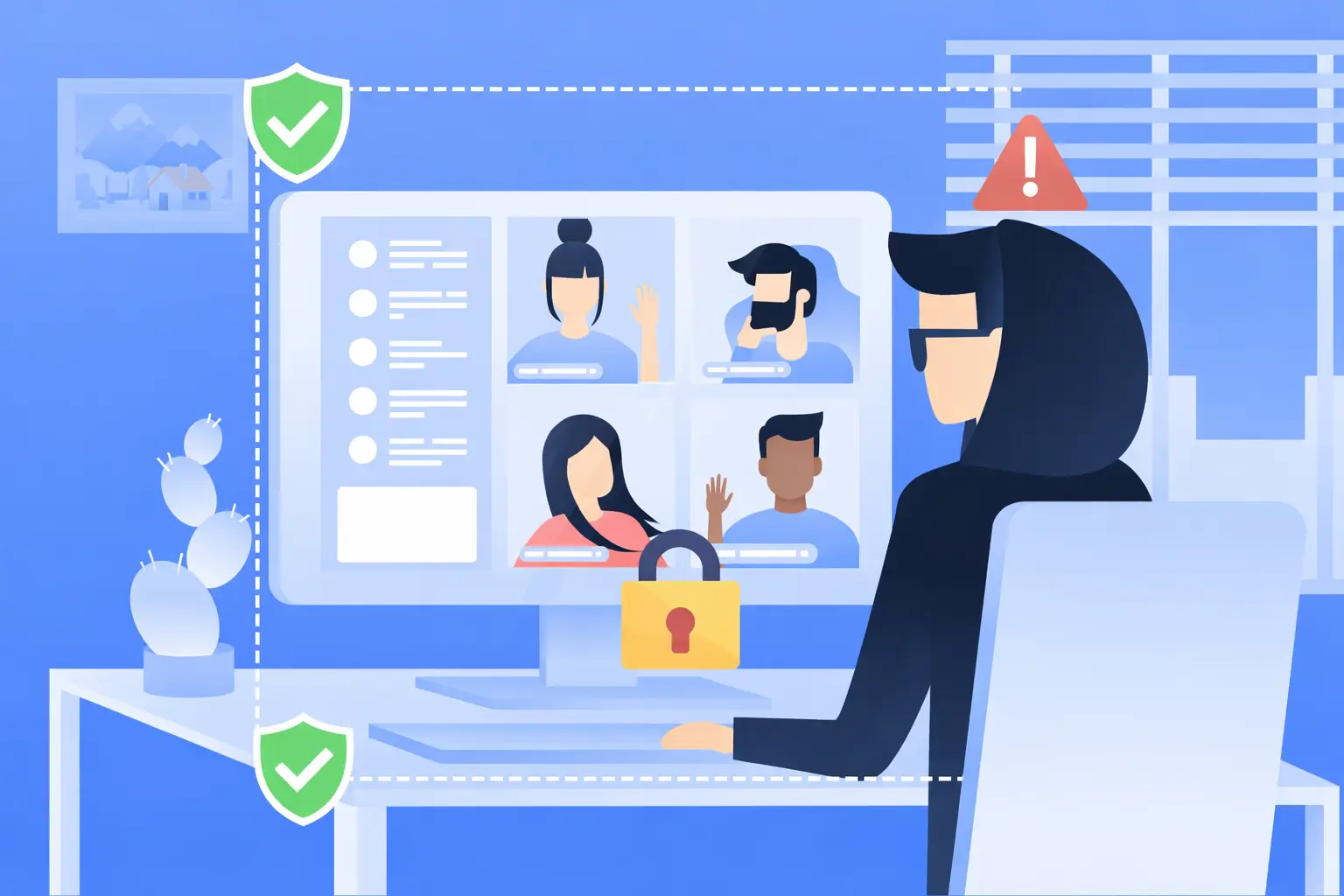
You’ve heard the horror stories about data breaches, leaked meeting links, and “someone random joining the call.”
