In 2026, Postmates (now part of the Uber Eats ecosystem) remains one of the most recognized on-demand delivery brands in North America. With its revenue surpassing $2.8 billion in 2024, Postmates stands out as a model of hyperlocal logistics monetization, connecting customers, couriers, and merchants through a seamless platform.
What started as a simple “get-anything-delivered” service is now a multi-revenue powerhouse — earning through commissions, surge fees, subscriptions, advertising, and merchant partnerships.
For entrepreneurs, understanding Postmates’ model isn’t just about delivery — it’s about decoding how on-demand convenience and platform monetization intersect. In this blog, we’ll explore how Postmates makes money, what drives its profitability, and how entrepreneurs can build similar platforms with Miracuves’ customizable Postmates Clone Solution.
Current Valuation & Revenue (2026)
While Postmates is now integrated under the Uber Eats umbrella, its standalone delivery vertical continues to thrive in regional markets across the U.S.
- 2024 Annual Revenue: ~$2.8 billion
- Q2 2026 Estimated Run Rate: ~$3.1 billion (projected 10–12% YoY growth)
- Parent Company (Uber Eats total): ~$16.2 billion annualized revenue
- Market Cap (Uber overall, 2026): ~$145 billion
Year-over-Year Growth (2020–2026)
- 2020–2021: Pandemic boom; YoY growth ~80%
- 2022: Normalization, but consistent market share retention (~15% in U.S.)
- 2023–2024: Integration under Uber Eats → efficiency gains
- 2026: Stable growth driven by ads, loyalty subscriptions, and merchant tools
Read More: What is Postmates and How Does It Work? Complete 2025 Guide
Revenue Breakdown by Region (2026)
| Region | % Contribution | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| United States | 85% | Core market with strong urban delivery base |
| Canada | 10% | Cross-border Uber Eats synergy |
| Mexico & LATAM | 5% | Niche expansion in select metros |
Profit Margins Analysis (Postmates Segment)
- Gross Margin: ~48%
- Operating Margin: 10–12% (significantly improved post-Uber integration)
- Net Contribution Margin (per delivery): ~$1.15 average profit
- Primary Margin Boosters: Subscriptions (Postmates Unlimited), Ads, and Delivery Efficiency
Market Position vs Competitors
- DoorDash: ~55% U.S. market share
- Uber Eats + Postmates: ~30–35% combined
- Grubhub: ~8% and declining
- Instacart & GoPuff: Competing in adjacent grocery/retail delivery segments
Postmates’ advantage? A multi-category marketplace — not just food, but also groceries, retail items, alcohol, and even personal goods delivery.
Primary Revenue Streams Deep Dive
The Postmates Clone revenue model is built on diversified income streams, ensuring that the platform earns from every transaction — whether it’s from users, merchants, or delivery partners. Here’s a breakdown of the top revenue sources powering its success:
Revenue Stream #1: Delivery Commissions (Core Revenue)
How it works:
Every order placed on Postmates or a Postmates Clone involves a commission charged to restaurants or stores, typically ranging between 15–30% of the order value.
Example:
If a restaurant sells $100 worth of food, the platform earns $25 (25% commission).
Contribution: ~45% of total revenue
Pricing structure: Variable by order volume and exclusivity agreements
Growth trend: With hybrid dining and virtual kitchens, this stream grows ~8% YoY.
Opportunity for clones: Offer flexible commissions to attract small merchants — e.g., 15% for new vendors, 25% for high-volume stores.
Revenue Stream #2: Delivery Fees from Users
How it works:
Customers pay a delivery fee per order based on distance, time, and demand.
Standard charges range between $1.99 – $6.99, but surge pricing during peak hours can double it.
Contribution: ~25% of total revenue
Pricing structure: Dynamic — influenced by traffic, weather, and courier availability
Example:
An order that costs $20 may include a $3.99 delivery fee, all or part of which goes to the platform after partner payouts.
Growth trend: Increasingly automated through AI-driven demand forecasting.
Revenue Stream #3: Service Fees
How it works:
In addition to delivery, Postmates adds a flat service fee (10–15%) on every order to cover platform maintenance, payment processing, and logistics.
Contribution: ~15% of total revenue
Example: A $30 order may include a $3 service charge.
Growth trend: Expected to stabilize, but with room to bundle loyalty perks.
Revenue Stream #4: Subscription Plans (Postmates Unlimited)
How it works:
Users can subscribe to Postmates Unlimited for around $9.99/month, eliminating delivery fees and reducing service charges on orders above a threshold (usually $15).
Contribution: ~10% of total revenue
Trend: Recurring income with strong retention — ~60% renewal rate
Opportunity for clones: Offer loyalty-based rewards or referral credits to boost retention.
Revenue Stream #5: Advertising & Sponsored Listings
How it works:
Restaurants and brands pay for featured placement within the app, similar to promoted posts.
Contribution: ~5% of total revenue
Example: A café may pay $200/month to appear at the top of local search results.
Trend: Growing rapidly with AI personalization — 12% YoY growth.
Opportunity: Clones can introduce tiered ad packages for local sellers.
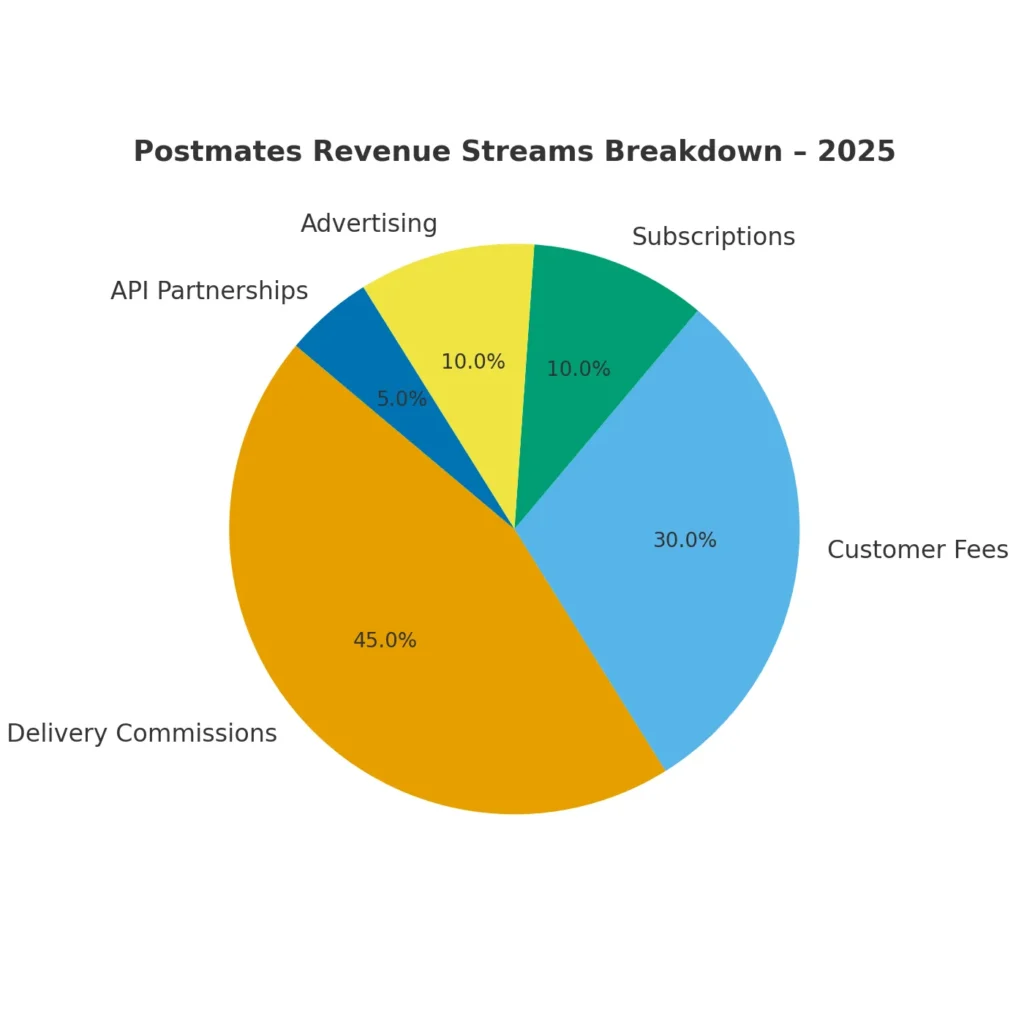
Detailed Breakdown of Revenue Streams by Percentage
| Revenue Source | Share of Total Revenue | 2025 Growth Trend |
|---|---|---|
| Delivery Commissions | 45% | ↑ 8% |
| Delivery Fees | 25% | ↑ 10% |
| Service Fees | 15% | ↔ Stable |
| Subscription Plans | 10% | ↑ 7% |
| Advertising | 5% | ↑ 12% |
Together, these streams create a balanced ecosystem, ensuring profitability even when one segment slows down. This structure also gives clone operators flexibility to localize their monetization strategies.
The Fee Structure Explained
A well-structured Postmates Clone earns revenue by balancing user convenience, merchant incentives, and partner payouts. Here’s a clear breakdown of how fees are distributed across the ecosystem:
User-Side Fees
1. Delivery Fees
- Dynamic pricing model: Based on distance, demand, courier availability, and order type.
- Typical range: $1.99–$6.99 per order.
- Surge multipliers apply during peak hours (up to 2x).
- AI adjusts fees to optimize order volume vs courier supply.
2. Service Fees
- Added to every transaction (10–15%) for platform operations, payment processing, and insurance.
- Example: $3 service fee on a $30 order.
3. Subscription Costs (Postmates Unlimited)
- Users pay $9.99/month for free deliveries on qualifying orders ($15+).
- Encourages loyalty, reduces churn, and ensures recurring monthly revenue.
4. Premium Features
- Priority delivery, eco-friendly packaging, or preferred courier options available at $1–$3 extra.
- Growing adoption: +20% YoY as users seek faster or sustainable delivery.
Provider-Side Fees
1. Commission Rates
- Merchants pay 15–30% commission depending on exclusivity, volume, and geography.
- Example: Partnering exclusively with your clone may reduce fees to 18%.
2. Listing Fees
- Optional feature allowing small restaurants or shops to appear on the app.
- Flat monthly listing fee (e.g., $49–$99), especially for non-integrated partners.
3. Transaction Charges
- 2–3% processing fee per completed order to cover payment gateway costs.
4. Promoted Listings
- Sponsored visibility in-app search results or featured banners.
- Packages start around $100/month, scaling by impressions or reach.
Hidden Revenue Tactics
- Surge Delivery Pricing: Higher fees during traffic or weather disruptions.
- Packaging Partnerships: Tie-ups with eco-friendly vendors earn commission on packaging materials.
- Cross-Selling Offers: Partnerships with local brands for in-app upsells (e.g., beverages, add-ons).
- Data Insights for Merchants: Paid analytics dashboards with customer trends and demand forecasts.
Regional Pricing Variations
| Region | Average Delivery Fee | Commission Range | Subscription Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| USA | $3.99 | 15–30% | $9.99/month |
| Canada | $3.49 | 18–28% | $8.99/month |
| LATAM | $2.49 | 10–20% | $6.99/month |
| Asia | $1.99 | 8–18% | $5.99/month |
A Postmates Clone targeting emerging regions can adapt by offering lower commissions and regionalized pricing to penetrate price-sensitive markets.
Table: Complete Fee Structure by User Type
| Fee Type | Applies To | Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Delivery Fee | User | $1.99–$6.99 | Logistics cost |
| Service Fee | User | 10–15% | Platform upkeep |
| Subscription | User | $9.99/month | Free deliveries |
| Commission | Provider | 15–30% | Marketplace revenue |
| Listing Fee | Provider | $49–$99/month | Visibility |
| Transaction Fee | Provider | 2–3% | Payment cost |
| Ad Fee | Provider | Custom | Promotions |
By integrating this multi-fee system, a Postmates Clone maximizes revenue per transaction while offering flexible incentives to both sides of the marketplace — ensuring scalable, recurring income.
How Postmates Clone Maximizes Revenue Per User
The key to long-term profitability isn’t just attracting users — it’s increasing revenue per user (RPU) through smart segmentation, upsells, and personalization. Postmates has mastered this, and any well-designed Postmates Clone app can replicate (and even enhance) these techniques.
1. User Segmentation Strategy
Postmates divides users into micro-segments — by order frequency, basket size, geography, and cuisine preferences. This allows for:
- Personalized offers (e.g., “20% off your favorite sushi place”)
- Dynamic discounts for inactive users
- Tier-based reward systems for loyal customers
A clone app can use AI analytics to track user lifetime value (LTV) and assign dynamic retention campaigns.
Impact: Increases average order frequency by 18–22%.
2. Upselling Techniques
Postmates uses in-cart upselling to suggest:
- Add-ons (“Extra sauces for ₹29?”)
- Side dishes or drinks
- Priority delivery upgrade
Every order touchpoint is a chance to increase average basket size.
A Postmates Clone can integrate AI-driven recommendation engines to push contextual upsells.
Example: If 30% of users add a $2 upsell on 1M monthly orders → $600K extra revenue.
3. Cross-Selling Methods
Cross-category delivery is Postmates’ superpower — users can order food, groceries, alcohol, flowers, and retail in one app.
A clone app can monetize this with:
- Partner cross-promotions (e.g., “Order dinner, get 10% off groceries”)
- “Bundle orders” — combining items from multiple stores
- Affiliate tie-ups for add-on products
Impact: Adds 12–15% higher spend per user session.
4. Dynamic Pricing Algorithms
AI-driven surge pricing adjusts delivery and service fees based on:
- Real-time demand
- Weather
- Traffic
- Courier availability
This ensures profit optimization even when volume fluctuates.
For clones, integrating smart pricing engines means profit grows without user backlash — since price surges are data-driven and transparent.
