limited monetization
- Focus on user adoption
Scaling Phase (2016–2020)
- Introduction of Buyer Protection
- Structured payments and shipping
- Expansion across Europe
Optimization Phase (2021–2026)
- Zero seller fee standardization
- Buyer-paid service fees
- Logistics monetization
- Operational efficiency and profitability focus
Each evolution reduced friction without breaking user trust.
Why This Model Works in 2026
Vinted’s model aligns perfectly with current market conditions:
- Cost-conscious consumers prefer resale over fast fashion
- Sustainability influences purchasing behavior
- Buyers are willing to pay small fees for safety and convenience
- Sellers abandon platforms that erode margins
By charging the side that values protection the most (buyers), Vinted achieves:
- Faster supply growth
- Healthier pricing dynamics
- Strong network effects
- Lower churn on both sides
At Miracuves, we often advise founders that who you charge matters more than how much you charge. Vinted proves that monetization architecture—not just revenue rate—defines long-term scalability.
Read more : What is Vinted and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Vinted’s growth didn’t come from trying to serve “everyone.”
It came from deeply understanding resale behavior and designing a marketplace that feels natural, social, and low-risk for specific user groups.
Instead of positioning itself as a fashion marketplace, Vinted positioned itself as a smart, guilt-free way to buy and sell clothes. That subtle shift defines its segmentation strategy.
Primary Customer Segments
1. Value-Conscious Fashion Buyers
- Age group: 18–40
- Price-sensitive but style-aware
- Comfortable with second-hand purchases
- Mobile-first behavior
- High browsing frequency, moderate basket size
Why they stay:
- Prices are meaningfully lower than retail
- Buyer Protection reduces risk
- Wide supply ensures constant discovery
2. Casual & Power Sellers
- Individuals, not businesses
- Selling to declutter or fund new purchases
- Price competitively due to zero seller fees
- High listing frequency among power sellers
Why they stay:
- No commission erosion
- Fast sales due to high buyer demand
- Simple logistics and payout flow
Secondary Customer Segments
3. Sustainability-Driven Consumers
- Motivated by circular fashion and waste reduction
- High engagement and advocacy behavior
- Often cross-post listings socially
4. Cross-Border Buyers
- Users accessing inventory from neighboring countries
- Benefit from Vinted’s integrated logistics pricing
- Higher average order value due to rarity and variety
Customer Journey: Discovery to Retention
Discovery
- Word-of-mouth and referrals
- App store visibility in European markets
- Organic social sharing of listings
Conversion
- Frictionless listing for sellers
- Competitive pricing attracts first-time buyers
- Trust signals: ratings, protection, delivery tracking
Retention
- Notifications on price drops and saved searches
- Repeat selling funds repeat buying
- Psychological loop: “sell → earn → spend”
This closed-loop ecosystem increases lifetime value without aggressive promotions.
Acquisition Channels by Segment
- Organic app installs and referrals
- SEO-driven category and brand searches
- Influencer and community-driven exposure
- Localized marketing per country
Vinted avoids heavy discounting and instead relies on market liquidity as the growth engine.
Market Positioning & Competitive Edge
Vinted occupies a clear position in the resale landscape:
- Affordable, not aspirational
- Mass-market, not niche luxury
- Community-first, not commission-driven
Compared to competitors:
- Depop emphasizes social resale and youth culture
- Vestiaire Collective focuses on luxury authentication
- eBay targets broad categories with seller fees
Vinted wins by being:
- Simple
- Cost-efficient
- Trust-led at scale
By 2026, this positioning helped Vinted dominate several European markets in second-hand fashion by transaction volume, not just brand buzz.
At Miracuves, we see this as a textbook example of segment clarity before scale—a principle founders must get right before expanding features or geographies.