And if you’re planning to launch a white-label Zoom app in 2026, one question becomes non-negotiable:
Is it actually safe?
The honest truth is this: a white-label Zoom app can be extremely secure, but only if the provider builds it with security-first architecture, compliance-ready policies, and continuous monitoring. Otherwise, it can turn into a privacy risk, legal liability, and reputation nightmare.
In this guide, I’ll give you a clear, practical, and honest assessment of white-label Zoom app security in 2026—what can go wrong, what standards you must meet, and how to protect your users from day one.
Understanding White-Label Zoom App Security Landscape
In 2026, white-label Zoom app security means more than just “adding a password to meetings.” It includes how your entire platform protects user identity, meeting content, shared files, recordings, chat logs, and admin access.
A secure white-label Zoom app is built with the same mindset as enterprise communication tools: prevent attacks, reduce exposure, and control access at every layer.
What “White-Label Security” Actually Means
White-label security means the app is pre-built, but the responsibility of protecting users still exists fully.
Security depends on:
- Code quality and secure development practices
- Cloud/server configuration
- Authentication system
- Meeting access controls
- Data storage and encryption
- Update and patch management
Common Security Myths vs Reality
- Private conversations
- Business meetings
- Screen sharing content
- Payment details (if subscriptions exist)
- Recordings and transcripts
- Personal identity data
Even one breach can destroy trust.
Current Threat Landscape for Zoom-Type Platforms (2026)
Common attacks in 2026 include:
- Meeting link hijacking and unauthorized joining
- Credential stuffing on weak passwords
- Phishing attacks using fake meeting invites
- API abuse (tokens leaked or misconfigured access)
- Cloud storage leaks for recordings
- Admin panel takeover due to weak authentication
Security Standards in 2026
A white-label Zoom app in 2026 is expected to follow:
- Secure SDLC (secure development lifecycle)
- Strong encryption for data in transit and at rest
- Zero-trust access principles
- Regular vulnerability scanning
- Penetration testing and audit trails
- Privacy-first compliance controls
Real-World Statistics on App Security Incidents
In 2026, the biggest real-world pattern is not “advanced hacking.”
It’s basic security gaps like:
- weak authentication
- misconfigured cloud storage
- outdated dependencies
- missing rate limits on APIs
That’s why choosing the right provider matters more than people think.
Read more : – Zoom Revenue Model: How Zoom Makes Money in 2026
Key Security Risks & How to Identify Them
A white-label Zoom app in 2026 can be secure, but only when you actively identify risks before launch. Most security failures happen because founders assume the vendor “already handled it.”
Below are the highest-risk areas you must evaluate.

1) Data Protection & Privacy Risks
User Personal Information
Your app may store:
- Name, email, phone number
- Profile photos
- Device info, IP logs
- Meeting history and usage data
Risk signs:
- No clear data retention policy
- Data stored without encryption
- Admins can access user data too easily
Payment Data Security
If your white-label Zoom app has paid plans, you must secure:
- Subscription payments
- Invoices and transaction records
- Payment tokens
Risk signs:
- Vendor stores card details directly
- No PCI DSS alignment
- No secure payment gateway integration
Location Tracking Concerns
Some meeting apps track location or approximate region via IP.
Risk signs:
- Location collected without consent
- No option to disable tracking
- No explanation in privacy policy
GDPR/CCPA Compliance
In 2026, compliance is not optional if you serve global users.
Risk signs:
- No cookie/data consent flow
- No “delete my data” feature
- No user export/download option
2) Technical Vulnerabilities
Code Quality Issues
Weak coding practices lead to hidden bugs and exploitable flows.
Risk signs:
- No secure coding standards
- No code review process
- No dependency scanning
Server Security Gaps
Even strong apps become unsafe with weak hosting setups.
Risk signs:
- Open ports and weak firewall rules
- No WAF (Web Application Firewall)
- No server hardening checklist
API Vulnerabilities
APIs are the biggest attack surface in 2026.
