In less than a decade, Coupang transformed from a small daily-deals startup into South Korea’s most powerful digital commerce ecosystem — often called “the Amazon of Asia,” but operating on a far more aggressive logistics-first model.
Here’s a striking stat to set the stage: By 2024, Coupang was delivering over 70% of orders within 24 hours, serving more than 21 million active customers — in a country of just 51 million people. Few platforms in the world have achieved that level of market penetration with such operational intensity.
business model of Coupang matters in 2025 because it challenges a long-held assumption in platform economics: that asset-heavy logistics and thin margins don’t scale. Coupang proved the opposite. By vertically integrating fulfillment, technology, last-mile delivery
How the Coupang Business Model Works
At its core, Coupang operates a vertically integrated, logistics-first marketplace model — a hybrid of first-party retail, third-party marketplace, and subscription commerce, all powered by one of the most advanced fulfillment networks in Asia.
Unlike traditional marketplaces that simply connect buyers and sellers, Coupang controls nearly every critical layer of the value chain. This operational ownership is what enables its defining promise: fast, reliable, and predictable delivery at scale.
Type of Business Model
Coupang’s model blends multiple structures into a single ecosystem:
- Hybrid Marketplace Model: First-party retail (Coupang-owned inventory) + third-party sellers
- Subscription Model: Rocket WOW membership drives loyalty and order frequency
- Logistics-as-a-Core-Product: Fulfillment and last-mile delivery are internal, not outsourced
- Platform Expansion Model: Adjacent services like Coupang Eats and Coupang Play extend lifetime value
This hybrid approach allows Coupang to capture more margin, more data, and more control than asset-light competitors.
Value Proposition by User Segment
Coupang’s success comes from aligning incentives across all participants:
- Consumers
- Next-day or same-day delivery for most SKUs
- Simple returns with door-step pickup
- Predictable pricing and minimal friction
- Sellers & Brands
- Access to Coupang’s logistics infrastructure
- High conversion rates due to trusted delivery SLAs
- Reduced operational burden compared to self-fulfillment
- Partners & Ecosystem Players
- APIs, advertising tools, and data insights
- Scalable demand without building logistics from scratch
Key Stakeholders in the Ecosystem
Coupang’s platform balance depends on:
- Customers demanding speed and reliability
- Sellers supplying inventory and selection
- Delivery drivers (Coupang Flex) ensuring last-mile execution
- Internal tech and logistics teams optimizing routing, inventory placement, and demand forecasting
Each stakeholder is tightly orchestrated through software, not manual processes.
Evolution of the Model
Coupang’s business model has evolved in clear phases:
- 2010–2014: Deals and marketplace experimentation
- 2015–2018: Heavy investment in fulfillment centers and delivery fleet
- 2019–2021: Rocket Delivery becomes the default consumer expectation
- 2022–2025: Ecosystem expansion through subscriptions, ads, content, and food delivery
This evolution shows a deliberate shift from growth-at-all-costs to efficiency-led scale.
Read more : What is Coupang and How Does It Work?
Target Market & Customer Segmentation Strategy
Coupang’s dominance is not built on serving “everyone” equally — it is built on deeply understanding high-frequency digital shoppers and designing the platform around their daily behavior. Its segmentation strategy prioritizes usage intensity, convenience sensitivity, and lifetime value, not just demographics.
Primary Customer Segments
Urban Consumers (Core Segment)
- Age: 20–49
- Profile: Working professionals, dual-income households, families
- Behavior: High order frequency, time-constrained, convenience-driven
- Why they stay: Next-day delivery, frictionless returns, subscription value
These users form the economic backbone of Coupang’s model, generating repeat orders and predictable demand.
Rocket WOW Subscribers
- Willing to pay for speed, free delivery, and bundled services
- Higher average order frequency and lower churn
- Strong lock-in through ecosystem benefits (delivery, streaming, exclusives)
Subscription customers are Coupang’s most valuable cohort.
Secondary Customer Segments
Value-Seeking Shoppers
- Price-sensitive but still convenience-oriented
- Engage during promotions and sales events
- Gradually upsold into subscriptions through experience
SMEs & Independent Sellers
- Use Coupang as a primary distribution channel
- Benefit from logistics, visibility, and demand aggregation
- Accept platform dependency in exchange for scale
Customer Journey: Discovery to Retention
Coupang optimizes the full lifecycle:
- Discovery: App-first UX, push notifications, personalized recommendations
- Conversion: One-click checkout, transparent delivery times
- Retention: Rocket WOW perks, easy returns, habit-forming reliability
Speed and predictability reduce decision fatigue, increasing repeat purchases.
