You’ve heard the horror stories—customer data leaks, payment breaches, hacked delivery apps, and startups losing their entire reputation overnight. In today’s digital food delivery economy, security failures don’t just cause technical issues—they destroy trust, invite lawsuits, and can permanently shut down a business.
In 2025, launching a white-label DoorDash app is no longer just about fast deployment and market entry. It is about how safely you can operate in a world of rising cybercrime, strict data protection laws, and increasingly sophisticated attacks on on-demand delivery platforms.
Food delivery apps now store and process:
- Real-time location data
- Personal customer information
- Restaurant business data
- Driver identity verification
- High-volume digital payment transactions
This makes them one of the most targeted app categories for cyberattacks today.
In this guide, we will provide a completely honest, practical, and security-first analysis of white-label DoorDash app safety in 2025—covering real risks, real compliance requirements, and real solutions that founders must implement before going live. You’ll also see how professional white-label platforms like Miracuves approach security differently by embedding protection at the infrastructure level, not as an afterthought.
This is not marketing hype. This is a real-world safety playbook for serious entrepreneurs.
Understanding White-Label DoorDash App Security Landscape
What “White-Label App Security” Actually Means
White-label app security refers to the protection mechanisms built into the core app framework provided by a solution vendor. It includes how user data is stored, how payments are processed, how servers are secured, and how vulnerabilities are monitored and fixed. Security is not controlled only by the app owner—it is largely determined by the provider’s infrastructure and policies.
Common Security Myths vs Reality
Many founders believe white-label apps are less secure than custom-built systems. In reality, professionally developed white-label apps often undergo more frequent testing and standardization than first-time custom projects. The real risk comes from low-quality providers, not from the white-label model itself.
Why People Worry About White-Label DoorDash Apps
Concerns mainly arise due to:
- Fear of shared code vulnerabilities
- Unclear data ownership policies
- Payment data exposure risks
- Third-party integrations
These fears are valid when vendors lack transparent security practices.
Current Threat Landscape for Food Delivery Platforms
Food delivery platforms are exposed to:
- Payment fraud
- Account takeover attacks
- Location data abuse
- Fake driver and restaurant profiles
- API exploitation
Attack volumes on delivery apps increased sharply between 2023–2025 due to automated bot-based fraud.
Security Standards in 2025
In 2025, secure on-demand apps are expected to meet:
- Zero-trust server architecture
- Encrypted cloud storage
- Continuous vulnerability monitoring
- Real-time API threat detection
Security is now treated as an operational requirement, not a one-time setup.
Real-World Statistics on App Security Incidents
Recent industry studies show:
- Over 38% of on-demand apps faced at least one major security incident in the last 24 months
- Payment-related breaches account for nearly 45% of reported cases
- Poor API security is responsible for more than 30% of mobile app attacks
Key Security Risks & How to Identify Them
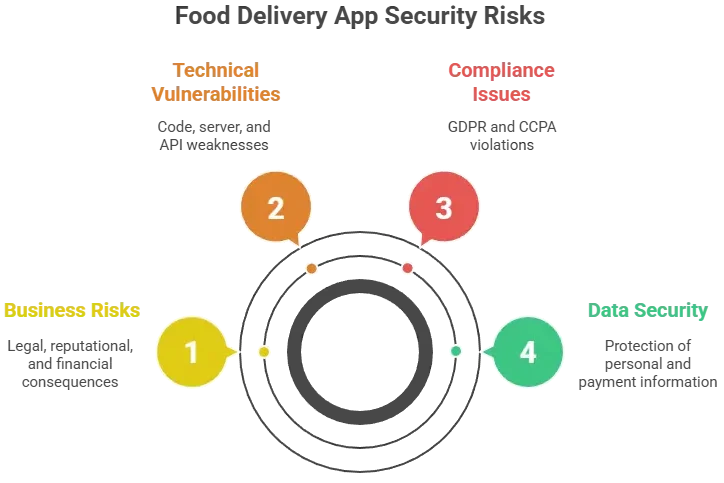
Risk Assessment Checklist
- Is all user and payment data encrypted at rest and in transit?
- Are servers protected by firewalls and intrusion detection systems?
- Are APIs authenticated, rate-limited, and monitored?
- Is the app fully GDPR and PCI DSS compliant?
- Are third-party services security-audited?
- Is there an active vulnerability patching policy?
- Is customer data backed up securely with disaster recovery?
Read more : – DoorDash Pricing Model and Strategy: How It Drives Success
Security Standards Your White-Label DoorDash App Must Meet
Essential Certifications
ISO 27001 Compliance
Ensures structured information security management across infrastructure, data, and operations.
SOC 2 Type II
Validates long-term control over data security, availability, and confidentiality.
GDPR Compliance
Mandatory for handling EU user data with strict consent and storage rules.
HIPAA (If Applicable)
Required only if health data such as prescriptions or medical orders are processed.
PCI DSS for Payments
Compulsory for handling card, wallet, and UPI payments securely.