Risk signs:
- No rate limiting
- Tokens never expire
- Missing input validation
Third-Party Integrations
Common integrations include:
- Payments
- SMS/email OTP
- Analytics
- Push notifications
Risk signs:
- Unknown SDKs installed
- Excessive permissions
- No vendor risk assessment
3) Business Risks
Legal Liability
If user data leaks, your business is accountable.
Real impact:
- User complaints
- Lawsuits
- Contract breaches
Reputation Damage
A single security incident can permanently reduce trust.
Financial Losses
Costs can include:
- Incident response team
- Refunds and churn
- Downtime losses
Regulatory Penalties
In 2026, penalties can be serious for poor compliance.
Risk Assessment Checklist (Quick Scan)
Use this checklist before finalizing any white-label Zoom app provider:
- Is all user data encrypted at rest and in transit?
- Is 2FA available for users and admins?
- Are meeting links protected with passwords + waiting room?
- Are recordings securely stored with access control?
- Are APIs rate-limited and token-protected?
- Is there a patch/update policy with timelines?
- Are audit logs available for admin actions?
- Is GDPR/CCPA compliance built-in (export + delete data)?
- Is payment handling PCI DSS aligned (no card storage)?
- Is penetration testing done at least annually?
Security Standards Your White-Label Zoom App Must Meet
In 2026, “secure app” is not a claim. It’s something you prove with certifications, documented controls, and real technical safeguards. If your white-label Zoom app handles business meetings, customer calls, recordings, or payments, these standards become mandatory.
Essential Certifications (What to Look For)
ISO 27001 Compliance
What it proves in 2026:
- Strong information security management system (ISMS)
- Risk assessment process
- Controlled access to systems and data
Best for: - Any serious enterprise-grade platform
SOC 2 Type II
What it proves:
- Security controls are not just designed, but continuously followed over time
Focus areas: - Security, availability, confidentiality, privacy
Best for: - SaaS-style communication platforms
GDPR Compliance
What it proves:
- Proper user rights management (delete/export/consent)
- Legal basis for processing data
Best for: - EU users, global platforms
HIPAA (If Applicable)
Needed if your Zoom-type app is used for:
- Telemedicine
- Patient consultations
- Health data discussions
HIPAA in 2026 requires: - Strict access controls
- Audit logs
- Encrypted storage
PCI DSS for Payments
Required if your app supports:
- Subscription payments
- Premium plans
PCI DSS ensures: - Secure payment processing
- No unsafe card storage
Technical Requirements (Non-Negotiable in 2026)
End-to-End Encryption (E2EE)
Protects meeting content from interception.
In 2026, users expect strong encryption especially for:
- Private meetings
- Business calls
- Client discussions
Secure Authentication (2FA / OAuth)
Minimum expectation:
- Email/phone verification
- Optional 2FA for users
- Mandatory 2FA for admins
OAuth options: - Google sign-in, Microsoft sign-in
Regular Security Audits
A secure white-label Zoom app must include:
- Vulnerability scanning
- Code review checks
- Security patch verification
Penetration Testing
In 2026, pentesting helps find real exploit paths like:
- API token abuse
- session hijacking
- privilege escalation
SSL Certificates
This is basic, but still essential:
- HTTPS everywhere
- No mixed-content warnings
- HSTS recommended
Secure API Design
Must include:
- Rate limiting
- Token expiration
- Role-based access control (RBAC)
- Input validation
- Logging and monitoring
Security Standards Comparison Table (2026)
| Standard / Requirement | What It Covers | Why It Matters for White-Label Zoom App |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Organization-wide security controls | Proves mature security governance |
| SOC 2 Type II | Ongoing operational security | Builds enterprise trust |
| GDPR | Privacy rights + data handling | Avoids legal risk in EU/global |
| HIPAA (if needed) | Health data protection | Required for medical use cases |
| PCI DSS | Payment security | Prevents payment data exposure |
| E2EE | Meeting content privacy | Protects calls from interception |
| 2FA / OAuth | Account protection | Stops admin takeover and misuse |
| Penetration Testing | Real attack simulation | Finds vulnerabilities before hackers |
| Secure APIs | App-to-server security | Prevents data leaks and abuse |
Red Flags: How to Spot Unsafe White-Label Providers
In 2026, the biggest mistake founders make is choosing a white-label Zoom app provider based only on price and demo screens. Security is invisible until something breaks. That’s why you must judge providers by proof, not promises.
