Shein didn’t disrupt fashion by copying Zara or H&M. It re-engineered the entire fast-fashion value chain for the internet era. By combining real-time consumer data, ultra-short production cycles, and a marketplace-style supplier ecosystem, Shein created a model that moves faster than trends themselves.
In 2025, the Business Model of Shein stands at the intersection of ecommerce, data science, supply chain automation, and influencer-driven demand generation. Its approach is not just about selling clothes—it’s about turning consumer behavior into production decisions at scale.
For entrepreneurs exploring D2C brands, marketplace hybrids, or AI-driven commerce platforms, Shein offers one of the most important modern case studies. It proves that operational speed, not brand legacy, is the new competitive moat.
At Miracuves, we study models like Shein because they demonstrate how technology-first platforms can dominate traditional industries by redesigning operations, monetization, and growth loops from the ground up.
How the Shein Business Model Works
Shein operates on a digitally-native, data-driven fast fashion platform model—a hybrid between D2C ecommerce, supply-chain-as-a-service, and marketplace orchestration. Unlike traditional fashion brands that forecast trends months in advance, Shein lets real-time consumer demand decide what gets produced, scaled, or killed.
At its core, Shein is not a clothing brand first. It is a fashion intelligence and fulfillment engine.
Type of Business Model
Shein uses a Hybrid Direct-to-Consumer + Marketplace + Data Platform model.
Key layers include:
- D2C Ecommerce Core – Shein sells directly to consumers through its app and website.
- On-Demand Manufacturing Network – Thousands of third-party suppliers produce in micro-batches.
- Marketplace Expansion (Shein Marketplace) – External brands and designers list products using Shein’s logistics and traffic.
- Data & AI Layer – Consumer behavior directly drives design, pricing, and inventory decisions.
This hybrid structure allows Shein to scale selection without scaling risk
Value Proposition by User Segment
For Consumers
- Ultra-low prices compared to traditional fashion brands
- Constantly refreshed styles aligned with micro-trends
- App-first discovery experience with gamified shopping
- Global access to trend-led fashion without retail markups
For Suppliers & Manufacturers
- Guaranteed demand signals before large-scale production
- Reduced inventory risk through small-batch testing
- Access to global customers without marketing spend
- Faster payment cycles than traditional fashion contracts
For Creators & Influencers
- Commission-based affiliate programs
- Rapid trend amplification through social platforms
- Creator-led product validation and promotion loops
Key Stakeholders & Their Roles
- Consumers generate demand data through browsing, wishlists, and purchases
- Design teams & AI systems convert trend data into SKUs
- Manufacturing partners produce small initial batches
- Logistics partners handle cross-border fulfillment
- Influencers & affiliates drive discovery and conversion
Each stakeholder feeds the data flywheel that keeps Shein ahead of trends
Business Model Evolution
- Early Phase: Pure cross-border ecommerce reseller
- Growth Phase: Shift to on-demand manufacturing and private-label dominance
- Scaling Phase: Marketplace onboarding + supplier tech enablement
- 2025 State: Platform-led fashion ecosystem powered by AI, data, and logistics
Shein evolved from a seller into a fashion operating system.
Why Shein’s Model Works in 2025
- Consumers expect fast, affordable, trend-aligned fashion
- Social platforms accelerate trend lifecycles
- Data-driven production reduces waste and risk
- Cross-border logistics tech enables global reach
- App-based discovery replaces traditional brand loyalty
Shein thrives because it matches internet speed with manufacturing speed—a combination most incumbents still struggle to achieve.
Read more : What is SHEIN and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Shein’s dominance is not driven by mass appeal alone—it is powered by precision segmentation and behavioral targeting at global scale. Instead of designing for a single “fashion consumer,” Shein operates as a multi-segment demand engine, adapting styles, pricing, and messaging by micro-audience.