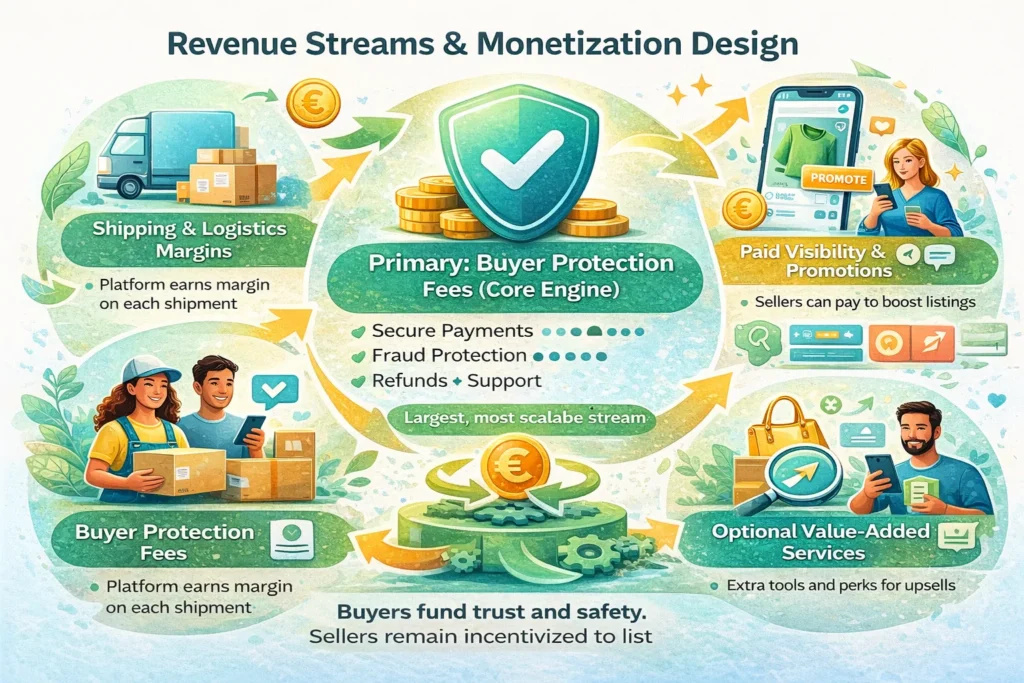
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Vinted’s monetization strategy is intentionally counterintuitive.
Instead of extracting value from sellers—the supply side that fuels liquidity—Vinted monetizes buyer confidence, convenience, and infrastructure.
This design keeps the marketplace liquid while still building a strong, scalable revenue engine.
Primary Revenue Stream 1: Buyer Protection Fees (Core Engine)
Mechanism
Buyers pay a mandatory service fee on each transaction that covers:
- Secure payments
- Fraud protection
- Refund handling
- Customer support and dispute resolution
Pricing Model (2026)
- Flat + percentage-based fee per order
- Varies by country and order value
- Typically low enough to feel negligible per purchase
Revenue Contribution
- Largest and most predictable revenue stream
- Directly tied to transaction volume
- Scales automatically with marketplace liquidity
Growth Trajectory
- Higher repeat purchase frequency
- Increased buyer trust leads to larger baskets
- Expansion into new markets multiplies fee volume
This stream works because buyers value safety more than sellers value margin protection.
Secondary Revenue Stream 2: Integrated Shipping & Logistics Margins
Mechanism
- Vinted negotiates bulk shipping rates with logistics partners
- Buyers select preferred delivery options at checkout
- Platform earns margin on each shipment
Why It Matters
- Logistics becomes a profit center, not a cost
- Improves delivery reliability and speed
- Reduces off-platform transactions
Revenue Contribution
- Meaningful per-transaction margin
- Increases average revenue per order
- Deepens dependency on the platform ecosystem
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: Paid Visibility & Item Promotion
Mechanism
- Sellers can pay to boost listings
- Promoted items appear higher in search and feeds
- Optional, performance-driven spend
Pricing Logic
- Micro-payments per boost
- Volume-based behavior from power sellers
Strategic Value
- Monetizes seller ambition without penalizing casual users
- High-margin digital revenue
- Scales with supply density
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Optional Value-Added Services
Examples include:
- Item verification in select categories
- Premium delivery options
- Enhanced customer support tiers (market-dependent)
These services reinforce trust while creating upsell opportunities.
How the Monetization Architecture Fits Together
Vinted’s revenue streams are non-conflicting:
- Buyers fund trust and infrastructure
- Sellers remain motivated to list freely
- Logistics increases platform stickiness
- Promotions monetize power users, not everyone
This interconnected design:
- Avoids pricing wars
- Preserves marketplace health
- Maintains strong unit economics
Psychologically, the model works because:
- Fees feel tied to value, not access
- Users pay per transaction, not upfront
- Trust reduces perceived risk of second-hand buying
At Miracuves, we often design similar architectures for marketplace founders—where monetization is layered after liquidity, not forced before it.