Technical Security Requirements
End-to-End Encryption
Protects all data moving between users, drivers, restaurants, and servers.
Secure Authentication
Mandatory use of 2FA, OAuth, and token-based session management.
Regular Security Audits
Quarterly testing to detect vulnerabilities before attackers do.
Penetration Testing
Simulated attacks on live systems to test real-world hacking resistance.
SSL Certificates
Ensures encrypted browser and app communication at all times.
Secure API Design
Role-based access, rate limiting, and request validation for all APIs.
Security Standards Comparison Table
| Security Standard | Required for White-Label DoorDash App | Risk If Missing |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Yes | Data governance failure |
| SOC 2 Type II | Yes | Weak operational security |
| GDPR | Yes | Heavy legal penalties |
| PCI DSS | Yes | Payment fraud & chargebacks |
| SSL/TLS | Yes | Man-in-the-middle attacks |
| API Rate Limiting | Yes | API abuse & DDoS attacks |
| Penetration Testing | Yes | Undetected vulnerabilities |
Red Flags: How to Spot Unsafe White-Label Providers
Warning Signs
No Security Documentation
If a provider cannot share security architecture, audit reports, or data handling policies, it signals serious risk.
Cheap Pricing Without Explanation
Unrealistic pricing often means security has been compromised to cut costs.
No Compliance Certifications
Absence of ISO, SOC, GDPR, or PCI references indicates weak regulatory preparedness.
Outdated Technology Stack
Old frameworks and unsupported libraries expose known vulnerabilities.
Poor Code Quality
Unstructured code, no version control, and no testing pipeline increase breach probability.
No Security Updates Policy
Apps without scheduled patches become easy targets over time.
Lack of Data Backup Systems
No disaster recovery plan means permanent data loss during failures or attacks.
No Insurance Coverage
Professional providers protect clients with cyber liability insurance. Unsafe vendors do not.
Evaluation Checklist
Questions to Ask Providers
- How is user data encrypted and stored?
- Do you conduct third-party security audits?
- What is your incident response time?
- How often are security patches released?
Documents to Request
- ISO or SOC certificates
- PCI compliance documents
- Data protection policy
- Privacy impact assessments
Testing Procedures
- Live penetration testing reports
- API vulnerability test results
- Payment gateway security validation
Due Diligence Steps
- Verify past security breaches
- Check long-term update policy
- Review infrastructure architecture
- Confirm legal compliance coverage
Read more : – DoorDash Business Model Explained: Key Revenue Streams
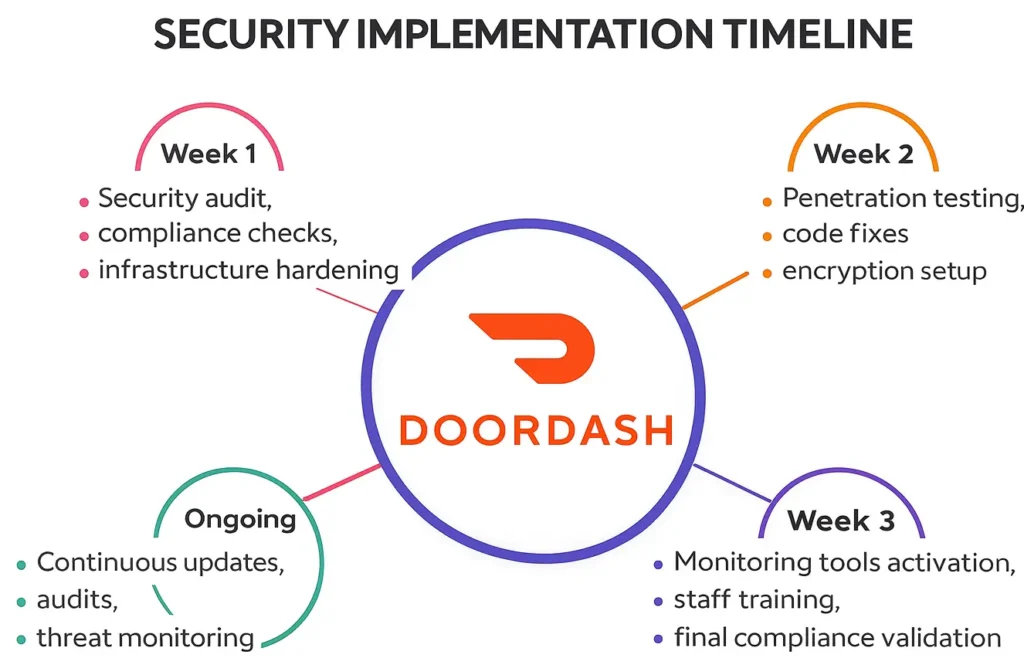
Best Practices for Secure White-Label DoorDash App Implementation
Pre-Launch Security
Security Audit Process
A full infrastructure and application security audit must be completed before launch to identify critical vulnerabilities.
Code Review Requirements
Source code should undergo automated and manual reviews to remove insecure logic, weak authentication, and exposed credentials.