Primary Customer Segments
1. Gen Z & Young Millennials (Ages 16–30)
- Mobile-first, social-media-native shoppers
- High trend sensitivity, low brand loyalty
- Value affordability, variety, and speed
- Heavy users of TikTok, Instagram, Snapchat, YouTube
Why they stay
- Constant new arrivals (thousands of SKUs weekly)
- Gamified app experience (flash sales, points, drops)
- Influencer validation and social proof
2. Budget-Conscious Global Shoppers
- Emerging markets + price-sensitive consumers in developed regions
- Seek fashion variety without premium pricing
- Comfortable with cross-border delivery timelines
Why they stay
- Extreme price-to-style ratio
- Wide size inclusivity and niche categories
- Promotions, bundles, and seasonal discounts
Secondary Customer Segments
3. Niche Fashion Communities
- Plus-size, petite, maternity, modest wear, cosplay, festival wear
- Micro-communities underserved by traditional brands
4. Trend Experimenters
- Consumers who buy frequently but in small ticket sizes
- Use fashion as content creation or identity expression
Shein captures these segments by testing styles at micro-scale and doubling down only on what converts
Customer Journey: From Discovery to Retention
Discovery
- Influencer content on TikTok & Instagram
- Affiliate links and creator haul videos
- App install incentives and referral bonuses
Conversion
- Ultra-low entry pricing
- Flash sales and scarcity cues
- Personalized recommendations driven by behavior data
Retention
- Daily new arrivals
- Loyalty points and wallet credits
- Push notifications tied to browsing history
- Gamified in-app engagement loops
Shein optimizes lifetime value through frequency, not high order values.
Acquisition Channels by Segment
- Gen Z → Influencers, TikTok trends, social commerce
- Budget shoppers → Paid ads, price-led SEO, referral loops
- Niche audiences → Community-led launches, category-specific feeds
Each channel feeds real-time data back into Shein’s production engine.
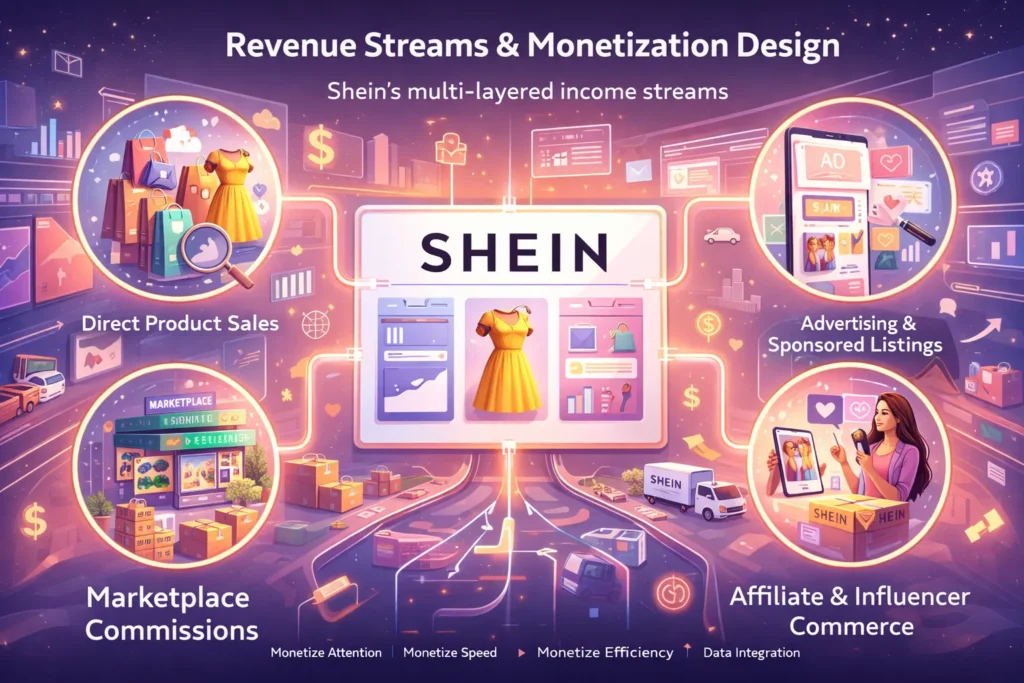
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Once Shein mastered demand sensing and ultra-fast production, its business model unlocked a layered monetization architecture. Rather than relying on a single revenue lever, Shein engineered multiple income streams that reinforce each other—maximizing volume, margin control, and data advantage.
Shein monetizes attention, speed, and supply-chain efficiency.
Primary Revenue Stream 1: Direct Product Sales (Core Engine)
Mechanism
Shein designs or curates fashion items and sells them directly to consumers via its app and website.
