Tokopedia is one of Indonesia’s biggest ecommerce success stories, and the business model of Tokopedia is built around a powerful marketplace ecosystem that connects millions of buyers and sellers. What started as a simple online platform to support small businesses has evolved into a digital commerce engine where products, payments, and logistics work together to create a smooth shopping experience. In 2026, Tokopedia continues to play a major role in shaping how Indonesians buy, sell, and grow online.
What makes Tokopedia stand out is its ability to scale trust in a fast-growing market. From verified sellers to secure transactions and strong delivery partnerships, the platform focuses on reducing friction for both customers and merchants. This is why the Tokopedia revenue model goes beyond product sales and captures value through multiple streams like commissions, ads, and value-added seller services.
For entrepreneurs, studying how Tokopedia works is a smart way to understand marketplace growth, user retention, and long-term monetization. Its strategy proves that when you build a reliable ecosystem, growth becomes repeatable and scalable.
How the Tokopedia Business Model Works
Tokopedia runs on a multi-sided marketplace model, meaning it doesn’t just sell products like a traditional retailer. Instead, it connects buyers with millions of sellers, while Tokopedia earns by enabling transactions, visibility, and value-added services. In 2026, this model works even better because customers want convenience, fast delivery, secure payments, and trusted sellers—all in one place.
Type of Business Model
Tokopedia follows a Hybrid Marketplace Model, combining:
- C2C marketplace (individual sellers and resellers)
- B2C marketplace (brands and official stores)
- Service-led monetization (ads, seller tools, logistics, fintech integrations)
Value Proposition (Who Gets What?)
Tokopedia creates value for multiple user groups:
1) For Buyers (Customers)
- Wide product variety (from essentials to electronics)
- Competitive pricing through seller competition
- Secure payments + buyer protection
- Fast delivery options via logistics partners
2) For Sellers (Merchants/SMEs/Brands)
- Instant access to a massive customer base
- Tools for store setup, promotions, and analytics
- Logistics support to deliver nationwide
- Advertising to boost product visibility
3) For Partners (Payments, Logistics, Brands)
- High transaction volume and user activity
- Integration opportunities via APIs and campaigns
- Shared growth through platform expansion
Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
Tokopedia’s ecosystem stays balanced because each stakeholder has a clear role:
- Buyers → demand, repeat orders, reviews, retention
- Sellers → supply, inventory, pricing competition
- Tokopedia platform → trust layer, traffic engine, monetization system
- Logistics partners → fulfillment speed and reliability
- Payment partners → smooth checkout + transaction security
- Brands/advertisers → marketing spend and conversion growth
How the Model Evolved Over Time
Tokopedia evolved in phases:
- Phase 1: Seller onboarding & trust building
Focus on getting SMEs online and improving platform reliability. - Phase 2: Marketplace expansion & category growth
Added deeper categories, promotions, and nationwide reach. - Phase 3 : Monetization + ecosystem strengthening
Stronger focus on seller services, ads, and efficiency-driven growth.
Why It Works in 2026
Tokopedia’s model wins today because:
- Consumers expect marketplace convenience + speed
- Sellers want digital reach without building websites
- Brands need performance marketing + conversion-ready traffic
- Marketplace competition drives better pricing and selection
Data + personalization improve retention and repeat purchases
Read more : What is Tokopedia and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Tokopedia scales because it doesn’t target “everyone” in the same way. It segments users based on buying behavior, trust needs, price sensitivity, and shopping frequency. In 2026, this segmentation becomes even more important because ecommerce customers expect faster delivery, better personalization, and reliable seller experiences.