Acquisition Channels & LTV Optimization
- Organic app installs via word-of-mouth
- Referral incentives and free Rocket WOW trials
- Heavy personalization powered by purchase and logistics data
- Cohort-based pricing and retention strategies
Rather than chasing constant new users, Coupang maximizes orders per customer per year.
Market Positioning & Competitive Edge
Coupang positions itself as:
- The most reliable e-commerce platform in Korea
- A daily-use app, not a discount marketplace
- A logistics-enabled technology company
Its differentiation lies in execution excellence, not branding hype.
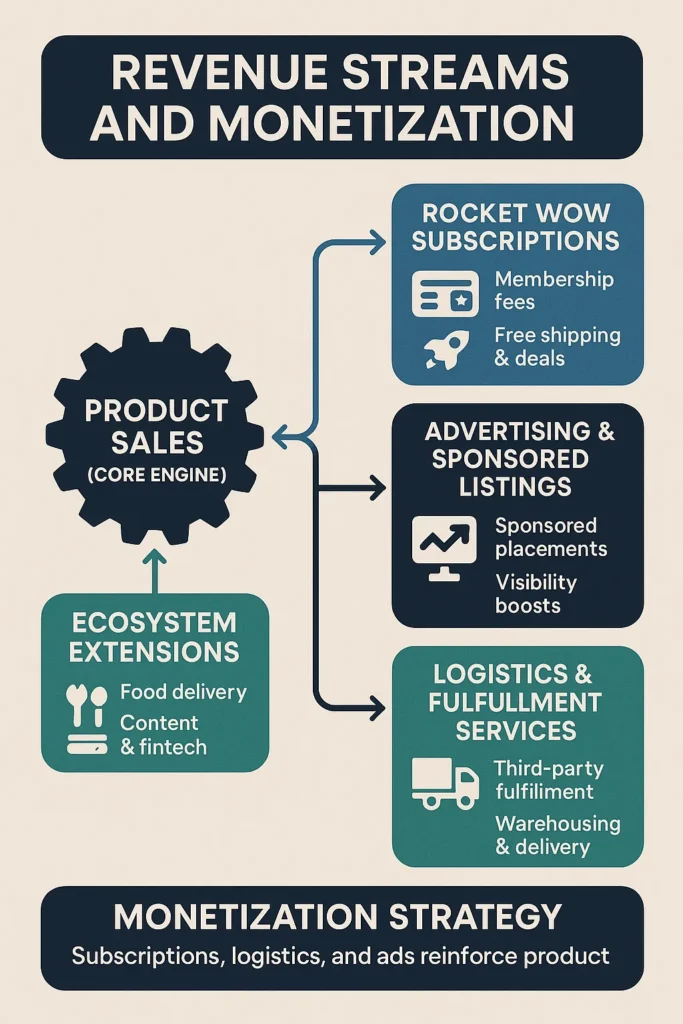
Revenue Streams and Monetization Design
Once Coupang secured daily user engagement and logistics dominance, its business model unlocked a layered monetization architecture. Instead of relying on a single revenue source, Coupang engineered multiple, interconnected income streams — some margin-thin but high-volume, others high-margin and compounding over time.
This diversification is what makes Coupang resilient in 2025.
Primary Revenue Stream: Product Sales (Core Engine)
Mechanism
- Direct sales of goods where Coupang owns inventory (first-party retail)
- Third-party marketplace sales with seller commissions
- Rocket Delivery SKUs prioritized for speed and reliability
Pricing Model
- Retail margins on owned inventory
- Commission-based fees for third-party sellers (category-dependent)
- Dynamic pricing optimized through demand and inventory data
Revenue Contribution
- Largest share of total revenue
- Lower margins but massive scale and repeat frequency
Growth Trajectory
- Driven by higher order frequency per customer
- Expansion of private-label and exclusive SKUs
- Improved inventory turnover through AI forecasting
Secondary Revenue Stream 1: Rocket WOW Subscriptions
Mechanism
- Monthly or annual membership fee
- Free delivery, faster shipping, exclusive deals, bundled services
Why it Matters
- Predictable recurring revenue
- Higher customer lifetime value
- Lower churn and stronger platform lock-in
Rocket WOW members order significantly more often than non-members, making this stream strategically critical even if it represents a smaller revenue percentage.
Secondary Revenue Stream 2: Advertising & Sponsored Listings
Mechanism
- Sponsored product placements
- Search and category-based visibility boosts
- Brand storefront promotions
Economics
- High-margin, software-driven revenue
- Scales with seller competition and GMV growth
- Similar to Amazon’s ad flywheel, but still early-stage in Korea
Secondary Revenue Stream 3: Logistics & Fulfillment Services
Mechanism
- Fulfillment services for third-party sellers
- Warehousing, picking, packing, and last-mile delivery
- Returns management and customer service
This effectively turns Coupang’s cost center into a monetizable infrastructure layer.
Secondary Revenue Stream 4: Ecosystem Extensions
- Coupang Eats: Food delivery commissions
- Coupang Play: Content bundled into subscriptions
- Fintech & Payments (emerging): Increased checkout conversion and data leverage
These extensions increase time spent in-app and cross-sell potential.
Monetization Strategy: How It All Connects
Coupang’s monetization works because:
- Subscriptions increase order frequency
- Higher frequency improves logistics efficiency
- Better logistics improve seller conversion
- Seller competition fuels advertising revenue
Pricing psychology emphasizes convenience over discounts, making customers less price-sensitive once habits form.
Read more : Best Coupang Clone Script 2025 — Build a Scalable E-Commerce Powerhouse
Operational Model & Key Activities
Coupang’s true competitive advantage is not its app interface — it is the operational machine running behind the scenes. The company treats logistics, technology, and execution as a single integrated system, where software decisions directly shape physical outcomes.
This tight coupling between code and concrete is what allows Coupang to deliver at a scale competitors struggle to match.
Core Operations
Coupang’s daily operations revolve around five tightly linked pillars:
- Platform & Technology Management
- Proprietary logistics software for routing, inventory placement, and demand forecasting
- Real-time order tracking and exception handling
- Continuous experimentation through A/B testing and data loops
- Fulfillment & Warehousing
- Dense network of fulfillment centers strategically placed near urban populations
- SKU-level inventory positioning to minimize delivery time
- Automated sorting and packing to reduce labor friction
- Last-Mile Delivery (Rocket Delivery)
- In-house delivery network rather than third-party couriers
- Coupang Flex drivers managed through internal systems
- Guaranteed delivery windows that build customer trust
- Quality Control & Returns
- Doorstep returns with minimal customer effort
- Centralized reverse logistics to recover value and improve CX
- Tight SLAs for damaged or delayed items
- Customer Support & Experience
- App-based self-service first, human support when needed
- Refunds often processed before returns are received
- Trust prioritized over short-term cost savings
Resource Allocation Strategy
Coupang’s spending reflects long-term thinking rather than short-term margins:
- Technology & Infrastructure
- Heavy investment in cloud, automation, and internal tooling
- Logistics tech treated as a core IP asset
- Logistics & Operations
- Largest cost center, but also the foundation of the moat
- Continuous capex into fulfillment expansion and optimization
- Marketing
- Relatively efficient compared to peers
- Strong reliance on word-of-mouth and habit formation
- Talent & R&D
- Focus on engineers, data scientists, and operations leaders
- Cross-functional teams linking tech and logistics execution
Why This Operational Model Scales
Most e-commerce platforms outsource complexity. Coupang internalizes it — then automates it. This results in:
- Lower marginal delivery costs at scale
- Fewer failure points across the customer journey
- Data compounding that improves decisions every day
For founders, the lesson is clear: control over core operations unlocks strategic flexibility.
Strategic Partnerships & Ecosystem Development
While Coupang is famously vertically integrated, it does not operate in isolation. Instead of relying on partners for core execution, Coupang uses partnerships strategically — to extend reach, accelerate innovation, and strengthen its ecosystem without diluting control over the customer experience.
This selective collaboration philosophy is a key reason its platform remains both scalable and defensible.
Coupang’s Partnership Philosophy
Coupang partners where partnerships increase leverage, not where they introduce dependency. Core logistics, fulfillment, and customer experience remain internal. External alliances are used to:
- Expand selection and services
- Reduce time-to-market for new offerings
- Navigate regulatory and regional complexity
Key Partnership Types
Technology & API Partners
- Cloud infrastructure providers
- AI, analytics, and security technology vendors
- Integration partners for seller tools and advertising systems
These partnerships accelerate innovation while keeping Coupang’s proprietary systems in control.
Payment & Financial Services Alliances
- Local payment providers and card networks
- BNPL and installment payment partners
- Fraud prevention and risk management platforms
Payment flexibility directly improves checkout conversion and basket size.
Seller & Brand Partnerships
- Large domestic and global brands for exclusive launches
- Private-label manufacturing partners
- SME onboarding programs to expand long-tail selection
Coupang uses data insights to help sellers optimize pricing, inventory, and promotions — deepening platform dependence.
Logistics & Infrastructure Partnerships
- Real estate and warehousing developers
- Automation and robotics suppliers
- Packaging and sustainability vendors
These partners help scale physical infrastructure faster without compromising operational standards.
Regulatory & Expansion Alliances
- Local governments and labor organizations
- Compliance and labor standards bodies
- Regional partners during international expansion (e.g., Taiwan)
Ecosystem Strategy: Why It Works
Coupang’s ecosystem compounds value through:
- Network effects: More sellers → more selection → more customers → better logistics density
- Embedded monetization: Ads, fulfillment, and subscriptions layered on top of core commerce
- High switching costs: Sellers and customers are locked in by operational dependence
Partnerships strengthen the moat without becoming the moat.
Growth Strategy & Scaling Mechanisms
Coupang’s growth story is not driven by explosive virality or aggressive global expansion. Instead, it follows a density-first, execution-led scaling strategy — win one market completely, then expand with discipline.
This approach has allowed Coupang to grow sustainably while maintaining service quality.
Core Growth Engines
Operational Density as a Growth Lever
- Higher order density lowers per-delivery costs
- Faster delivery increases repeat usage
- Repeat usage improves demand predictability
This creates a self-reinforcing loop between logistics efficiency and customer loyalty.
Subscription-Led Growth
- Rocket WOW increases purchase frequency
- Bundled services (delivery, content, exclusives) raise switching costs
- Free trials accelerate conversion into paid membership
Organic Virality
- Exceptional delivery experience drives word-of-mouth
- Consistency turns customers into advocates
- Minimal reliance on influencer or discount-heavy growth
Ecosystem Expansion
- Coupang Eats captures food consumption moments
- Coupang Play increases daily app engagement
- Each new service increases cross-sell opportunities
Geographic Expansion Model
Coupang expands cautiously:
- Focus on markets with high urban density
- Heavy upfront infrastructure investment
- Long-term profitability prioritized over rapid footprint expansion
Taiwan serves as a testbed for replicating the Korea playbook.
Scaling Challenges & How Coupang Solved Them
Operational Complexity
- Challenge: Managing millions of SKUs with guaranteed delivery
- Solution: AI-driven inventory placement and routing algorithms
Margin Pressure
- Challenge: Thin e-commerce margins
- Solution: Subscriptions, ads, and logistics monetization to offset costs
Labor & Regulation
- Challenge: Delivery workforce management
- Solution: Structured shifts, automation, and compliance-first policies
Why This Growth Model Is Defensible
Coupang’s scale is hard to attack because:
- New entrants can’t easily replicate logistics density
- Capital alone cannot buy execution excellence
- Customer expectations reset around speed and reliability
Competitive Strategy & Market Defense
Coupang operates in one of the most competitive e-commerce markets in the world — yet it continues to strengthen its position. Its competitive strategy is built not on price wars, but on structural advantages that are difficult to copy.
Rather than reacting to competitors, Coupang forces competitors to react to it.
Core Competitive Advantages
Logistics-Driven Network Effects
- Faster delivery increases customer frequency
- Higher frequency improves logistics utilization
- Better utilization lowers marginal costs
This creates a feedback loop that improves with scale.
High Switching Barriers
- Rocket WOW subscriptions lock in habits
- Saved preferences, purchase history, and returns trust
- Sellers depend on Coupang’s fulfillment and demand
Leaving Coupang means sacrificing convenience or revenue.
Brand Trust & Reliability
- Consistent delivery SLAs
- Transparent returns and refunds
- Strong consumer confidence in execution
Trust becomes a competitive asset, not just a brand metric.
Technology & Data Advantage
- Proprietary routing and inventory algorithms
- Personalization at SKU and customer level
- Continuous learning from millions of daily transactions
Market Defense Tactics
Handling New Entrants
- Coupang rarely matches unsustainable discounts
- Instead, it raises service expectations
- New entrants struggle to meet delivery promises
Defending Against Pricing Wars
- Convenience-first positioning reduces price sensitivity
- Subscription benefits outweigh small price differences
Strategic Feature Timing
- Rolling out features only when operationally scalable
- Avoiding half-baked launches that hurt trust
Selective M&A and Expansion
- Acquiring capabilities, not users
- Building internally when integration matters most
Why Coupang Is Hard to Disrupt
Competitors can copy interfaces, pricing, or promotions. They cannot easily replicate:
- Years of logistics data
- Operational muscle memory
- Cultural obsession with execution
Coupang’s defense is not walls — it is momentum.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Implementation
Coupang’s journey offers rare, practical lessons for founders who want to build defensible, large-scale platforms rather than short-lived growth stories. Its success was not driven by a clever hack — it was driven by long-term conviction and disciplined execution.
Key Factors Behind Coupang’s Success
- Execution Over Ideation
Many companies had the idea of fast delivery. Coupang committed to making it reliable at scale. - Operational Control as a Moat
By owning logistics, Coupang controlled customer experience end-to-end. - Density Before Expansion
It dominated one market deeply before expanding geographically. - Habit Formation Beats Discounts
Convenience and reliability created daily usage, not constant promotions. - Patience With Profitability
Long-term infrastructure investment paid off through compounding advantages.
Replicable Principles for Startups
Entrepreneurs can adapt Coupang’s playbook without copying its scale:
- Identify the one operational bottleneck that defines your category
- Internalize what matters most to customer trust
- Use subscriptions to stabilize demand and cash flow
- Build systems that get better with every transaction
- Design for repeat usage, not one-time conversion
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Outsourcing core experience too early
- Expanding across geographies before achieving density
- Competing only on price without differentiation
- Ignoring operational readiness while scaling marketing
Adapting the Model for Local or Niche Markets
Coupang’s model works best when adapted, not cloned:
- Focus on high-density urban regions first
- Start with limited SKUs or services
- Build micro-fulfillment or partner-assisted logistics
- Gradually introduce subscriptions once trust is earned
At Miracuves, we help founders translate models like Coupang’s into practical, scalable platforms — without burning unnecessary capital. From marketplace architecture to logistics-enabled systems, our team has supported 200+ entrepreneurs in launching profitable digital ecosystems.
Ready to implement Coupang’s proven business model for your market?
Miracuves builds scalable platforms with tested business models and growth mechanisms.
Get your free business model consultation today.
Conclusion :
Coupang’s business model proves a powerful truth about modern platform economics: innovation creates opportunity, but execution creates dominance. In a world where most digital platforms race to become asset-light, Coupang went in the opposite direction — investing deeply in infrastructure, software, and operational control to deliver an experience competitors could not match.
For founders and operators, the lesson is clear: sustainable platforms are not built by chasing trends, but by owning the critical moments in a customer’s journey and executing them flawlessly, day after day.
As platform economies evolve beyond simple marketplaces into logistics-led, subscription-powered ecosystems, Coupang stands as a blueprint for what the future can look like — where technology and operations move as one, and scale is earned through reliability, not hype.
FAQs :
What type of business model does Coupang use?
Coupang operates a hybrid business model that combines first-party retail, third-party marketplace, subscription commerce, and vertically integrated logistics. Unlike asset-light marketplaces, Coupang owns and controls fulfillment and last-mile delivery, which is central to its value proposition.
How does Coupang’s business model create value?
Coupang removes friction through fast delivery, easy returns, and transparent pricing, building strong customer trust and repeat usage. Sellers benefit from built-in demand, logistics, and high conversion efficiency.
What are Coupang’s key success factors?
Coupang’s success comes from dense logistics infrastructure, high order frequency, Rocket WOW subscriptions, data-driven operations, and full control of the customer experience.
How scalable is Coupang’s business model?
The model scales effectively in dense urban markets where higher order volume improves logistics efficiency and lowers delivery costs. However, it requires significant upfront infrastructure investment.
What are the biggest challenges in Coupang’s model?
Major challenges include high logistics capex, labor and regulatory complexity, thin retail margins, and operational scale management. Coupang offsets these through automation and diversified revenue streams.
How can entrepreneurs adapt Coupang’s model to their region?
Founders should start in high-density cities, limit initial SKUs, partner for fulfillment early, and introduce subscriptions after earning customer trust.
What resources and timeframe are needed to launch a similar platform?
A localized platform can launch in 6–12 months using a marketplace and logistics-enabled tech stack, fulfillment partnerships, and capital focused on operations over marketing.
What are alternatives to Coupang’s model?
Alternatives include asset-light marketplaces, drop-shipping platforms, on-demand delivery aggregators, and subscription-only commerce models, each trading control for lower capital needs.
How has Coupang’s business model evolved over time?
Coupang evolved from a deals marketplace into a logistics-led ecosystem, adding subscriptions, advertising, content, and food delivery to become a daily-use platform.
Related Article :