Pricing Model
- Cost-plus pricing with aggressive affordability targets
- Dynamic pricing based on demand, trend velocity, and inventory performance
- Bundling, flash sales, and cart-level discounts
Revenue Contribution
- Largest share of total revenue
- High volume, low average order value model
Growth Trajectory
- Expansion into new categories (menswear, beauty, home, kids)
- Faster SKU refresh cycles increase purchase frequency
- Improved margin control via supplier competition and data-driven production
Shein wins not by high margins per item—but by massive transaction velocity.
Secondary Revenue Stream 2: Marketplace Commissions (Scale Layer)
Mechanism
Third-party brands and sellers list products on the Shein Marketplace.
Pricing Model
- Commission per transaction
- Value-added fees for logistics, promotion, and visibility
Revenue Contribution
- Rapidly growing share of total revenue
- Asset-light expansion of assortment
Growth Trajectory
- Onboarding global brands and independent designers
- Localized seller ecosystems by region
This turns Shein from a seller into a fashion commerce platform
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: Advertising & Sponsored Listings
Mechanism
- Brands pay for visibility inside Shein’s high-intent shopping environment
- Sponsored product placements and homepage exposure
Why It Works
- Purchase-ready users, not casual browsers
- Rich behavioral data enables precise targeting
Growth Outlook
- Retail media-style monetization similar to Amazon
- High-margin revenue stream
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Affiliate & Influencer Commerce
Mechanism
- Influencers earn commissions on referred sales
- Performance-based payouts tied to conversions
Impact
- Reduces customer acquisition cost
- Converts creators into distributed sales teams
Overall Monetization Strategy
Shein’s monetization is vertically integrated and data-synchronized:
- Sales data informs production
- Production speed supports pricing flexibility
- Pricing drives volume
- Volume generates data
- Data strengthens every revenue stream
Pricing psychology is built around:
- Low friction entry prices
- Scarcity and urgency
- Reward loops through discounts and credits
Shein monetizes frequency and insight, not just products.
Read more : Shein Revenue Model: How Shein Makes Money in 2025
Operational Model & Key Activities
Shein’s real competitive advantage lives behind the interface. What looks like a simple shopping app is supported by a highly optimized, software-driven operational machine that synchronizes data, suppliers, logistics, and marketing in near real time.
Shein operates less like a fashion company—and more like a distributed manufacturing and commerce platform.
Core Operational Activities
Platform & Technology Management
- AI-driven trend detection from search, clicks, saves, and social data
- Automated SKU testing and performance tracking
- Recommendation engines and personalization systems
Design & Product Development
- Rapid digital design creation based on trend signals
- Micro-batch production (as low as 100–200 units per SKU)
- Continuous iteration based on live performance metrics
Supply Chain Orchestration
- Thousands of manufacturing partners, primarily in Asia
- Real-time production instructions tied to demand signals
- Fast reorders only for proven SKUs
Quality Control & Compliance
- Supplier performance scoring
- Quality audits and material checks
- Increasing investments in compliance and traceability (2024–2025 focus)
Customer Support & Experience
- App-based support workflows
- Automated returns and refunds
- Multilingual global customer service teams
Resource Allocation Strategy
Technology & Data (High Priority)
- Heavy investment in AI, forecasting, and automation
- Internal tools for supplier coordination and demand planning
Marketing & Growth
- Influencer and affiliate spend over traditional brand ads
- Performance marketing tied directly to conversion data
Human Capital
- Engineers, data scientists, supply chain specialists
- Regional operations teams for localization and compliance
Infrastructure & Logistics
- Global fulfillment centers
- Cross-border shipping optimization
- Regional warehousing to reduce delivery times
Shein allocates capital where speed compounds.
Regional Expansion Operations
- Centralized tech platform
- Localized pricing, sizing, and assortment
- Regional compliance and logistics adaptations
This allows Shein to scale globally without rebuilding its core systems.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Shein does not scale alone. Its dominance is reinforced by a carefully engineered partner ecosystem that turns suppliers, creators, logistics providers, and technology vendors into growth multipliers.
Rather than owning everything, Shein coordinates value creation across its network—a classic platform strategy applied to fashion.
Collaboration Philosophy
Shein’s partnership approach is built on three principles:
- Data transparency instead of long-term inventory commitments
- Performance-based rewards over fixed contracts
- Speed and flexibility as the primary partnership currency
Partners succeed when they move as fast as Shein’s data signals.
Key Partnership Types
Technology & API Partners
- Cloud infrastructure providers
- AI and analytics tools
- Payment gateway integrations
These enable scale, uptime, and real-time intelligence.
Manufacturing & Supplier Alliances
- Thousands of independent manufacturers
- Digital production dashboards and order forecasting tools
- Training programs to improve speed, quality, and compliance
This transforms factories into on-demand production nodes
Logistics & Fulfillment Partners
- Cross-border shipping providers
- Regional warehousing partners
- Last-mile delivery services
Logistics partnerships allow Shein to operate globally without owning fleets.
Creator & Influencer Ecosystem
- Affiliate networks and commission-based creators
- Social commerce integrations
- Performance-tracked influencer campaigns
Creators act as trend sensors and distribution channels.
Regulatory & Market Expansion Alliances
- Local compliance consultants
- Regional trade and customs partners
- Sustainability and traceability partners
These alliances reduce friction during geographic expansion.
Ecosystem Strategy Insights
- Network effects increase as more suppliers and creators join
- Supplier competition improves cost efficiency and speed
- Platform dependency strengthens Shein’s bargaining power
- Ecosystem monetization expands beyond product sales
By embedding itself at the center of its ecosystem, Shein builds defensive moats that are operational, not just brand-based.
Read more : Best Shein Clone Scripts 2025 – Build Your Global Fashion App Fast
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Shein’s growth is not accidental—it is the result of engineered feedback loops that turn data, demand, and distribution into compounding scale. Instead of relying on seasonal campaigns or physical expansion, Shein grows by shortening the distance between trend discovery and global delivery.
Primary Growth Engines
Organic Virality & Social Commerce
- Influencer hauls and try-on videos drive continuous discovery
- TikTok and Instagram act as external demand generators
- User-generated content validates trends faster than surveys
This creates a self-reinforcing virality loop.
Paid Performance Marketing
- Highly optimized paid ads tied to SKU-level performance
- Rapid budget reallocation toward converting products
- App-install campaigns with aggressive incentives
Marketing spend is treated as a scalable variable, not a fixed cost.
Product & Category Expansion
- Expansion beyond women’s fast fashion into:
- Menswear
- Kids and maternity
- Beauty and lifestyle products
- Each category uses the same demand-testing framework
Shein launches categories like startups—fast, cheap, and data-backed.
Marketplace & Seller Scaling
- Onboarding external brands increases assortment without inventory risk
- Local sellers reduce shipping times and compliance friction
Geographic Expansion Model
- Centralized tech + localized execution
- Region-specific pricing, sizing, and promotions
- Gradual warehousing localization to reduce delivery times
Shein scales countries the way SaaS platforms scale markets.
Scaling Challenges & How Shein Addressed Them
Operational Complexity
- Solved through automation and supplier dashboards
Logistics Delays
- Addressed via regional fulfillment centers
Regulatory & Sustainability Pressure
- Increased transparency programs
- Supplier audits and reporting systems
Brand Trust & Quality Perception
- Improved quality checks
- More consistent product standards
Shein scales by fixing bottlenecks faster than competitors can react
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Shein operates in one of the most competitive industries in the world, yet it consistently outpaces both legacy fashion brands and digital-first challengers. Its defense strategy is not built on exclusivity or brand heritage—but on system-level advantages that are extremely hard to replicate.
Shein competes at the level of infrastructure, data, and execution speed.
Core Competitive Advantages
Network Effects & Switching Barriers
- More consumers → more demand data
- More data → better trend prediction
- Better prediction → higher supplier success
- Higher supplier success → lower costs and faster delivery
This feedback loop strengthens Shein’s position with every transaction.
Data & Algorithmic Advantage
- SKU-level performance tracking in real time
- Predictive demand forecasting instead of seasonal planning
- Personalized feeds increase conversion and frequency
Traditional brands operate on intuition. Shein operates on live market signals.
Cost Leadership at Scale
- On-demand production minimizes inventory risk
- Supplier competition keeps production costs low
- No physical stores reduce overhead
Shein can underprice competitors without sacrificing velocity.
Brand Equity Through Relevance
- Shein’s brand is defined by what’s trending now, not heritage
- Always-on social presence
- High engagement with Gen Z culture
Relevance becomes its brand moat.
Market Defense Tactics
Handling New Entrants
- Rapid trend imitation at global scale
- Aggressive pricing to compress competitor margins
Pricing Wars
- Micro-discounts instead of blanket price cuts
- Personalized offers protect margins
Feature & Experience Defense
- Faster checkout, localized payments
- Gamified app features increase stickiness
Strategic Acquisitions & Investments
- Selective investments in logistics and supply-chain tech
- Ecosystem partnerships instead of large M&A risk
Shein doesn’t block competition—it outpaces it.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Shein’s success is not about fashion—it is about system design. For entrepreneurs, the biggest takeaway is that platforms win when operations, data, and monetization are architected together from day one.
Think like a builder, not a brand.
Key Factors Behind Shein’s Success
- Data-driven decision-making replaces gut instinct
- Micro-batch testing reduces risk before scaling
- Speed beats perfection in trend-based markets
- Platform leverage outperforms linear growth
- Global reach is achieved without physical expansion
Shein proves that execution velocity compounds faster than marketing spend.
Replicable Principles for Startups
- Build feedback loops between users, data, and supply
- Test before you scale—across products, regions, and pricing
- Design marketplaces where partners win when the platform wins
- Use technology to replace fixed costs with variable ones
These principles apply far beyond fashion—to food delivery, logistics, fintech, and SaaS marketplaces.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Overproducing before validating demand
- Building supply chains without data visibility
- Chasing brand image before operational strength
- Scaling geography before unit economics stabilize
Shein avoided these by letting data lead every decision.
Adapting the Model for Local or Niche Markets
Entrepreneurs can localize Shein’s approach by:
- Focusing on a single category or niche community
- Using local suppliers for faster fulfillment
- Leveraging creators instead of heavy ad spend
- Building lightweight MVPs before full platforms
Shein’s model scales down as effectively as it scales up.
Ready to implement Shein’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps and marketplaces.
Get your free business model consultation today.
Conlcusion
business model of Shein proves a powerful truth about modern platform economies: the companies that win are not the ones with the strongest brand stories, but the ones with the strongest systems.
By turning consumer behavior into real-time production decisions, Shein collapsed the traditional fashion cycle from months into days. It replaced forecasting with feedback, inventory risk with data certainty, and brand intuition with algorithmic execution. That shift—not low prices alone—is what allowed Shein to scale into a global powerhouse.
As we move deeper into 2025 and beyond, platform businesses across industries will face the same question Shein answered early: Can your infrastructure move as fast as your customers?
For founders, the lesson is clear. Sustainable growth is no longer about being first—it’s about being fast, adaptive, and relentlessly data-driven.
FAQs
What type of business model does Shein use?
Shein follows a hybrid business model combining direct-to-consumer ecommerce, on-demand manufacturing, and a growing marketplace. Data and AI drive every production and pricing decision.
How does Shein’s business model create value?
Shein turns real-time consumer behavior into fast production, reducing inventory risk and costs. Customers get trend-led fashion at low prices, while suppliers gain predictable demand.
What are Shein’s key success factors?
Ultra-fast supply chain execution, data-driven decision-making, low-cost operations, and strong social commerce distribution are Shein’s biggest success drivers.
How scalable is Shein’s business model?
Shein’s model is highly scalable because it relies on partners, data, and technology—not physical stores. It can expand categories and countries without heavy fixed costs.
What are the biggest challenges Shein faces?
Shein faces regulatory pressure, sustainability concerns, and quality consistency challenges due to its massive scale. Managing compliance across global markets is also complex.
How can entrepreneurs adapt Shein’s model to their region?
Entrepreneurs can start with a niche category, use local suppliers, and apply data-driven testing before scaling. Speed and feedback loops matter more than large inventories.
What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a Shein-style platform?
A lean MVP can launch in 30 – 90 day months with ecommerce, supplier management, and analytics tools. Full-scale platforms typically evolve over 12–18 months.
What are alternatives to Shein’s business model?
Alternatives include traditional fast fashion, niche D2C brands, curated marketplaces, and subscription-based fashion platforms, each with different cost and speed trade-offs.
How has Shein’s business model evolved over time?
Shein evolved from a simple ecommerce retailer into a data-driven fashion platform, integrating AI, on-demand manufacturing, logistics, and marketplace monetization.
Related Article :