Primary Customer Segments
1) Mass-Market Online Shoppers (Core Users)
- Age group: 18–45
- Behavior: frequent browsing, deal-driven buying
- Needs: affordability, convenience, trusted delivery
- Typical purchases: daily essentials, fashion, electronics, home products
2) Value-Seeking Customers (Discount & Promo Buyers)
- Highly price-sensitive
- Wait for flash sales, bundles, cashback offers
- High conversion during mega-campaigns
Secondary Customer Segments
3) SMEs & Small Sellers (Ecosystem Builders)
- Home businesses, resellers, micro-entrepreneurs
- Need: easy store setup, traffic, logistics help
- Retention driver: seller tools + sales performance
4) Brands & Official Stores (Premium Sellers)
- Want control, verified trust, and brand visibility
- Use ads + campaigns to increase conversion
- Strong contribution to long-term platform credibility
Customer Journey (Discovery → Conversion → Retention)
Tokopedia’s customer journey is designed like a conversion funnel:
1) Discovery
- Search results + category browsing
- Campaign banners and trending products
- Influencer-led demand spikes (external channels)
2) Conversion
- Ratings + reviews build trust
- Fast checkout + payment options reduce drop-offs
- Promotions and vouchers trigger purchase decisions
3) Retention
- Personalized recommendations
- Repeat purchase incentives
- Strong customer support + refund protection improves loyalty
Acquisition Channels Tokopedia Uses
Tokopedia acquires and retains users through:
- SEO + app store discovery
- Paid campaigns during mega sales
- Social media + influencer-led traffic
- Referral programs and voucher loops
- Seller-led marketing (sellers bring customers too)
Market Positioning & Competitive Edge
Tokopedia’s positioning is built on trust + variety + seller scale.
Its key advantage is that it acts as a “digital mall” for Indonesia—where customers can find almost anything while sellers can grow without heavy upfront investment.
Tokopedia differentiates by:
- Strong seller ecosystem and SME onboarding
- Consistent promotional strategy to drive repeat usage
- Platform trust systems (reviews, verification, buyer protection)
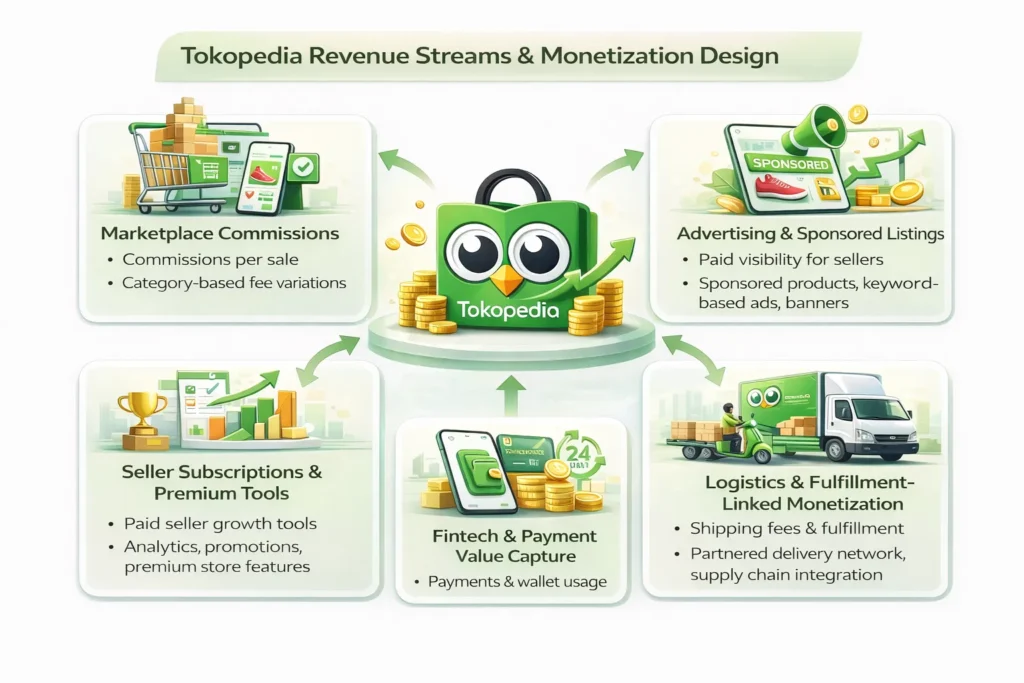
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Once you understand who Tokopedia serves, the next question becomes simple: how does Tokopedia actually make money?
The Tokopedia revenue model is designed like a layered marketplace engine. Instead of relying only on product margins, Tokopedia monetizes transactions, seller growth tools, and visibility—which makes revenue more stable and scalable over time.
Primary Revenue Stream 1: Marketplace Commissions (Core Engine)
Mechanism
Tokopedia charges sellers a fee/commission on successful orders, especially for sellers using premium services or specific categories.
Pricing Model
- Commission-based fee per transaction
- Category-based fee variations
- Higher fees for value-added seller programs
Revenue Contribution
- One of the most consistent income sources
- Scales automatically with platform order volume
Growth Trajectory
- Growth driven by increasing GMV (gross merchandise value)
- More premium seller adoption boosts take-rate
- Stronger monetization from high-performing categories
Secondary Revenue Stream 2: Advertising & Sponsored Listings
Mechanism
Sellers pay Tokopedia to increase visibility through:
- sponsored product placements
- keyword-based ads
- banner placements during campaigns
Why it matters
- High-margin revenue
- Works like “performance marketing inside the marketplace”
- Sellers spend more as competition increases
Growth Trajectory
- Rising seller competition increases ad demand
- Better targeting improves conversion, increasing ad ROI
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: Seller Subscriptions & Premium Tools
Mechanism
Tokopedia offers seller-focused services like:
- premium store features
- analytics tools
- promotional boosts and campaign participation benefits
Pricing Model
- monthly/feature-based packages
- tiered seller solutions based on scale
Revenue Contribution
- Recurring income (more stable than one-time fees)
- Strong retention because sellers become dependent on tools
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Logistics & Fulfillment-Linked Monetization
Mechanism
Tokopedia partners with logistics providers and earns through:
- shipping service facilitation
- fulfillment support programs
- delivery upgrades and speed options
Why it works
- Faster delivery improves customer satisfaction
- More orders = more logistics-linked revenue opportunities
Secondary Revenue Stream 5: Fintech & Payment Ecosystem Value Capture
Mechanism
Tokopedia benefits from integrated payments and fintech partnerships via:
- transaction enablement
- wallet usage and incentives
- installment/payment convenience adoption
Revenue impact
- Higher conversion rates due to easy payments
- Increased repeat usage due to stored payment behavior
Overall Monetization Strategy (How It All Connects)
Tokopedia’s monetization strategy is powerful because every revenue stream supports the next:
- More sellers → more products → more customers
- More customers → more transactions → more commissions
- More competition → more ad spend → higher platform revenue
- Better logistics + payments → higher conversion → more repeat purchases
The psychology behind the model is simple: Tokopedia reduces friction, increases trust, and then monetizes the growth layer—not the entry layer. This is why the Tokopedia business model stays scalable even in competitive ecommerce markets.
Read more : Tokopedia Clone Revenue Model: How Tokopedia Makes Money in 2026
Operational Model & Key Activities
Tokopedia’s success isn’t only about what users see on the app—it’s about the operating system running behind the scenes, Tokopedia functions like a high-scale digital commerce machine where technology, seller quality, logistics coordination, and customer trust systems work together daily.
Core Operations (How Tokopedia Runs Daily)
1) Platform Management & Marketplace Governance
Tokopedia continuously manages the balance between buyers and sellers by:
- maintaining seller policies and listing rules
- monitoring pricing abuse, fake products, and misleading listings
- improving search and discovery relevance
2) Technology Infrastructure
Tokopedia invests heavily in:
- scalable cloud systems to handle traffic spikes
- product search and recommendation algorithms
- fraud detection and secure checkout systems
- app performance optimization for low-to-mid bandwidth regions
3) Seller Enablement & Quality Control
To keep the marketplace reliable, Tokopedia focuses on:
- seller onboarding and verification processes
- seller education and growth support
- rating/review systems to maintain quality signals
- dispute resolution frameworks
4) Customer Support & Trust Operations
Trust is a major pillar of the Tokopedia business model, so daily operations include:
- refund and return management
- buyer protection programs
- support tickets and escalation systems
- handling fraud complaints and transaction disputes
5) Marketing & Campaign Execution
Tokopedia runs high-frequency growth cycles through:
- mega sale campaigns and seasonal promotions
- seller-led discount events
- performance marketing and retention loops
- personalized vouchers and reactivation strategies
Key Activities (What Tokopedia Must Do Well to Win)
Tokopedia’s key activities can be summarized as:
- marketplace liquidity management (supply + demand balance)
- seller performance improvement
- conversion rate optimization across product pages
- logistics coordination and delivery experience improvement
- user retention through personalization and incentives
Resource Allocation Strategy
Tokopedia’s resources are typically distributed across growth and stability priorities:
- Tech & Infrastructure: improving speed, reliability, security, AI-driven personalization
- Marketplace Operations: seller support, quality checks, policy enforcement
- Marketing & Growth: campaign budgets, acquisition, retention offers
- Customer Experience: support systems, dispute resolution, buyer trust mechanisms
- Expansion Focus: deeper penetration into regional cities and new shopping categories
Tokopedia’s operational model works because it treats ecommerce like an ecosystem, not a store. The company doesn’t just “list products”—it actively manages trust, delivery experience, and seller performance at scale.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Tokopedia doesn’t scale alone. A marketplace becomes powerful only when it builds an ecosystem where partners grow alongside the platform. In 2026, Tokopedia’s partnership strategy is focused on one goal: reduce friction for users and increase performance for sellers.
That’s why Tokopedia collaborates deeply across logistics, payments, technology, and brand distribution.
Tokopedia’s Collaboration Philosophy
Tokopedia partners with companies that strengthen its marketplace engine in three ways:
- improve customer experience (faster delivery, smoother checkout)
- help sellers sell more (better reach, tools, conversion support)
- build trust and reliability (secure transactions, verified services)
Key Partnership Types in Tokopedia’s Ecosystem
1) Technology & API Partners
Tokopedia works with tech enablers to improve platform performance and seller efficiency, such as:
- cloud infrastructure providers
- data and analytics tools
- automation systems for inventory and order management
- AI-driven personalization and fraud detection support
Impact: Better uptime, faster search, stronger recommendations, lower risk.
2) Payment & Fintech Alliances
Payments are critical for conversion. Tokopedia strengthens checkout success through:
- digital wallet integrations
- installment and pay-later options (through partners)
- secure payment gateways
- banking collaborations for broader access
Impact: Higher conversion rates + lower cart abandonment.
3) Logistics & Fulfillment Partnerships
Delivery experience defines marketplace trust. Tokopedia partners with logistics players to provide:
- nationwide shipping reach
- faster delivery options for key cities
- tracking and delivery transparency
- fulfillment-linked seller programs
Impact: Faster shipping increases repeat orders and customer satisfaction.
4) Marketing & Distribution Partners
Tokopedia boosts visibility and customer acquisition through:
- influencer ecosystems and affiliate campaigns
- co-branded mega sale campaigns
- brand collaborations for product launches
- digital advertising networks for retargeting
Impact: Higher traffic inflow and better campaign performance.
5) Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
Scaling across regions requires compliance and local execution. Tokopedia builds relationships with:
- local business communities
- SME development programs
- policy and compliance support networks
- regional partners to strengthen trust and adoption
Ecosystem Strategy: Why Partnerships Create a Competitive Moat
Tokopedia’s ecosystem becomes a moat because partnerships create compounding advantages:
- more logistics partners → faster delivery → more customer trust
- more payment options → smoother checkout → higher conversion
- more seller tools → better seller success → higher product availability
- more brands → stronger credibility → higher customer retention
This creates a flywheel where every partner strengthens the marketplace, and Tokopedia captures value through commissions, ads, and premium seller services.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Tokopedia’s growth didn’t happen only because “more people started shopping online.” It scaled because the company built repeatable growth engines—systems that keep pulling users back, keep sellers earning, and keep the marketplace expanding into new categories and regions. In 2026, Tokopedia’s growth strategy is focused on improving efficiency, increasing seller success, and strengthening user retention.
Growth Engines (How Tokopedia Grows)
1) Organic Growth Through Marketplace Liquidity
Tokopedia grows naturally when:
- more sellers list products → more variety
- more variety attracts buyers → more demand
- more demand increases seller revenue → more sellers join
This is classic marketplace flywheel growth.
2) Referral Loops, Promotions & Repeat Purchase Triggers
Tokopedia uses growth loops like:
- referral incentives (user-to-user invites)
- vouchers, cashback, and campaign rewards
- personalized deals based on user behavior
- cart reminders and reactivation notifications
These tactics increase:
- conversion rates
- purchase frequency
- customer lifetime value (LTV)
3) Paid Marketing & Campaign-Based Acquisition
Tokopedia runs large acquisition pushes through:
- mega sale events (high-intent buying windows)
- performance marketing campaigns
- retargeting ads for cart abandoners
- category-specific campaigns (electronics, fashion, home essentials)
This works because campaigns don’t just drive traffic—they drive high purchase intent traffic.
4) New Product Lines & Category Expansion
Tokopedia scales by expanding into categories where demand is high and repeat buying is common, such as:
- groceries and essentials
- home improvement and lifestyle products
- electronics and accessories
- beauty and personal care
Category expansion increases:
- repeat usage
- average order value (AOV)
- daily relevance of the platform
5) Geographic Expansion Strategy
Tokopedia’s scaling model includes:
- expanding deeper into Tier 2 and Tier 3 cities
- improving logistics access for remote regions
- enabling small sellers outside metro areas
- localizing campaigns based on regional demand
This helps Tokopedia win where ecommerce adoption is still growing.
Scaling Challenges & How Tokopedia Solves Them
Challenge 1: Marketplace Quality Control
As sellers grow, the risk of:
- fake listings
- low-quality products
- delayed shipping
also grows.
Solution
- stronger seller verification
- rating/review enforcement
- policy-based penalties and dispute resolution
Challenge 2: Logistics Complexity
Scaling nationwide delivery creates delays and customer dissatisfaction.
Solution
- multiple logistics partnerships
- fulfillment support programs
- improved tracking and delivery transparency
Challenge 3: Competition & Price Wars
Marketplaces often enter discount battles that reduce margins.
Solution
Tokopedia protects growth by focusing on:
- trust and experience
- seller tools and ecosystem strength
- ad monetization (not only commissions)
Challenge 4: Retention in a Multi-App World
Users can switch platforms easily if experience is weak.
Solution
Tokopedia strengthens retention with:
- personalization
- campaign rewards
- improved checkout + payment convenience
reliable customer support systems
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
If you’re a founder planning to build a marketplace, ecommerce platform, or multi-vendor app, Tokopedia is a strong example of what real scale looks like. The biggest lesson is simple: Tokopedia didn’t win because it had “more products.” It won because it built a system where buyers trust the platform and sellers can grow consistently.