Infrastructure Hardening
Cloud servers must be configured with firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and restricted access controls.
Compliance Verification
All legal and regulatory compliance such as GDPR and PCI DSS must be validated before accepting real users.
Staff Training Programs
Your internal team should be trained on data handling, breach response, and access control procedures.
Post-Launch Monitoring
Continuous Security Monitoring
Real-time monitoring tools must track unusual login attempts, transaction anomalies, and API abuse.
Regular Updates and Patches
Security patches should be released on a fixed schedule to counter new vulnerabilities.
Incident Response Planning
A documented response workflow is required for quick containment and recovery during breaches.
User Data Management
Data retention, deletion, and access requests must be handled as per privacy laws.
Backup and Recovery Systems
Encrypted daily backups and disaster recovery mechanisms protect against ransomware and server failures.
Legal & Compliance Considerations
Regulatory Requirements
Data Protection Laws by Region
Different regions impose different obligations such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in the USA, and DPDP Act in India. Non-compliance leads to heavy fines.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Food safety, consumer protection, and digital payment regulations apply alongside data protection laws.
User Consent Management
Explicit consent for data collection, tracking, and marketing communication is legally mandatory.
Privacy Policy Requirements
Privacy policies must clearly define data usage, storage duration, user rights, and third-party data sharing.
Terms of Service Essentials
User responsibilities, platform liabilities, delivery disputes, and refund policies must be legally defined.
Liability Protection
Insurance Requirements
Cyber liability insurance protects against financial losses caused by data breaches and system failures.
Legal Disclaimers
Disclaimers limit platform liability where legally permitted and clarify role as a technology provider.
User Agreements
Structured agreements protect against misuse, fraud, and unauthorized access.
Incident Reporting Protocols
Legal timelines for reporting security incidents to authorities and users must be followed strictly.
Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
Continuous legal monitoring ensures ongoing adherence as laws evolve.
Compliance Checklist by Region
- Europe: GDPR, PSD2, PCI DSS
- USA: CCPA, PCI DSS, FTC Consumer Protection
- India: Digital Personal Data Protection Act, IT Act, RBI payment rules
- Middle East: Local data residency and cybersecurity laws
- APAC: Country-specific data protection and cross-border transfer rules
Why Miracuves White-Label DoorDash App is Your Safest Choice
Miracuves Security Advantages
Enterprise-Grade Security Architecture
Miracuves builds its white-label DoorDash app on hardened cloud infrastructure with multi-layer security controls.
Regular Security Audits and Certifications
Independent audits, vulnerability scans, and compliance validations are performed at regular intervals.
GDPR and CCPA Compliant by Default
All core data handling mechanisms follow global data protection laws from day one.
24/7 Security Monitoring
Real-time threat detection systems actively monitor server traffic, login behavior, and API usage.
Encrypted Data Transmission
All user, driver, and restaurant data is encrypted during storage and transmission.
Secure Payment Processing
Payment flows are protected using PCI DSS compliant gateways with tokenization.
Regular Security Updates
Continuous patching ensures protection against newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Insurance Coverage Included
Cyber liability protection is included to safeguard businesses from unexpected financial risks.
Final thought
Do not compromise on security. Miracuves white-label DoorDash app solutions come with enterprise-grade protection built into the core architecture. With 600+ successful projects and zero major public security breaches, Miracuves offers businesses a secure, compliant, and reliable platform foundation. Get a free security assessment and understand how your app can meet global safety standards from day one.
Security is not an optional feature in a white-label DoorDash app—it is the foundation of long-term trust, legal safety, and business survival. Choosing a security-first platform from the start protects your users, your brand, and your revenue in an increasingly regulated digital market.
FAQs
1. How secure is a white-label DoorDash app compared to custom development?
A professionally built white-label app is often more secure than first-time custom builds because it follows tested security frameworks and certified compliance standards.
2. What happens if there is a security breach?
Immediate isolation, legal notification, user communication, data recovery, and insurance-backed financial protection are triggered through incident response protocols.
3. Who is responsible for security updates?
The white-label provider manages core security updates, while the app owner handles operational security policies.
4. How is user data protected in a white-label DoorDash app?
Through end-to-end encryption, role-based access control, secure cloud storage, and continuous monitoring.
5. What compliance certifications should I look for?
ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, PCI DSS, and region-specific data protection laws.
6. Can white-label apps meet enterprise security standards?
Yes, when built with certified infrastructure, secure DevOps practices, and continuous audits.
7. How often should security audits be conducted?
At least once every quarter, along with continuous automated vulnerability scanning.
8. What is included in the Miracuves security package?
Encrypted infrastructure, compliance readiness, monitoring, secure payments, audits, and cyber insurance coverage.
9. How is security handled across different countries?
By implementing region-specific data protection laws, data residency rules, and cross-border compliance frameworks.
10. What insurance is required for app security?
Cyber liability insurance, data breach insurance, and professional indemnity coverage.
Related Articles:








