The business model of AliExpress was created with a simple yet revolutionary vision — empower Chinese manufacturers to sell directly to global consumers without relying on intermediaries. When Alibaba launched AliExpress in 2010, the platform wasn’t designed to challenge Amazon’s inventory-heavy structure; it was built to unlock worldwide demand for factory-direct products.
By eliminating warehouses, inventory ownership, and major logistics burden, AliExpress grew into a pure cross-border marketplace. This asset-light structure allowed the company to scale rapidly across 200+ markets, serving millions of monthly buyers with unmatched product variety and competitive pricing.
Today, the business model of AliExpress stands as the world’s largest cross-border commerce engine. For entrepreneurs exploring marketplace platforms, drop shipping systems, multi-vendor ecosystems, or international eCommerce, AliExpress offers a masterclass in hyper-scale growth and low-risk monetization.
How the AliExpress Business Model Works
AliExpress operates as a global online marketplace where mostly Asian (especially Chinese) manufacturers and merchants sell directly to international consumers. Unlike Alibaba.com (B2B) or Amazon (1P inventory), AliExpress is built as a cross-border B2C and C2C marketplace with low platform risk and high seller density.
1. Type of Model
- Core Model:
- Marketplace + Cross-Border eCommerce
- Marketplace + Cross-Border eCommerce
- Sub-Models Inside the Ecosystem:
- Multi-vendor marketplace
- Dropshipping enabler (for global resellers)
- Discount-driven, promo-heavy retail
- Hybrid logistics (merchant shipping + AliExpress Standard Shipping)
AliExpress earns primarily from commissions, advertising, and value-added services, while merchants handle product sourcing, pricing, and fulfilment (unless using AliExpress’s logistics solutions)
2. Value Proposition by Segment
For Consumers (Global Shoppers):
- Access to ultra-cheap products across categories (fashion, electronics, home, gadgets).
- Massive catalog with millions of SKUs and niche items not found in local retail.
- Regular flash sales, mega campaigns (11.11, 12.12, etc.), coupons and coins.
- Buyer protection policies, dispute resolution, and escrow-style payment flows.
For Merchants / Manufacturers:
- Direct access to global consumers without intermediaries.
- Ability to clear inventory quickly with promo campaigns and discounts.
- Built-in traffic from AliExpress’s global marketing engine.
- Logistics assistance via Cainiao & AliExpress Standard Shipping.
3. Key Stakeholders & Their Roles
- Sellers / Merchants / Factories
- List products, manage pricing, handle packaging.
- Participate in campaigns and flash sales.
- Maintain ratings and service levels to remain competitive.
- Consumers (Global Buyers)
- Discover products via search, recommendations, campaigns.
- Pay in their local currency via integrated payment methods.
- Provide ratings, reviews, disputes → critical to trust and ranking.
- AliExpress Platform (Alibaba Group)
- Operates marketplace infrastructure & recommendation engine.
- Manages payments, fraud checks, dispute system, and promotions.
- Monetizes via commissions, ads, and service fees.
4. Evolution of the Model
- 2010–2014 (Launch & Discovery):
- Focused on exporting cheap Chinese goods globally.
- Minimal branding; price arbitrage was the main hook.
- 2015–2019 (Growth & Category Expansion):
- Improvement in buyer protection, tracking, logistics SLAs.
- Growth in categories: fashion, electronics, home décor, accessories.
- Entry into more emerging markets (Russia, Brazil, Eastern Europe, MENA).
- 2020–2023 (Logistics & Experience Upgrade):
- Heavy investment in Cainiao logistics, faster delivery lanes.
- Better mobile app experience, gamification, coins, and cashback.
- More localized experiences (languages, currencies, local campaigns).
- 2024–2025 (Quality & Brand Focus):
- Push towards higher-quality merchants & branded stores.
- Shorter delivery times in key markets using regional warehouses and partners.
- More creator marketing, TikTok-style content commerce, and AI-powered personalization.
5. Why the Model Works in 2025
- Cross-border appetite has exploded — global buyers are now comfortable ordering from international marketplaces as long as there’s tracking, buyer protection, and reasonable delivery.
- The macro trend of price sensitivity + inflation makes AliExpress attractive: buyers are willing to trade speed for significant cost savings.
- AliExpress sits in a sweet spot:
- Lower operational risk (no inventory).
- High scalability (more sellers = more SKUs = more buyers).
- Strong network effects: as product variety and reviews increase, conversion and retention improve.
For entrepreneurs, this model proves that you don’t need to own inventory to build a massive, defensible commerce platform — you need the right multi-vendor architecture, trust mechanisms, logistics integrations, and growth loops.
This is exactly where Miracuves-style marketplace platforms come in:
- Multi-vendor engines with ratings, commissions, dispute workflows.
- Cross-border payment & logistics integration.
Read more : What is AliExpress App and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
AliExpress’s success comes from understanding its diverse global audience and tailoring product selection, pricing, and marketing to meet different consumer expectations — from budget-conscious buyers to resellers and hobbyists. By 2025, AliExpress operates in 200+ countries, each with unique shopping patterns, currencies, and cultural triggers.
1. Primary & Secondary Customer Segments
Primary Segments
1. Price-Sensitive Global Consumers
This is AliExpress’s largest user group.
- Look for low-cost products unavailable locally.
- Accept longer shipping if pricing is attractive.
- Engage heavily during mega sales (11.11, 12.12, Ramadan, Black Friday)
- Categories: fashion, electronics accessories, home items, beauty tools.
2. Hobby-Based & Niche Buyers
People searching for products not sold in their region.
- DIY tools, 3D printing consumables, cosplay items, collectibles.
- Long-tail SKUs fuel AliExpress’s differentiation.
3. International Dropshippers & Small Resellers
A fast-growing segment.
- Buy from AliExpress to resell via Shopify, Amazon, or local markets.
- Depend on cheap product sourcing, seller reliability, and steady stock.
- Significant volume buyers for specific SKUs.
Secondary Segments
4. Brand-Conscious Buyers Seeking Discounts
- Not the cheapest segment, but value deals on branded stores.
- AliExpress promotes official stores heavily in 2025.
5. Emerging Market Shoppers
India, Brazil, Russia, South Africa, Eastern Europe.
- High growth markets with increasing eCommerce adoption.
- Influenced strongly by social commerce and influencer deals.
2. Customer Journey (Discovery → Conversion → Retention)
Discovery
- Performance ads (Facebook, TikTok, Google).
- Influencer unboxing content.
- Price comparison sites.
- App store optimization (ASO) — AliExpress consistently ranks in the top retail apps.
Conversion
- Attractive product pages with videos + reviews + Q&A.
- Global currency display.
- Flash deals and countdown timers.
- AliExpress Coins & coupons improving cart conversion
Retention
- Daily check-in rewards.
- Personalised recommendations via Alibaba’s AI.
- App-exclusive discounts.
- Buyer protection and dispute resolution reducing churn.
- Gamification loops (spin wheels, coins, cashback)
Read more : Best AliExpress Clone Script 2025: Launch a Scalable eCommerce Marketplace
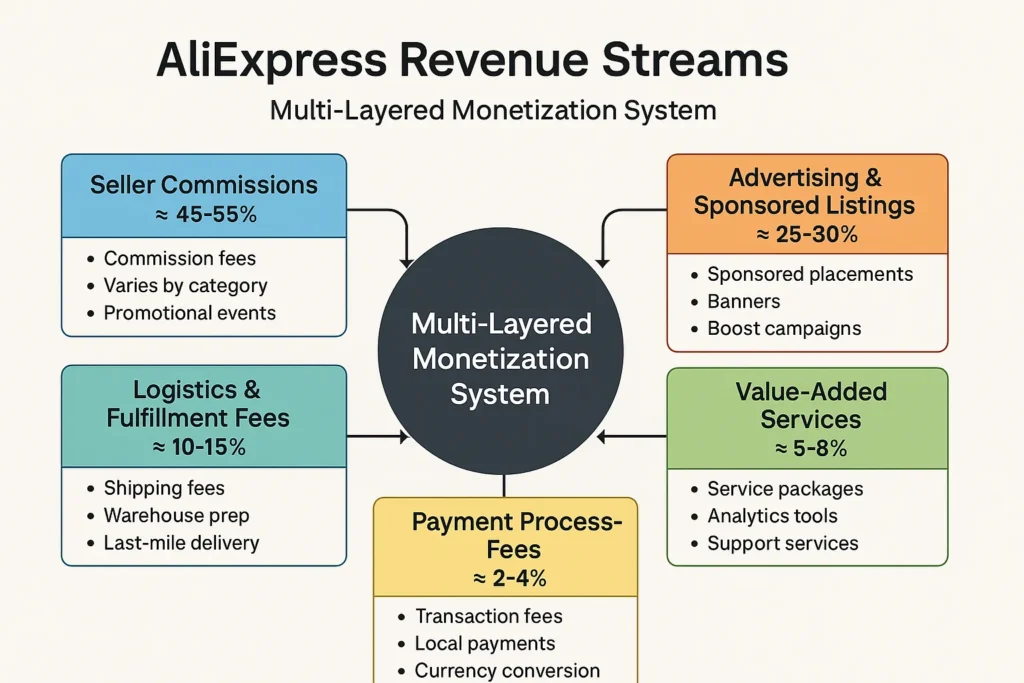
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
AliExpress generates revenue through a multi-layered monetization system designed for scalability without owning inventory. The beauty of AliExpress’s model is that each revenue channel strengthens the platform flywheel — more sellers → more ads → more commissions → more buyers → more data → more sales.
Let’s break it down.
1. Primary Revenue Stream – Seller Commissions (≈ 45–55%)
Mechanism
AliExpress charges merchants a commission fee on every completed order.
This varies by category and country.
Pricing Model (2025)
- 5% – 10% commission for most categories
- 3% – 5% on electronics
- Up to 15% for high-demand or high-return categories (e.g., fashion, beauty )
Growth Trajectory
- Increased seller onboarding from Southeast Asia & Middle East in 2024–2025.
- Commission revenue grows in proportion to GMV expansion.
- Global promotional events (11.11, Ramadan sales, Black Friday) boost earning cycles .
This remains AliExpress’s most stable and predictable revenue stream.
2. Secondary Revenue Stream – Advertising & Sponsored Listings (≈ 25–30%)
Mechanism
Sellers pay to improve visibility:
- Sponsored product placements
- Home-page banners
- Flash deal placements
- Boost campaigns for new listing
3. Logistics & Fulfillment Fees (≈ 10–15%)
AliExpress partners with Cainiao Logistics and third-party express providers.
Earning Sources
- Shipping fees (partially subsidized, partially paid by customers).
- Warehouse prep fees (for regional warehouses).
- Consolidation and last-mile delivery fees.
- Premium shipping (AliExpress Standard Shipping upgrades).
As cross-border shipping increases, logistics earnings have grown significantly.
4. Value-Added Services (≈ 5–8%)
These include:
- Seller service packages
- Store design tools
- Analytics dashboards
- Premium dispute support
- Return-processing assistance
- Local advertising tools
Many high-volume merchants subscribe to these services to improve selling performance.
5. Payment Processing Fees (≈ 2–4%)
AliExpress charges small fees for:
- Card transactions
- Wallet payments
- Local payment rails in different countries
- Currency conversion margins
Combined across millions of orders per month, this becomes a meaningful revenue contributor .
AliExpress’ Overall Monetization Strategy (2025)
The platform uses a flywheel monetization system:
- Low commissions attract more sellers
- More sellers → more product diversity
- More diversity → more buyers
- More buyers → more ads
- More ads → more revenue
- More revenue → reinvest in logistics + features
- Better logistics → higher customer satisfaction
- Higher satisfaction → even more buyers & sellers
Read more : AliExpress Revenue Model: How AliExpress Makes Money in 2025
Operational Model & Key Activities
AliExpress runs one of the world’s most complex yet lean and scalable operational structures. Because it does not own inventory, the platform focuses heavily on technology, logistics coordination, seller quality, and global experience management.
Below is a complete breakdown of how AliExpress operates behind the scenes.
1. Core Operational Activities
a) Platform & Tech Infrastructure Management
AliExpress invests massively in engineering teams to maintain:
- Global marketplace architecture
- Search & recommendation algorithms
- Fraud detection & risk engines
- Multi-language, multi-currency support
- Category-specific merchandising engines
- Mobile-first product experience across 200+ countries
Alibaba’s cloud (Alicloud) powers the platform, ensuring 99.9% uptime and fast page loads even during mega events like 11.11.
b) Quality Control & Merchant Performance Management
Since AliExpress does not own the products, quality control happens at the merchant level — but AliExpress enforces strict rules.
Key activities include:
- Seller onboarding verification
- Product authenticity checks
- Return/refund compliance checks
- Real-time monitoring of ratings, complaints, cancellations
- Automated penalties for fake tracking, late dispatch, or misrepresentation
- Monthly Seller Performance Score recalculation .
This ensures a minimum global trust standard.
c) Order Processing & Fulfillment via Logistics Network
AliExpress uses its logistics arm Cainiao plus 3PL partners.
Operational workflows include:
- Consolidation warehouses in China & key international regions
- First-mile pickup from sellers
- Cross-border customs clearance
- Air & sea freight lane optimization
- Country-specific last-mile delivery partnerships
- End-to-end shipment tracking
By 2025, AliExpress Standard Shipping delivers to many major cities in 7–12 days, a major improvement over earlier 30–45 day timelines.
d) Customer Support & Dispute Resolution
AliExpress runs a massive global support center with AI + human intervention.
Core processes:
- 24/7 live chat
- Buyer protection enforcement
- Dispute arbitration (refund/return/partial refund)
- Payment hold & escrow-based systems
- Multi-language communication workflows
Disputes are one of the most important operational tasks because they directly impact platform trust.
How Miracuves Helps Entrepreneurs Replicate This Model
Miracuves builds marketplace ecosystems with operational logic similar to AliExpress:
- Multi-vendor engine with commissions, ads & seller dashboards
- Built-in dispute management flows
- Cross-border payment integration
- Scalable hosting and 99.9% uptime
- Multi-country language & currency setup
- Logistics API integrations
This allows entrepreneurs to launch AliExpress-style marketplaces in 3–9 days, fully customized and enterprise-ready.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
AliExpress’s long-term dominance in global eCommerce is not built on product inventory — it is built on partnerships, integrations, and an ecosystem that enables sellers, buyers, logistics players, and fintech providers to work together seamlessly.
AliExpress operates like a global commerce network, where every partnership enhances speed, trust, and reach.
1. Collaboration Philosophy of AliExpress
AliExpress follows a platform-first partnership approach:
- Don’t own everything — integrate everything.
- Reduce friction in cross-border commerce through partnerships.
- Empower sellers with global access.
- Ensure buyers get protection, convenience, and delivery accuracy.
- Localize through regional partners while leveraging Alibaba’s global backbone.
This approach allows AliExpress to scale into 200+ countries without building infrastructure in each market.
2. Key Partnership Categories
a) Technology & API Partners
These partners support platform functionality across markets:
- AI-driven product recommendation engines
- Third-party analytics systems
- Search optimization and fraud-detection APIs
- App performance monitoring & cloud partners (Alicloud globally, regional CDNs)
Tech partnerships allow AliExpress to keep performance high during mega sales where transactions run into millions within hours.
b) Payment & Fintech Partners
AliExpress integrates hundreds of payment solutions depending on the region:
- Visa, Mastercard, Maestro
- PayPal in select markets
- Klarna, AfterPay, and other BNPL solutions
- Local payment rails in Brazil, Russia, India, MENA
- Wallets & EMI options
Payment partners increase conversion rates by offering trusted local options.
c) Logistics Partners (Cainiao + 3PLs)
Logistics is AliExpress’s backbone.
Key partners include:
- Cainiao Smart Logistics Network (Alibaba-owned)
- DHL, FedEx, UPS
- Local last-mile delivery partners in every country
- Regional warehouses collaborating with AliExpress Standard Shipping
These partnerships ensure end-to-end shipping visibility and faster delivery compared to older cross-border models.
d) Marketing, Influencer & Distribution Partners
AliExpress works with:
- TikTok influencers
- Instagram creators
- Affiliate marketers
- Comparison engines
- Cashback apps
- YouTube review channels
Influencer-driven commerce is one of AliExpress’s fastest-growing acquisition channels in 2024–2025.
e) Regulatory & Expansion Partnerships
To operate worldwide, AliExpress collaborates with:
- Customs authorities
- Local compliance bodies
- Consumer protection agencies
- Cross-border commerce regulators
These ensure smooth import/export flows and legal compliance across markets.
3. Ecosystem Strategy & Competitive Advantage
AliExpress builds an ecosystem where every participant (buyer, seller, courier, payment provider, influencer) adds value to the next.
Network Effects
- More sellers → more products
- More products → more buyers
- More buyers → more logistics & payment partnerships
- Better partnerships → better experience
- Better experience → more sellers
This creates a self-reinforcing flywheel.
Monetization Within the Ecosystem
- Sellers pay for ads.
- Brands pay for campaign participation.
- Logistics earns through volume.
- Payment partners earn fees.
- Influencers earn commissions.
- AliExpress earns commissions + ads + service fees.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
AliExpress’s explosive international scale is not an accident — it is the result of data-driven expansion, high-frequency sales events, deep logistics innovation, influencer-led marketing, and hyper-local adaptation. By 2025, AliExpress has mastered how to grow a platform across continents without owning inventory or physical stores.
Let’s break down the engines that fuel this growth.
1. Core Growth Engines
a) Organic Virality & Social Commerce Loops
AliExpress was one of the earliest global platforms to leverage social proof + viral pricing.
Growth loops include:
- Sharing deals for coins/cashback
- Referral bonuses
- Group buying (Buy Together discounts)
- Influencer unboxing videos
- User-generated content (reviews, product videos)
In 2024–2025, AliExpress leaned heavily into short-video commerce, mirroring TikTok Shop’s success .
b) Paid Performance Marketing
AliExpress invests heavily in paid acquisition across regions:
- Facebook + Instagram ads
- TikTok Shops & creator collabs
- Google Shopping ads
- Retargeting through push, SMS, and email
- Affiliate networks and cashback apps
Paid ads fuel new market entries and accelerate seasonal sales pushes.
c) New Product Lines & Category Expansion
AliExpress grows by continuously adding profitable, high-retention categories:
- Smart home devices
- Personal gadgets
- Beauty accessories
- Fashion & fast apparel
- Home décor
- Vehicle accessories
- DIY/Professional tools
By expanding SKU density, AliExpress increases search volume, relevance, and lifetime value.
2. Scaling Challenges & How AliExpress Solved Them
Challenge 1: Long Shipping Times
Solution:
- Cainiao logistics
- Aviation partnerships
- Regional warehouses
- Faster sorting + automated customs clearance
Now many countries receive packages in 7–12 days.
Challenge 2: Counterfeit or Low-Quality Sellers
Solution:
- Authenticity tags
- Seller scorecards
- Penalties for misrepresentation
- Better dispute management
- Branded stores onboarding
Quality has significantly improved since 2022.
Challenge 3: Competition from Amazon & Shein
Solution:
- Aggressive pricing
- Category diversification
- Influencer commerce
- Country-specific strategies
- Faster cross-border lanes
AliExpress competes on price + variety, not speed.
Challenge 4: Regulatory Restrictions
Solution:
- Partnerships with customs
- Local payment integrations
- Country-specific compliance teams
AliExpress has one of the most sophisticated cross-border compliance frameworks in the world.
Why This Growth Strategy Works (2025)
AliExpress combines:
- cross-border efficiency
- low prices
- massive SKU diversity
- highly repeatable global sale events
- influencer commerce
- localized experiences
This creates a scalable, defensible global marketplace.
Miracuves helps entrepreneurs replicate this same model with:
- multi-vendor capabilities
- commission + ads monetization
- global logistics integrations
- scalable cloud architecture
customizable apps & web platforms
Read more : The Genius Behind AliExpress App Marketing Strategy
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
AliExpress operates in one of the most competitive categories in the world — global eCommerce. Its rivals include Amazon, eBay, Shein, Wish, Temu, Flipkart Cross-Border, Shopee International, and dozens of regional players. Despite this fierce landscape, AliExpress has maintained a powerful global position through pricing dominance, logistics innovation, ecosystem scale, and strategic defensibility.
Here’s how AliExpress stays ahead.
1. Core Competitive Advantages
a) Price Leadership & Global Supply Density
AliExpress wins the price war because:
- It sources directly from manufacturers (not retailers).
- It has millions of sellers competing via dynamic pricing.
- It operates with zero inventory, reducing overhead.
This allows AliExpress to offer items 40–70% cheaper than local retail in many markets.
b) Massive SKU Variety (Long-Tail Advantage)
AliExpress offers millions of niche SKUs that:
- Amazon doesn’t list
- Local retailers don’t import
- Regional marketplaces cannot match
This long-tail depth drives search volume, discovery, and repeat usage.
c) Cainiao-Backed Logistics Superiority
Cainiao gives AliExpress an edge with:
- Faster cross-border lanes
- Dedicated air cargo partnerships
- Local delivery integrations
- Real-time end-to-end tracking
This logistics advantage is extremely difficult for competitors to replicate.
d) Strong Seller Ecosystem & Global Buyer Network
AliExpress’s seller and buyer density create network effects:
- More sellers → more products → more buyers
- More buyers → higher GMV → more sellers
The platform becomes more valuable to each stakeholder over time.
2. Market Defense Tactics
a) Handling New Entrants (Temu, Shein, Wish)
AliExpress defends its position using:
- Extreme discount events (11.11, 12.12)
- Coin systems + gamified bonuses
- Official store partnerships with higher-quality brands
- Localized content commerce (short video reviews)
- Better shipping SLAs via Cainiao
This makes it harder for new players to win price-sensitive regions.
b) Countering Amazon’s Speed Advantage
AliExpress does not try to beat Amazon on speed — instead it focuses on:
- Better prices
- Better variety
- Better niche categories
- Massive festival-based price campaigns
This is why AliExpress has sustained growth even in markets where Amazon dominates.
c) Strategic Feature Rollouts
AliExpress releases features strategically such as:
- Video reviews
- Group buying
- Instant coupons
- Limited-time flash deals
- Interactive live shopping
- Local seller onboarding for faster domestic deliveries
These keep shoppers engaged and lower churn.
d) Partnerships & Country-Specific Defense
AliExpress strengthens its moat by partnering with:
- Local fintech firms
- Customs and regulatory bodies
- Regional logistics networks
- Influencer clusters on TikTok & YouTube
This localized adaptation protects market share.
e) Occasional Acquisitions & Ecosystem Mergers
Though rare, AliExpress and Alibaba strategically acquire or integrate:
- Algorithms
- Logistics technologies
- Payment technologies
Affiliate networks
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
AliExpress is one of the clearest proofs that you don’t need to own inventory, warehouses, or logistics fleets to build a billion-dollar commerce ecosystem. You need the right model, the right technology foundation, and the right growth levers.
This section distills AliExpress’s success blueprint into actionable insights for founders ready to build their own global or regional marketplace.
1. Key Factors Behind AliExpress’s Success
a) Platform-First Approach (Not Inventory-First)
AliExpress scaled because it:
- Never bought products
- Never operated retail warehouses
- Focused entirely on connecting demand and supply
This dramatically reduced the operational risk.
b) Cross-Border Differentiation
AliExpress dominated global markets by offering:
- Unique products
- Lower prices
- Wide SKU variety
- Reliable shipping options
This positioned it as the #1 international shopping destination.
c) High-Frequency Promotions & Gamification
Mega sale events created recurring demand cycles.
Coins, coupons, and gamification → higher retention.
d) Technology as the Growth Engine
AI recommendations, personalized offers, seller scoring, and automated dispute management kept marketplace quality high.
e) Logistics Partnerships Instead of Owning Delivery Fleets
AliExpress scaled by orchestrating logistics, not by owning it.
2. Replicable Principles for Startups
Entrepreneurs can apply AliExpress’s model by:
- Launching a multi-vendor marketplace rather than a traditional retail store.
- Onboarding sellers/importers to offer their catalog.
- Introducing buyer protection flows to build trust.
- Offering fastest possible logistics integrations in each region.
- Building seasonal sales events & localized offers.
- Using AI-based personalization engines to boost conversion.
3. Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Trying to manage inventory or warehousing too early
- Poor seller verification → leads to disputes
- Weak payments integration
- No logistics APIs → slow delivery
- Overdependence on ads instead of organic loops
- No gamification or retention strategy
4. How Entrepreneurs Can Localize the Model
Adaptations for Regional Markets:
- Partner with local delivery providers
- Local payment options (UPI, M-Pesa, Pix, Paytm, etc.)
- Local-language support
- Culturally relevant promotions
- Import-friendly categories
- Compliance with customs regulations
Ready to build your own AliExpress-style global marketplace?
Miracuves empowers founders with scalable, enterprise-grade commerce platforms built for growth, security, and customization.
We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch multi-vendor apps with proven business models and rapid go-live capabilities.
Get your free business model consultation today and launch in 3–9 days with Miracuves.
Conclusion :
AliExpress proves a powerful truth about digital commerce in 2025:
You don’t win by owning products — you win by owning the ecosystem.
Its rise from a simple cross-border marketplace to a global eCommerce giant shows how technology, partnerships, network effects, and a relentless focus on affordability can build a platform that reshapes consumer behavior worldwide.
For founders, the lesson is clear:
- Think platform-first.
- Leverage partnerships instead of assets.
- Build trust at scale.
- Design repeatable growth loops.
- Use data to personalize, predict, and power every interaction.
As global eCommerce becomes more competitive, the winners will be those who master ecosystem building — the same playbook AliExpress executed with precision.
The next generation of billion-dollar platforms won’t just sell products.
They’ll orchestrate markets, empower sellers, and create value chains that connect continents.
And with the right technology partner — like Miracuves — this future is not just possible; it’s launch-ready.
FAQs :
1. What type of business model does AliExpress use?
AliExpress operates on a cross-border multi-vendor marketplace model, where sellers list products and consumers buy directly from them. AliExpress doesn’t hold inventory — it earns from commissions, ads, logistics, and value-added services.
2. How does AliExpress’ business model create value?
AliExpress connects global buyers directly with low-cost manufacturers, offering huge product variety at unbeatable prices. Its buyer-protection system and Cainiao-backed logistics ensure trust and reliable delivery.
3. What are AliExpress’s key success factors?
Its success comes from strong Chinese supply chains, ultra-competitive pricing, fast logistics, and massive global demand. AI-powered personalization and seasonal mega-sales further accelerate growth.
4. How scalable is AliExpress’s business model?
The asset-light marketplace model scales effortlessly since AliExpress doesn’t hold inventory. Growth simply requires onboarding more sellers and buyers — enabling rapid global expansion.
5. What are the biggest challenges in AliExpress’s model?
Quality control, counterfeit risks, and long shipping times in some regions pose challenges. Competition from Temu, Shein, and Amazon plus regulatory changes also impact cross-border operations.
6. How can entrepreneurs adapt the AliExpress model to their region?
Localize language, payments, and logistics, while adding regional sellers for faster delivery. Build buyer protection, run seasonal promos, and focus on niche categories competitors miss.
7. What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a similar app?
With Miracuves, a marketplace like AliExpress can launch in 3–9 days, with full branding, logistics, and seller onboarding completed in 60–90 days. Core needs include marketplace engine, payment APIs, and logistics partners.
8. What are alternatives to the AliExpress model?
Alternatives include Amazon FBA (inventory-based), TikTok Shop (social commerce), D2C marketplaces, niche vertical platforms, and peer-to-peer resale models like eBay.
9. How has the AliExpress business model evolved over time?
AliExpress evolved from a basic export marketplace to a fast-shipping, AI-powered global platform. 2024–2025 brought brand stores, short-video commerce, and improved logistics for faster delivery.
Related Article :