Key Factors Behind Tokopedia’s Success
Tokopedia scaled because it mastered the marketplace fundamentals:
- Trust at scale through reviews, verified sellers, and buyer protection
- Seller-first growth by enabling SMEs with tools, traffic, and logistics support
- Strong ecosystem partnerships (payments + logistics) that reduced friction
- Multiple monetization layers (commissions + ads + seller services)
- Retention-driven campaigns that increased repeat buying behavior
Replicable Principles for Startups
Here’s what entrepreneurs can copy from the Tokopedia business model:
1) Build liquidity before monetization
- focus on supply (sellers) + demand (buyers) first
- monetize only after repeat usage starts
2) Make trust your first product
- verified sellers, secure payments, strong dispute resolution
- trust improves conversion faster than discounts
3) Monetize growth tools, not just transactions
- sellers will pay for visibility and performance
- ads and premium tools scale revenue without hurting user experience
4) Use partnerships to scale faster
- logistics and payments are hard to build alone
- partner-first scaling reduces cost and time-to-market
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many marketplace founders fail because they:
- launch without solving trust and quality control
- depend only on discounts for growth
- ignore seller retention and support systems
- monetize too early and push sellers away
- underestimate logistics complexity and customer experience issues
How to Adapt Tokopedia’s Model for Local or Niche Markets
Tokopedia’s framework can be adapted to:
- local city-based marketplaces
- niche marketplaces (fashion, electronics, home services, B2B supplies)
- hyperlocal commerce platforms
- category-specific multi-vendor ecommerce apps
The key is to narrow your focus first:
- start with one region + one strong category
- create trust + repeat demand
- then expand into new segments
Implementation & Investment Priorities
A practical rollout plan inspired by Tokopedia looks like this:
Phase 1 : MVP + Trust Setup
- buyer app + seller panel
- onboarding + listing system
- payments + basic order flow
- ratings, reviews, dispute process
Phase 2 : Growth + Seller Tools
- promotions, coupons, referrals
- seller analytics dashboard
- ad/sponsored listing MVP
- customer support workflows
Phase 3 : Scale + Monetization Expansion
- advanced search + personalization
- logistics integrations
- premium seller subscriptions
- category expansion and city rollout
Ready to implement Tokopedia’s proven business model for your market? Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps. Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion
Tokopedia’s journey proves a powerful truth about platform businesses: long-term winners don’t just sell products—they build ecosystems that make commerce easier, safer, and more repeatable for everyone involved. The Tokopedia business model works because it combines marketplace liquidity, seller empowerment, and trust-building into one scalable engine, then monetizes the growth layer through commissions, ads, and premium seller services.
For entrepreneurs, the bigger lesson is not “copy Tokopedia’s features.” It’s to copy Tokopedia’s execution mindset: start with a clear value proposition, build trust early, keep sellers profitable, and design monetization that grows as the ecosystem grows. That’s how platforms move from being “an app” to becoming an everyday habit.
In 2026 and beyond, the future of digital marketplaces will belong to businesses that master efficiency, personalization, and ecosystem partnerships—because platform economies will keep expanding, but only the most trusted and well-structured mod els will stay ahead.
FAQs
What type of business model does Tokopedia use?
Tokopedia uses a hybrid marketplace business model. It connects buyers and sellers on one platform and earns through commissions, ads, and seller services.
How does Tokopedia’s model create value?
It creates value by offering buyers variety, trusted shopping, and smooth payments. Sellers benefit from ready traffic, marketing tools, and logistics support.
What are its key success factors?
Tokopedia’s success comes from strong seller ecosystem growth, customer trust systems, and multi-layer monetization. Its partnerships in logistics and payments also improve conversion.
How scalable is it?
It’s highly scalable because marketplace growth compounds over time. More sellers attract more buyers, and higher demand pulls in even more sellers.
What are the biggest challenges?
Major challenges include counterfeit risk, seller quality control, delivery delays, and customer support pressure. Competition and discount wars can also impact margins.
How can entrepreneurs adapt it to their region?
Start with one niche or city and build trust with verified sellers and reliable delivery. Then expand categories and scale using partnerships.
What are alternatives to this model?
Alternatives include first-party ecommerce, subscription commerce, D2C brand apps, or niche marketplaces. Each model changes how revenue and operations work.
How has it evolved over time?
Tokopedia evolved from a basic marketplace into a full ecosystem. In 2026, it focuses more on ads, seller tools, logistics efficiency, and retention-led growth.
Related Article :