Read more : Vinted Clone Revenue Model: How Vinted Makes Money in 2026
Operational Model & Key Activities
Behind Vinted’s simple user experience is a highly disciplined operating machine.
Because Vinted doesn’t own inventory, its operational excellence is centered on platform reliability, trust enforcement, and cost control rather than warehousing or fulfillment.
The goal of operations is clear: maximize transaction velocity while minimizing friction and fraud.
Core Operational Functions
Platform & Product Management
- Continuous optimization of search, feeds, and recommendations
- Listing quality control and category structuring
- UX improvements to reduce listing and checkout friction
Technology Infrastructure
- Scalable marketplace architecture
- Secure payment processing and escrow logic
- Real-time order tracking and status updates
- Data systems for pricing, behavior, and fraud detection
Trust, Safety & Moderation
- AI-assisted content moderation for fake or prohibited items
- Fraud pattern detection and user flagging
- Dispute resolution workflows
- Seller and buyer reputation systems
Customer Support Operations
- Multi-language support across European markets
- Automated ticket triaging
- Cost-efficient resolution for refunds and claims
Marketing & Lifecycle Engagement
- Push notifications and behavioral nudges
- Personalized search alerts
- Retention-focused campaigns instead of heavy acquisition spend
Resource Allocation Strategy (2026)
While exact numbers are private, Vinted’s operating focus reveals clear priorities:
- Technology & Product: High investment
Core to scaling transactions without increasing headcount. - Trust & Safety: Strategic investment
Essential to maintaining buyer willingness to pay fees. - Marketing: Controlled and ROI-driven
Emphasis on organic growth, referrals, and retention. - Human Resources: Lean, product-heavy teams
Engineering, data science, and moderation over sales-heavy structures. - Geographic Expansion: Phased, data-led
Launch only when liquidity and logistics partnerships are secured.
Operational Efficiency as a Competitive Advantage
Vinted’s operational model creates leverage:
- Each new transaction costs marginally less to support
- Automation absorbs volume growth
- Trust systems reduce dispute costs over time
This allows Vinted to:
- Maintain low fees
- Stay profitable in core markets
- Scale without inflating operational risk
At Miracuves, we often caution founders that marketplace failure is usually operational, not conceptual. Vinted proves that strong operational design is what turns a good idea into a durable platform.
Read more : Best Vinted Clone Scripts 2025: Build Your Own Resale Marketplace Fast
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Vinted’s growth is not powered by isolation—it’s powered by carefully chosen partnerships that extend capability without increasing internal complexity. Rather than building everything in-house, Vinted focuses on orchestrating an ecosystem where partners strengthen liquidity, trust, and reach.
The guiding philosophy is simple:
Own the user experience, partner for infrastructure.
Core Partnership Philosophy
Vinted partners where:
- Scale matters more than differentiation
- Fixed costs can be converted into variable costs
- Speed-to-market is critical across regions
This approach allows Vinted to expand rapidly while staying asset-light.
Key Partnership Types
1. Technology & API Partners
- Cloud infrastructure providers
- Fraud detection and identity verification services
- Analytics and experimentation tools
Value created:
- Faster feature rollout
- Scalable infrastructure without heavy capex
- Continuous performance optimization
2. Payment & Financial Partners
- Payment gateways and digital wallets
- Escrow-style transaction handling
- Cross-border currency processing
Value created:
- Secure buyer payments
- Delayed release of funds until delivery confirmation
- Reduced chargeback and fraud risk
3. Logistics & Delivery Alliances
- National and regional courier services
- Cross-border shipping partners
- Pickup point and locker networks
Why this matters:
- Competitive shipping prices
- Faster delivery times
- Predictable logistics experience across countries
Logistics partnerships are especially strategic because they:
- Increase transaction completion rates
- Create additional monetization margins
- Lock users into the platform workflow
4. Marketing & Distribution Partnerships
- Influencer collaborations
- Local brand and sustainability initiatives
- Community-led resale campaigns
These partnerships reinforce Vinted’s identity as a responsible, circular fashion platform, not just a resale app.
5. Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Local compliance advisors
- Market-entry consultants
- Policy and consumer protection partners
This enables:
- Faster market entry
- Reduced legal friction
- Better adaptation to local resale regulations
Ecosystem Strategy & Competitive Moat
Vinted’s partnerships create compound advantages:
- Network effects grow stronger with each logistics and payment integration
- Partner switching costs increase as systems interlock
- New entrants face higher operational and capital barriers
From a monetization perspective:
- Logistics partners enable shipping margins
- Payment partners reduce fraud-related losses
- Tech partners support scalable trust systems
At Miracuves, we often design marketplace ecosystems with the same principle: build defensibility through collaboration, not ownership. Vinted shows how partnerships, when structured well, become a long-term competitive moat.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Vinted’s growth story is not driven by aggressive discounting or vanity metrics.
It is driven by repeat behavior, market liquidity, and disciplined expansion.
Instead of asking “How do we grow fast?”, Vinted consistently asks:
“How do we grow without breaking trust or unit economics?”
Core Growth Engines
1. Organic Virality & Referral Loops
- Every sale creates a new seller and buyer advocate
- Users invite others to buy or sell their items
- Listings are often shared socially, driving organic installs
Result:
Growth compounds naturally as liquidity improves.
2. Marketplace Liquidity Flywheel
- More sellers → wider selection
- Wider selection → more buyers
- More buyers → faster sales for sellers
This flywheel reduces the need for paid acquisition once critical mass is reached.
3. Paid Marketing (Selective & ROI-Driven)
- Used mainly during new market entry
- Focused on app installs and first transactions
- Pulled back once organic growth takes over
Vinted avoids over-reliance on paid ads to protect long-term margins.
4. Product-Led Expansion
- Category expansion within fashion
- Improved discovery and personalization
- Enhanced trust and logistics features
Product improvements directly increase transaction frequency.
5. Geographic Expansion Model
- Country-by-country rollout
- Logistics and payments secured before launch
- Localized pricing, language, and regulations
This phased approach prevents supply-demand imbalance.
Scaling Challenges & How Vinted Solved Them
Operational Complexity
- Challenge: Managing disputes and logistics at scale
- Solution: Automation, AI moderation, standardized workflows
Trust & Fraud Risks
- Challenge: Increased fraud with higher volume
- Solution: Data-driven risk scoring and reputation systems
Cross-Border Logistics
- Challenge: Shipping costs and delivery delays
- Solution: Negotiated regional courier networks and pickup points
Regulatory Differences
- Challenge: Different consumer protection laws
- Solution: Local compliance frameworks and flexible policies
Sustaining Growth in 2026
By 2026, Vinted’s growth is characterized by:
- High repeat usage
- Strong unit economics
- Controlled expansion rather than blitzscaling
This makes the business resilient during economic slowdowns and shifts in consumer spending.
At Miracuves, we often remind founders that scaling is about repeatable systems, not explosive launches. Vinted’s growth strategy proves that patience and structure outperform short-term growth hacks.
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Vinted operates in one of the most competitive digital markets—fashion resale—yet it has managed to defend its position against both global marketplaces and niche vertical platforms. Its advantage doesn’t come from flashy branding, but from structural strength built into the business model.
The core question Vinted answers better than competitors is:
“Why should users stay here and not switch?”
Core Competitive Advantages
1. Network Effects
- More sellers create better selection
- Better selection attracts more buyers
- More buyers mean faster sales for sellers
This self-reinforcing loop makes it difficult for new entrants to gain liquidity at scale.
2. Zero Seller Fee Structure
- Sellers earn more per item
- Lower prices attract buyers
- Competing platforms with seller fees struggle to match pricing
This pricing structure acts as a natural switching barrier for supply.
3. Brand Trust & User Confidence
- Buyer Protection normalizes second-hand buying
- Transparent ratings and reviews
- Reliable logistics and payments
Trust reduces friction, which directly increases transaction frequency.
4. Data-Driven Personalization
- Search and recommendation algorithms improve discovery
- Saved searches and alerts increase engagement
- Behavioral data optimizes pricing and listing visibility
Personalization strengthens retention without heavy incentives.
5. Operational & Compliance Strength
- Strong moderation systems
- Local compliance across markets
- Scalable dispute resolution
This allows Vinted to grow without regulatory shocks.
Market Defense Tactics
Handling New Entrants
- Maintains low fees to protect liquidity
- Expands supply density faster than competitors
- Relies on user habit, not exclusivity
Responding to Pricing Wars
- Avoids deep discounting
- Competes on total transaction value, not headline price
- Uses logistics efficiency to keep costs low
Strategic Feature Timing
- Introduces monetized features only after adoption is proven
- Rolls out trust features before expansion
- Improves core flows rather than adding distractions
Acquisitions & Strategic Moves
- Focuses more on organic dominance than M&A
- Consolidates position through ecosystem depth rather than brand aggregation
Why Vinted Is Hard to Disrupt
To challenge Vinted, a competitor would need:
- Massive supply-side incentives
- Comparable trust and logistics infrastructure
- Patience to operate with thin margins early on
Most fail because they monetize too early or misalign incentives.