Warning Signs (High-Risk Red Flags)
No Security Documentation
If they cannot share security practices, it usually means they don’t have any.
What you should expect:
- Security policy overview
- Data handling explanation
- Incident response process
Cheap Pricing Without Explanation
Low pricing often means:
- Reused unsafe code
- No audits
- No monitoring
- No patching commitment
No Compliance Certifications
Even if they are “working on it,” in 2026 you need clarity:
- ISO 27001 alignment
- SOC 2 readiness
- GDPR/CCPA controls
Outdated Technology Stack
Old frameworks and unsupported libraries increase risk.
Common issues:
- Unpatched dependencies
- Old server configs
- Weak authentication methods
Poor Code Quality
Signs include:
- App crashes during demo
- Slow performance under load
- No documentation
- No staging/testing environment
No Security Updates Policy
This is extremely dangerous.
Ask:
- How often are updates released?
- How fast do they patch vulnerabilities?
Lack of Data Backup Systems
If backups are missing, recovery becomes impossible after:
- ransomware
- data corruption
- server failure
No Insurance Coverage
Serious providers in 2026 often carry:
- cyber liability insurance
- professional indemnity coverage
Evaluation Checklist (What to Ask Providers)
Questions to Ask
- Do you provide 2FA for admin and users?
- Is meeting data encrypted at rest and in transit?
- How are recordings stored and protected?
- Do you perform penetration testing? How often?
- What is your vulnerability patch timeline?
- How do you prevent unauthorized meeting access?
- Do you log admin actions and security events?
Documents to Request
- Security architecture overview
- Data flow diagram (where data is stored)
- Privacy policy template (GDPR/CCPA ready)
- Backup and disaster recovery policy
- Incident response plan summary
Testing Procedures
Before launch, request:
- Vulnerability scan report
- Pen test summary report
- Authentication testing proof
- API security testing checklist
Due Diligence Steps
- Check past client reviews for security issues
- Verify how long they provide support
- Confirm ownership of code and update rights
- Ensure you can run independent security audits
Best Practices for Secure White-Label Zoom App Implementation
In 2026, security is not a one-time setup. It’s a full process that starts before launch and continues every week after your app goes live. The safest white-label Zoom apps are the ones treated like enterprise systems, not just “software delivery.”
Pre-Launch Security (Before You Go Live)
1) Security Audit Process
Before launch, validate:
- authentication flow
- meeting access controls
- encryption settings
- admin panel permissions
- API exposure
A basic security audit in 2026 should include:
- automated vulnerability scanning
- manual review of high-risk features
2) Code Review Requirements
You should ensure:
- secure coding standards followed
- sensitive data not logged
- no hardcoded keys/tokens
- dependency vulnerabilities checked
3) Infrastructure Hardening
This includes:
- firewall rules
- WAF protection
- secure database access
- private network configuration
- DDoS protection
4) Compliance Verification
Before launch, confirm:
- GDPR/CCPA features exist (export/delete/consent)
- privacy policy is updated
- terms of service include user responsibilities
- data retention rules are clear
5) Staff Training Programs
In 2026, many breaches happen due to human mistakes.
