Business model of Cdiscount is one of the most interesting ecommerce success stories in France because it blends marketplace scale with retail control. What started as a discount-first online store evolved into a multi-category platform where millions of customers shop for electronics, home essentials, groceries, and everyday deals. In 2026, Cdiscount continues to compete by focusing on value pricing, wide product variety, and fast delivery options that match modern buyer expectations.
What makes the Cdiscount business model powerful is how it balances two engines at once: selling products directly and enabling third-party sellers to grow on its marketplace. This hybrid approach helps Cdiscount expand inventory without holding heavy stock in every category, while still maintaining strong margins on key high-demand products.
For entrepreneurs, studying the business model of Cdiscount is useful because it shows how a platform can scale through smart pricing strategy, seller ecosystem growth, and customer retention tactics. It proves that discount positioning can still build long-term brand trust when supported by reliable operations and a strong digital shopping experience.
How the Cdiscount Business Model Works
The Cdiscount business model works as a hybrid ecommerce ecosystem, combining first-party retail (Cdiscount sells products directly) with a third-party marketplace (external sellers list and sell through the platform). This structure allows Cdiscount to scale faster than a traditional online store because it can expand product variety without owning all inventory. In 2026, this hybrid model is one of the key reasons Cdiscount stays competitive against Amazon and other European ecommerce platforms.
1) Type of Business Model
Cdiscount operates mainly as a:
- Hybrid Ecommerce Model (Retail + Marketplace)
- Supported by Subscription-style loyalty benefits (via delivery/benefits programs)
- Strengthened by digital services add-ons (warranties, financing, seller tools)
2) Value Proposition (Who Gets What?)
Cdiscount creates value for multiple user groups:
For Customers (Buyers)
- Discount pricing and deal-driven shopping
- Wide selection across categories (electronics, home, appliances, etc.)
- Convenient delivery and trusted payment options
For Sellers (Marketplace Partners)
- Access to a large French buyer base
- Ready infrastructure: product pages, traffic, payments, logistics options
- Ability to scale without building their own ecommerce store
For Brands & Partners
- Performance-based visibility and promotions
- Sponsored placements and campaign-driven sales boosts
- Faster market access in France through Cdiscount’s platform
3) Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
Cdiscount’s ecosystem stays balanced because each stakeholder plays a role:
- Customers → demand + repeat purchases
- Marketplace Sellers → expand inventory and selection
- Cdiscount (Platform Owner) → manages trust, payments, tech, and delivery experience
- Logistics partners & fulfillment network → speed + reliability
- Payment providers & financing partners → improve conversion rates
- Advertisers/brands → boost revenue via visibility and promotion spend
Read more : What is Cdiscount and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Cdiscount growth is driven by a simple insight: in ecommerce, price attracts users, but convenience and trust keep them loyal. The platform targets value-focused shoppers across France while also enabling thousands of third-party sellers to reach those buyers at scale. In 2026, Cdiscount’s customer segmentation strategy is built around high-frequency household needs, deal-seeking behavior, and category expansion into everyday commerce.
1) Primary Customer Segments (Core Users)
Value-Conscious Online Shoppers (Mass Market Buyers)
These customers come to Cdiscount for:
- Discounted pricing on popular products
- Seasonal deals and flash sales
- Reliable delivery and easy returns
Electronics & Appliance Buyers (High-Intent Shoppers)
This segment is important because it has:
- Higher average order value (AOV)
- Strong upgrade cycles (new phones, TVs, kitchen appliances)
- Financing and warranty add-on potential
2) Secondary Customer Segments (Growth Users)
Home & Lifestyle Shoppers
Users buying:
- Furniture, décor, bedding, home improvement
- Bulk household essentials
- Daily-use items at discounted rates
Marketplace Sellers (Revenue & Scale Segment)
Not buyers, but critical “customers” of the platform. Sellers join Cdiscount to:
- Access ready-made demand
- Reduce customer acquisition cost
- Scale without building a full ecommerce brand from scratch
3) Customer Journey: Discovery → Conversion → Retention
Discovery
- Google search for deals and product comparisons
- Promotions and seasonal campaigns
- Price-sensitive browsing behavior (multiple tabs, comparison sites)
Conversion
- Discount pricing + trust signals (reviews, delivery estimates)
- Multiple payment options and financing support
- Bundles, warranties, and protection plans increase checkout value
Retention
- Repeat purchase triggers through:
- New deals and category expansion
- Faster delivery options
- Personalized recommendations based on browsing and purchase history
4) Acquisition Channels & LTV Optimization
Acquisition Channels
- SEO-driven product/category pages
- Deal-based marketing campaigns
- Marketplace inventory expansion (more listings = more organic reach)
Lifetime Value (LTV) Optimization
Cdiscount increases customer lifetime value by:
- Keeping pricing competitive in high-demand categories
- Cross-selling related products (electronics → accessories, appliances → warranties)
- Encouraging repeat purchases through wide product availability
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Once you understand who Cdiscount serves, the next question becomes clear :
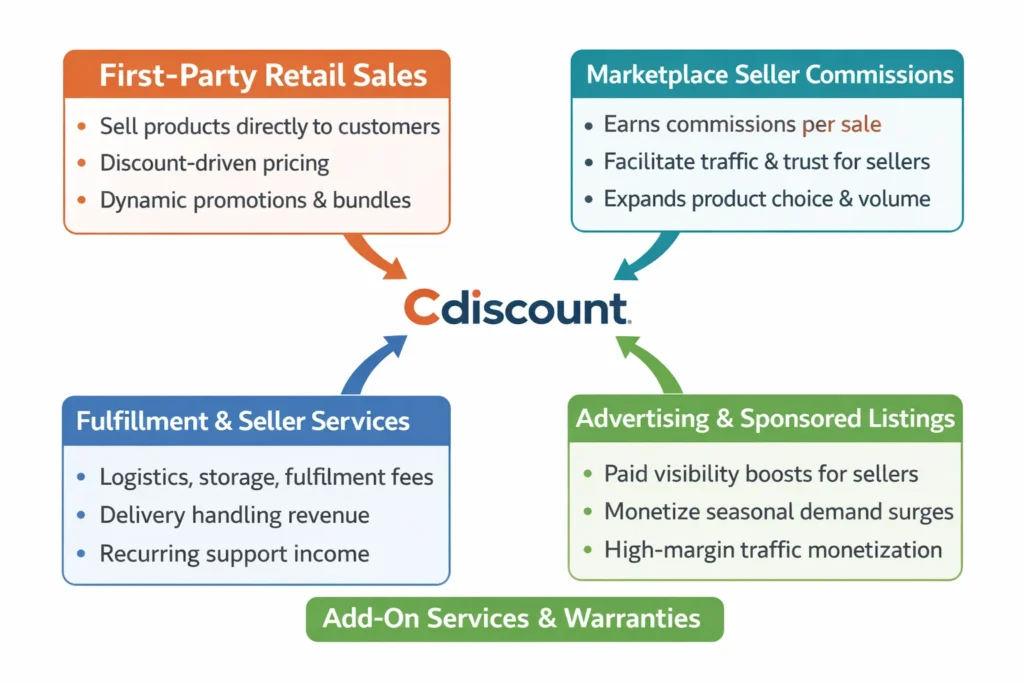
The Cdiscount revenue model is designed as a layered monetization system. Instead of relying only on product margins, Cdiscount combines retail profits, marketplace commissions, advertising income, and service-based upsells—creating multiple revenue channels that reduce risk and improve long-term stability.
Primary Revenue Stream 1: First-Party Retail Sales (Core Engine)
Mechanism
Cdiscount sells products directly to customers (electronics, appliances, home products, essentials) by sourcing inventory and managing pricing.
Pricing Model
- Discount-driven pricing strategy
- Dynamic promotions during high-demand periods
- Bundled offers to increase cart value
Revenue Contribution
- A major share of total revenue, especially in high-ticket categories
- Strong control over customer experience and product quality
Growth Trajectory (2026)
- Focus on profitable categories where Cdiscount can win on price and volume
- Improved margin strategy through smarter inventory planning and private-label opportunities
Secondary Revenue Stream 2: Marketplace Seller Commissions
Mechanism
Third-party sellers list products on Cdiscount, and the platform earns a commission per transaction.
How it works
- Sellers gain access to traffic and buyer trust
- Cdiscount earns without owning inventory
Why it scales well
- More sellers → more products → more customer choice
- More choice → more traffic → higher marketplace GMV
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: Fulfillment, Logistics & Seller Services
Mechanism
Cdiscount offers operational support to sellers through logistics and platform services.
Monetization examples
- Fulfillment/storage services
- Delivery handling and shipping support
- Seller tools and account-level services
This stream is important because it creates recurring, service-driven income, not just transaction income.
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Advertising & Sponsored Product Visibility
Mechanism
Brands and sellers pay to increase product visibility through sponsored placements.
Examples
- Sponsored listings on category pages
- Paid campaigns during seasonal demand spikes
- Performance-based visibility boosts
This is high-margin revenue because it monetizes attention and traffic, not inventory.
Secondary Revenue Stream 5: Add-On Services (Warranties, Protection, Financing)
Mechanism
Cdiscount earns extra revenue by selling add-ons during checkout.
Examples
- Extended warranties for appliances/electronics
- Protection plans and insurance-style add-ons
- Installment/financing partnerships
These add-ons work because they increase revenue per order while solving buyer anxiety about expensive purchases.
Overall Monetization Strategy (How It All Connects)
Cdiscount’s monetization is designed like a “stack”:
- Retail sales build trust + bring volume
- Marketplace commissions scale product selection without heavy inventory risk
- Ads monetize seller competition for visibility
- Services and warranties increase profit per customer
Psychologically, the pricing strategy is built on deal urgency + value perception, while the business model captures revenue from both buyers (shopping)
Read more : Cdiscount Revenue Model: How Cdiscount Makes Money in 2026
Operational Model & Key Activities
Cdiscount may look like a simple ecommerce website from the outside, but behind the scenes it runs like a high-speed operations machine. In 2026, the success of the Cdiscount business model depends heavily on execution—because in ecommerce, pricing attracts customers, but operations decide profitability and retention.
To keep the marketplace stable and customers satisfied, Cdiscount manages daily activities across technology, logistics, seller performance, customer support, and marketing optimization.
1) Core Operations (What Runs Daily)
Platform Management & Technology
Cdiscount’s core engine is its platform infrastructure, which includes:
- Product catalog and listing systems
- Search, filters, and recommendation algorithms
- Secure payment flow and fraud monitoring
- App + website performance optimization (speed, uptime, UX)
Marketplace Quality Control
Since many products come from third-party sellers, Cdiscount must control trust through:
- Seller onboarding and verification
- Product authenticity monitoring
- Review and rating systems
- Policy enforcement (returns, delays, customer complaints)
Logistics & Fulfillment Operations
Delivery speed and reliability are major differentiators in 2026. Cdiscount manages:
- Warehouse planning and inventory movement (for retail products)
- Shipping partnerships and last-mile coordination
- Delivery tracking and customer communication
- Reverse logistics (returns and exchanges)
Customer Support & Dispute Handling
To protect trust, Cdiscount invests in:
- Buyer support for refunds, returns, and delivery issues
- Seller dispute resolution
- Issue escalation systems for high-risk categories (electronics/appliances)
Marketing & Growth Execution
Daily marketing operations focus on performance and conversion:
- Deal campaigns and flash sales
- SEO-driven category and product optimization
- Paid ads and remarketing
- Sponsored product placements and ad inventory management
2) Resource Allocation (Where the Company Focuses Investment)
In a platform like Cdiscount, resources are split across the areas that protect both scale and trust:
Technology & Product Development
- Platform stability and scalability
- Search optimization and personalization
- Seller dashboards and marketplace tools
- Automation for fraud prevention and dispute resolution
Operations & Logistics
- Warehousing and fulfillment efficiency
- Delivery speed improvements
- Cost control in shipping and returns
Marketing & Customer Acquisition
- Deal-led campaigns to drive volume
- Paid acquisition for competitive categories
- Retention efforts through repeat purchase triggers
HR & Expansion Focus
- Marketplace seller support teams
- Category managers for growth verticals
- Regional performance teams for local market execution
Why This Operational Model Works
Cdiscount’s operations are designed to handle two businesses at once:
- Retail business (inventory + pricing + delivery control)
- Marketplace business (seller ecosystem + trust + transaction scale)
This dual-engine execution is what makes the model scalable, but it also demands strong systems—because one weak link (bad sellers, slow delivery, poor support) can damage the entire platform’s credibility.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
Cdiscount doesn’t scale alone. Like every strong marketplace in 2026, it grows through partnerships that increase speed, trust, reach, and efficiency. The Cdiscount business model becomes stronger when the platform builds an ecosystem where sellers can sell faster, customers can buy with confidence, and operations can run smoothly without Cdiscount owning every piece of the chain.
Instead of trying to control everything internally, Cdiscount’s partnership strategy is about plugging into the right networks—logistics, payments, sellers, and marketing channels—so the platform keeps expanding without slowing down.
1) Technology & API Partnerships
Technology partnerships help Cdiscount improve platform performance and marketplace operations.
Key partnership types include:
- Ecommerce integrations for seller onboarding
- Inventory and order management tools
- Analytics and performance tracking systems
- Security and fraud-prevention technology
Why it matters:
Better seller tools = smoother listings + faster order processing = higher customer satisfaction.
2) Payment & Financing Alliances
Payment and financing partnerships are critical because they directly affect conversion rates—especially for high-ticket categories like electronics and appliances.
Cdiscount benefits from:
- Secure payment gateways
- Fraud detection and risk scoring support
- Installment/financing options for customers
- Faster settlement systems for sellers
Why it matters:
Flexible payments increase purchase confidence and reduce cart abandonment.
3) Logistics & Delivery Partnerships
In 2026, delivery speed is a competitive moat. Cdiscount relies on logistics alliances to maintain reliability and manage cost efficiency.
Partnership support includes:
- Shipping carriers for national delivery coverage
- Last-mile delivery networks
- Warehouse distribution coordination
- Reverse logistics partners for returns handling
Why it matters:
A marketplace can’t scale if delivery fails. Logistics partnerships protect trust.
4) Marketing & Distribution Partnerships
Cdiscount also strengthens growth through visibility-driven collaborations.
These include:
- Affiliate and referral networks
- Brand-led campaigns and promotions
- Sponsored product partnerships with top sellers
- Strategic placements across high-traffic deal platforms
Why it matters:
These partnerships increase reach while keeping customer acquisition cost more controllable.
5) Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
Ecommerce marketplaces face constant pressure around consumer protection, seller compliance, and fair competition.
Cdiscount benefits from partnerships and alliances that support:
- Compliance readiness
- Cross-border seller enablement
- Category-level regulation handling (electronics, warranties, returns)
Why it matters:
Strong compliance systems reduce risk and support long-term scalability.
Ecosystem Strategy Insight (Why Partnerships Create a Moat)
Cdiscount’s ecosystem strategy is designed around one goal: increase network effects while protecting trust.
- More sellers → more selection → more buyers
- More buyers → higher demand → more sellers join
- Partner services (logistics + payments + tech) reduce friction at every step
This creates a platform advantage where competitors must not only match pricing—but also match the ecosystem depth that keeps Cdiscount operationally strong and profitable
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Cdiscount’s growth has never been only about selling more products. Its real scaling advantage comes from building a system where demand grows, supply expands, and customer trust stays stable—all at the same time. In 2026, the Cdiscount business model scales through a mix of marketplace expansion, deal-driven acquisition, and operational execution that keeps repeat purchases high.
Growth Engines (How Cdiscount Expands)
1) Deal-Driven Organic Growth
Cdiscount’s brand identity is built around value and affordability, which naturally creates organic traction through:
- Price comparison behavior
- Seasonal deal spikes (festive sales, clearance events)
- Word-of-mouth around “best price” moments
This works because customers don’t just shop—they actively search for deals, and Cdiscount is positioned to capture that intent.
2) Marketplace Expansion (Supply-Side Scaling)
A major growth lever is increasing product variety through third-party sellers.
Cdiscount scales supply by:
- Onboarding more sellers across categories
- Encouraging sellers to expand catalog depth
- Supporting seller performance through tools and services
Why it matters:
More listings = more SEO pages = more traffic = more conversions.
3) Paid Marketing & Performance Acquisition
To compete in high-demand categories, Cdiscount uses performance marketing to win high-intent shoppers.
Common strategies include:
- Search ads for product keywords
- Retargeting for cart abandoners
- Category-level campaigns for electronics, appliances, home essentials
- Promotional pushes during high-competition sales periods
This helps Cdiscount capture buyers exactly when purchase intent is highest.
4) Category Expansion to Increase Repeat Purchases
Cdiscount grows by moving beyond “one-time electronics buyers” into repeat shopping behavior.
It scales by expanding into:
- Home essentials and lifestyle
- Daily-use categories
- Broader household shopping needs
This increases retention because customers return more frequently when the platform supports both “big buys” and “small needs.”
5) Logistics and Delivery Improvements
Speed and reliability directly impact growth in ecommerce.
Cdiscount strengthens scaling by:
- Improving delivery timelines
- Enhancing tracking and communication
- Reducing friction in returns and refunds
- Offering more consistent delivery experience across regions
Operational strength turns first-time buyers into repeat customers.
Scaling Challenges & How Cdiscount Handles Them
Challenge 1: Marketplace Trust Issues
Marketplaces risk quality problems when sellers grow too fast.
Cdiscount manages this by:
- Seller verification and monitoring
- Review-based transparency
- Dispute resolution and policy enforcement
Challenge 2: Logistics Cost Pressure
Delivery and returns can destroy margins.
Cdiscount reduces this through:
- Partner logistics optimization
- Better fulfillment planning
- Category-level shipping strategies (heavy vs light items)
Challenge 3: Competing Against Global Giants
Competing with Amazon-level expectations is difficult.
Cdiscount counters this by:
- Winning on price perception
- Building strong seller supply locally
- Increasing customer loyalty through convenience + trust
challenge 4: Technology Scaling
High traffic during deal events creates platform load issues.
Cdiscount invests in:
- Scalable infrastructure
- Performance optimization
- Better search and personalization system
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Cdiscount operates in one of the most competitive digital markets in the world—where global giants, local retailers, and niche marketplaces all fight for the same customer. In 2026, Cdiscount protects its position by combining value leadership, marketplace scale, operational trust, and smart platform control. The Cdiscount business model stays strong not because it tries to copy Amazon, but because it builds a defensible identity around affordability and selection, supported by a scalable ecosystem.
Competitive Advantages (Why Cdiscount Stays Ahead)
1) Value Leadership & Discount Positioning
Cdiscount’s strongest advantage is its brand perception:
- “Good deals”
- “Affordable pricing”
- “Wide product selection at low cost”
This positioning is powerful because in 2026, customers are more price-sensitive and compare options before purchasing.
2) Marketplace Scale & Product Variety
Cdiscount defends market share by ensuring customers find what they need without leaving the platform.
Marketplace scaling creates:
- More categories
- More sellers
- More price competition inside the platform
- More inventory depth
This reduces the risk of customers switching to another marketplace due to lack of options.
3) Network Effects & Switching Barriers
Cdiscount benefits from marketplace network effects:
- More sellers → better selection and pricing
- Better selection → more customers
- More customers → more seller demand
As the ecosystem grows, it becomes harder for competitors to replicate quickly because they must build both demand and supply at the same time.
4) Brand Trust Through Platform Controls
Trust is a defensive moat, especially in marketplaces.
Cdiscount protects trust through:
- Ratings and reviews
- Seller monitoring and penalties
- Buyer protection systems
- Secure payments and dispute handling
This reduces platform risk and keeps customer retention stable.
5) Data-Driven Personalization & Merchandising
Cdiscount uses customer behavior data to strengthen conversion and repeat purchases.
Key areas include:
- Personalized recommendations
- Category-level bundling
- Dynamic deal targeting
- Retargeting based on browsing intent
This makes the platform feel more relevant and improves average order value (AOV).
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
If you’re a founder planning to build a marketplace, ecommerce platform, or multi-vendor business in 2026, Cdiscount gives a very practical blueprint. The biggest lesson from the Cdiscount business model is simple: you don’t need to be the biggest player in the market—you need the smartest system. Cdiscount scaled by combining value pricing, marketplace expansion, and operational execution in a way that keeps growth consistent even under heavy competition.
Key Factors Behind Cdiscount’s Success
Here’s what Cdiscount did right—and why it worked:
- Clear positioning: Cdiscount stayed focused on being value-first, not luxury-first.
- Hybrid model advantage: It scaled using both retail sales and marketplace sellers.
- Selection flywheel: More sellers increased product variety, which increased customer demand.
- Trust systems: Reviews, seller controls, and dispute handling protected credibility.
- Monetization layers: It earned through product margins, seller commissions, ads, and add-ons.
- Operational discipline: Delivery, returns, and customer support kept repeat purchases strong.
Replicable Principles for Startups
You can apply these lessons even if you’re building a smaller or niche platform:
- Start with one strong category
Don’t launch with “everything.” Win one vertical first (electronics, fashion, groceries, home services, etc.). - Build supply and demand together
Marketplaces fail when they focus only on users or only on sellers. Balance both sides early. - Design trust as a product feature
Trust is not a legal policy—it’s a conversion strategy. Add:
- reviews and ratings
- seller verification
- clear returns/refund process
- Monetize beyond transactions
Don’t depend on only one revenue stream. Add layers like:
- seller services
- sponsored listings
- premium delivery options
- warranties or protection plans
- Use deals smartly, not emotionally
Discounts should drive acquisition, not destroy margins. Plan promotions around:
- high-intent products
- seasonal spikes
- inventory strategy
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Many entrepreneurs copy the “marketplace idea” but miss the execution:
- Launching without enough sellers (empty platform problem)
- Allowing low-quality sellers to ruin trust
- Depending only on commissions for revenue
- Ignoring logistics and returns until customers complain
- Competing on price without operational efficiency
Implementation & Investment Priorities
A realistic build-and-scale plan looks like this:
- Phase 1 : MVP marketplace + core categories + payments
- Phase 2 : seller onboarding system + reviews + order management
- Phase 3 : logistics partnerships + returns workflow + scaling marketing
- Phase 4 : sponsored ads + seller services + retention engine
Ready to implement Cdiscount’s proven business model for your market? Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms. We’ve helped 200+ entrepreneurs launch profitable apps. Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion
The real lesson behind the Cdiscount business model is not just that discounts can win customers—it’s that a well-designed ecosystem can win markets. Cdiscount proved that when you combine value pricing with marketplace scale, operational trust, and layered monetization, you create a platform that can survive competition, economic shifts, and changing consumer behavior.
In 2026 and beyond, platform businesses will not be judged only by how many users they have, but by how efficiently they turn demand into repeat behavior and revenue. Cdiscount’s journey reminds founders that sustainable growth comes from aligning three things: customer value, seller success, and operational execution. The future of ecommerce platforms belongs to businesses that build systems—not just websites.
FAQs
What type of business model does Cdiscount use?
Cdiscount uses a hybrid ecommerce business model combining first-party retail sales and a third-party marketplace. This allows it to scale product variety while maintaining control over key categories.
How does the Cdiscount business model create value?
It creates value by offering low prices, wide selection, and convenient delivery for customers. For sellers, it provides ready traffic, payment systems, and marketplace tools to grow faster.
What are Cdiscount’s key success factors?
Cdiscount succeeds through discount positioning, marketplace expansion, and strong operations. Its layered monetization (retail + commissions + ads + services) also improves stability.
How scalable is the Cdiscount business model?
It is highly scalable because the marketplace model grows inventory without heavy stock investment. More sellers bring more listings, which increases traffic and sales volume over time.
What are the biggest challenges in Cdiscount’s model?
The biggest challenges include seller quality control, delivery performance, and return management. Competition from global ecommerce giants also requires constant pricing and service improvements.
How can entrepreneurs adapt Cdiscount’s model to their region?
Start with one category and one location, then expand step by step with verified sellers. Focus on trust, pricing, and smooth delivery experience to build repeat customers.
What are alternatives to the Cdiscount business model?
Alternatives include a pure marketplace model (only third-party sellers) or a direct-to-consumer retail model (only owned inventory). Some brands also use subscription-based ecommerce for loyalty and retention.
How has Cdiscount’s business model evolved over time?
Cdiscount evolved from a discount online retailer into a full marketplace ecosystem. Over time, it expanded into services, seller monetization, and advertising to strengthen profitability.
Related Article