At Miracuves, we often tell founders that defense is designed, not added later. Vinted’s competitive strategy shows how smart incentive alignment creates long-term protection.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
This is where Vinted’s story becomes especially valuable for founders.
Its success is not about fashion—it’s about how incentives, trust, and monetization are sequenced.
Vinted didn’t win by doing more. It won by doing the right things in the right order.
Key Factors Behind Vinted’s Success
- Monetized trust, not access
- Removed friction for the supply side early
- Designed pricing psychology around perceived value
- Built liquidity before maximizing revenue
- Treated operations as a growth function, not a cost center
These are structural decisions, not surface-level tactics.
Replicable Principles for Startups
Founders can adapt Vinted’s model by:
- Charging the user who benefits most from protection or convenience
- Keeping entry barriers low for supply creators
- Layering monetization only after repeat behavior exists
- Designing logistics and payments as platform features
- Investing early in trust and moderation systems
These principles apply beyond fashion—to rentals, services, B2B marketplaces, and local platforms.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Monetizing too early and killing liquidity
- Overbuilding features before solving trust
- Copying pricing without understanding incentives
- Expanding geographically without operational readiness
- Underestimating support and dispute costs
Vinted avoided these by prioritizing system design over speed.
Adapting the Model for Local or Niche Markets
To localize this model:
- Start with a single high-liquidity category
- Partner locally for payments and delivery
- Adjust buyer protection pricing to purchasing power
- Build community norms early
- Scale region-by-region, not all at once
Implementation & Investment Focus
Phase 1 :
- Core marketplace architecture
- Payments and trust flows
- Basic logistics integration
Phase 2 :
- Liquidity optimization
- Buyer protection monetization
- Moderation automation
Phase 3 :
- Expansion and partnerships
- Advanced personalization
- Margin optimization
Ready to implement Vinted’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable marketplace apps. Get your free business model consultation today.
conclusion
Vinted’s journey proves that business model design is strategy, not a financial afterthought.
By choosing to monetize trust instead of participation, Vinted aligned incentives across buyers, sellers, and the platform itself. This alignment created a marketplace that feels fair, scales efficiently, and remains resilient even as competition intensifies.
In a world where many platforms chase short-term revenue, Vinted shows the power of patient architecture—building systems that reward healthy behavior and punish friction naturally.
For founders in 2026 and beyond, the lesson is clear:
The future of platform economies belongs to businesses that engineer trust, respect user economics, and scale with discipline.
FAQs
What type of business model does Vinted use?
Vinted operates a peer-to-peer marketplace model where buyers fund the platform through protection and service fees, while sellers list items with zero commission.
How does Vinted’s business model create value?
Vinted creates value by lowering prices for buyers, maximizing earnings for sellers, and providing trust, payments, and logistics infrastructure at scale.
What are the key success factors of Vinted?
Zero seller fees, strong buyer protection, efficient logistics partnerships, high marketplace liquidity, and disciplined expansion are Vinted’s core success drivers.
How scalable is Vinted’s business model?
The model is highly scalable because Vinted doesn’t hold inventory, uses automation for trust and support, and benefits from strong network effects.
What are the biggest challenges in Vinted’s model?
Fraud prevention, dispute resolution costs, cross-border logistics complexity, and regulatory differences across markets are the main challenges.
How can entrepreneurs adapt Vinted’s model to their region?
Entrepreneurs can localize the model by focusing on one category, partnering locally for logistics and payments, and pricing buyer protection according to regional purchasing power.
What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a similar platform?
A basic version can launch in 30 – 90 days with strong focus on marketplace architecture, trust systems, and logistics integrations, followed by phased scaling.
What are alternatives to the Vinted business model?
Alternatives include seller-commission marketplaces, subscription-based resale platforms, and managed resale or buyback models.
How has Vinted’s business model evolved over time?
Vinted evolved from a community resale app to a structured, buyer-funded marketplace with integrated payments, logistics, and trust systems.
Related Article :