Train teams on:
- phishing awareness
- admin access control
- password hygiene
- incident reporting steps
Post-Launch Monitoring (After You Go Live)
1) Continuous Security Monitoring
Your platform should track:
- unusual login attempts
- failed OTP/2FA attempts
- suspicious meeting join patterns
- API abuse and rate-limit triggers
2) Regular Updates and Patches
A secure white-label Zoom app needs:
- monthly planned updates
- emergency patches within days for critical issues
- dependency updates (libraries, SDKs)
3) Incident Response Planning
You need a clear plan for:
- detecting incidents
- isolating systems
- notifying users (if needed)
- reporting to regulators (if required)
- restoring from backups
4) User Data Management
In 2026, data safety also means control.
Ensure:
- minimal data collection
- role-based access for admins
- secure deletion and retention rules
5) Backup and Recovery Systems
A strong setup includes:
- daily encrypted backups
- backup testing every month
- recovery drills to confirm restore works
Security Implementation Timeline (Simple 2026 Plan)
Week 1: Foundation
- choose secure hosting setup
- enable SSL + WAF
- set role-based admin access
Week 2: App Hardening
- secure authentication (2FA/OAuth)
- secure meeting controls (waiting room, passwords)
- protect recordings storage
Week 3: Testing
- vulnerability scan
- API testing
- penetration testing
Week 4: Compliance + Go-Live
- GDPR/CCPA verification
- finalize policies (privacy/terms)
- monitoring dashboards setup
- launch with incident response plan ready
Read more : – Top 16 Features for a Professional Zoom Clone App in 2025
Legal & Compliance Considerations (2026)
A white-label Zoom app is not just a tech product in 2026. It is a communication platform that handles sensitive conversations, recordings, and identity data. That means legal compliance becomes part of your security strategy.
If you ignore compliance, even a small incident can turn into a regulatory issue.
Regulatory Requirements (What You Must Handle)
Data Protection Laws by Region
In 2026, the most common compliance expectations are:
- EU/EEA: GDPR
- UK: UK GDPR + Data Protection Act
- USA: CCPA/CPRA (California) + state privacy laws
- India: DPDP Act (Digital Personal Data Protection) compliance principles
- Global users: Privacy-by-design expectations
Your app must clearly define:
- what data you collect
- why you collect it
- where it is stored
- how long it is kept
- how users can delete it
Industry-Specific Regulations
Your compliance changes based on use case:
- Education platforms: student data handling
- Corporate usage: confidentiality and access controls
- Healthcare usage: HIPAA (if medical consultations exist)
- Finance usage: stronger identity verification and audit logs
User Consent Management
Consent in 2026 must be:
- clear
- trackable
- reversible
Example requirements:
- recording consent prompt
- cookie/data consent banners
- opt-in for marketing communication
Privacy Policy Requirements
Your privacy policy must include:
- data categories collected
- third-party sharing disclosure
- security practices summary
- user rights (export/delete)
- contact method for privacy requests
Terms of Service Essentials
Your terms should cover:
- user behavior rules
- meeting misuse prevention
- account suspension policy
- content responsibility
- limitation of liability language
Liability Protection (How to Reduce Business Risk)
Insurance Requirements
In 2026, many serious businesses take:
- cyber liability insurance
- errors and omissions coverage
- data breach response coverage
This helps cover:
- legal costs
- incident response costs
- customer claims
Legal Disclaimers
Disclaimers help clarify:
- platform usage boundaries
- user responsibilities
- recording policies
User Agreements
Your user agreements must clearly define:
- what is allowed
- what is prohibited
- consequences of violations
Incident Reporting Protocols
You should document:
- who handles incidents internally
- response timeline
- user notification process
- regulator reporting steps (if required)
Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
Compliance is ongoing in 2026.
You must review:
- new privacy law updates
- security audit results
- data processing agreements with vendors
Compliance Checklist by Region (2026 Quick View)
EU (GDPR)
- lawful basis for processing
- user data export + deletion
- breach notification readiness
- DPA with vendors
USA (CCPA/CPRA)
- opt-out rights
- privacy disclosure updates
- data access request handling
India (DPDP principles)
- consent-first approach
- secure processing of personal data
- grievance/contact mechanism
Global Best Practice
- privacy-by-design
- minimal data collection
- strong authentication + encryption
- audit logs
Read more : – Business Model of Zoom : Complete Strategy Breakdown 2025
Why Miracuves White-Label Zoom App is Your Safest Choice
In 2026, choosing a white-label Zoom app provider is not just about launching faster. It’s about choosing a partner who protects your users, your brand, and your business future.
Miracuves positions itself as a security-first solution provider, built for businesses that want growth without risking privacy, compliance, and trust.
Miracuves Security Advantages (2026)
Enterprise-Grade Security Architecture
Miracuves focuses on building white-label Zoom app systems with security at the core, including:
- secure role-based access control
- protected admin panels
- safe meeting access layers
Regular Security Audits and Best-Practice Controls
A secure platform in 2026 must be reviewed continuously, not once.
Miracuves follows audit-driven improvement to reduce real-world attack exposure.
GDPR/CCPA Compliance Ready by Default
Compliance is treated as a default requirement, not an add-on.
This includes:
- consent handling
- user data export and deletion readiness
- privacy policy alignment support
24/7 Security Monitoring Mindset
For modern communication apps, threats don’t wait for office hours.
Miracuves promotes continuous monitoring practices for:
- suspicious login patterns
- API abuse
- meeting access anomalies
Encrypted Data Transmission
In 2026, encryption is mandatory for trust.
Miracuves prioritizes secure transmission to reduce interception risk.
Secure Payment Processing
If your white-label Zoom app includes subscriptions, Miracuves supports secure payment handling aligned with modern payment safety expectations.
Regular Security Updates
Security updates are not optional in 2026.
Miracuves emphasizes:
- scheduled patching
- emergency fixes for critical vulnerabilities
Business-Ready Security Support
Miracuves solutions are designed to support long-term operations, not just launch-day delivery.
Final Thought
Don’t compromise on security. Miracuves white-label Zoom app solutions come with enterprise-grade security built-in. Our 600+ successful projects have maintained zero major security breaches. Get a free security assessment and see why businesses trust Miracuves for safe, compliant platforms.
In 2026, a white-label Zoom app can be safe, scalable, and fully trusted, but only when security is treated as a core product feature, not a “later fix.”
If you choose the right provider, follow compliance rules, and maintain continuous monitoring, you can confidently launch a platform that users feel safe using every day.
FAQs
1) How secure is white-label vs custom development?
In 2026, both can be secure. White-label Zoom apps are safe when built with strong standards, audits, and updates. Custom apps are only safer if security is done correctly.
2) What happens if there’s a security breach?
You must follow an incident response plan, secure systems, notify affected users (if required), and report to regulators depending on your region and compliance rules in 2026.
3) Who is responsible for security updates?
In 2026, the provider should deliver patches and updates, but the business owner must ensure updates are applied and security monitoring is active.
4) How is user data protected in white-label apps?
User data is protected through encryption, access control, secure servers, and limited admin permissions. GDPR/CCPA-ready features also help manage user rights in 2026.
5) What compliance certifications should I look for?
For 2026, look for ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, GDPR readiness, and PCI DSS for payments. HIPAA is needed only for healthcare use cases.
6) Can white-label apps meet enterprise security standards?
Yes. In 2026, white-label Zoom apps can meet enterprise standards when they include audits, penetration testing, secure authentication, and strict access controls.
7) How often should security audits be conducted?
In 2026, do vulnerability scanning monthly and penetration testing at least once a year, or more often for high-risk platforms.
8) What’s included in Miracuves security package?
Miracuves focuses on enterprise-grade architecture, encryption, compliance readiness, security monitoring practices, and regular security updates in 2026.
9) How to handle security in different countries?
In 2026, follow region-based compliance like GDPR (EU), CCPA/CPRA (USA), and DPDP principles (India). Keep policies and consent flows updated.
10) What insurance is needed for app security?
In 2026, cyber liability insurance and professional indemnity coverage are commonly recommended to reduce financial and legal risks.
Related Articles