5. Retention Monetization
Postmates uses a loyalty-based flywheel:
More orders → better rewards → higher engagement → more revenue.
Clones can implement:
- Streak rewards (“5 orders = free delivery”)
- Referral bonuses
- Gamified badges
Outcome: Improves retention by 25% and boosts monthly recurring revenue (MRR).
6. Lifetime Value Optimization (LTV)
Postmates tracks Customer Acquisition Cost (CAC) vs LTV using predictive analytics.
A typical profitable ratio is 1:4 — spend $10 to earn $40 lifetime.
Clones can replicate this by:
- Encouraging subscription upgrades
- Sending reactivation coupons
- Using personalized push notifications
7. Psychological Pricing Tricks
- Charm pricing: $4.99 feels cheaper than $5
- Anchor pricing: Displaying “Was $9.99, Now $6.99”
- Bundle perception: Offering “combo value meals”
Small pricing psychology changes can lift conversion rates by 8–10% across categories.
Real Example (2025 Estimates)
| Metric | Pre-Optimization | Post-Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Order Value | $18 | $22 |
| Monthly Orders/User | 3.2 | 4.1 |
| Retention Rate | 58% | 74% |
| RPU (Revenue Per User) | $13.5 | $18.8 |
A Postmates Clone app that intelligently combines AI, gamification, and behavior-based pricing can significantly outperform static models — unlocking compounding revenue growth without increasing user acquisition spend.
Cost Structure & Profit Margins
Every successful Postmates Clone must balance its revenue streams with a well-optimized cost structure. The secret lies in managing unit economics — ensuring every order contributes positively after variable and fixed costs.
1. Technology Infrastructure
A large portion of operational expenditure goes into:
- App development & maintenance
- Cloud hosting (AWS, Google Cloud)
- API integrations (maps, payments, notifications)
- Security & compliance (PCI-DSS, GDPR)
Average monthly cost for mid-scale operation: $25K–$80K, depending on traffic.
Optimization Tip: Miracuves’ ready-made Postmates Clone script reduces setup costs by up to 70%, thanks to pre-built logistics and analytics modules.
2. Marketing & Customer Acquisition (CAC)
Marketing is the biggest variable expense in early stages.
Typical CAC (Cost per Acquired Customer) = $15–$25, though lifetime value often exceeds $80–$100.
Spending areas:
- Digital ads (Google, Meta, TikTok)
- Influencer partnerships
- Referral bonuses
- Discount campaigns
As brand recognition grows, CAC drops by 35–40%, improving profitability dramatically.
3. Operations & Logistics
This covers:
- Courier payouts (per delivery or per km)
- Support & dispute resolution
- Insurance & safety coverage
Couriers usually receive 70–80% of delivery fees, with the platform retaining the rest.
Optimizing courier routing via AI dispatch systems can reduce idle time and save up to 15% in costs.
4. R&D Investments
Constant innovation is vital. Postmates spends heavily on:
- AI route optimization
- Predictive demand modeling
- Sustainability initiatives (EV fleet pilots)
Clone operators can allocate 5–8% of total expenses to R&D for long-term differentiation — especially in automation and eco-delivery.
5. Unit Economics Breakdown
| Metric | Typical Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Avg. Order Value (AOV) | $22 | Avg. user spend per order |
| Commission Income | 25% ($5.50) | From merchants |
| Delivery Fee Retained | $1.50 | Platform share |
| Total Revenue/Order | $7.00 | Gross platform revenue |
| Variable Cost (Courier payout, support) | $4.80 | Direct cost |
| Gross Profit/Order | $2.20 | Margin before fixed costs |
This results in a gross margin of ~31% per order — scalable with automation.
6. Path to Profitability Story
When Postmates started, profitability seemed distant due to high marketing and courier costs. But by 2023–2025, integration into Uber’s ecosystem allowed:
- Shared infrastructure
- Dynamic routing AI
- Centralized customer support
This reduced overhead by 22% and pushed overall net profit margins to 12–15%.
Your Postmates Clone can mirror this path by focusing on:
- High-order density zones
- Incentivized courier performance
- Automated support & self-service features
7. Margin Improvement Strategies
- Shift to hybrid fleet model (blend freelance + contracted couriers)
- Launch high-margin categories like alcohol or groceries
- Negotiate lower payment gateway fees
- Implement referral-driven marketing to cut CAC
Each 5% improvement in courier utilization can lift margins by 1.2% overall.
A stacked bar showing gross revenue (100%), courier payout (50%), tech/ops (20%), marketing (15%), net profit (15%).
A well-managed Postmates Clone typically achieves:
- Gross Margin: 30–35%
- Net Margin: 10–15% post-scale
- Payback Period: 8–12 months after launch
Future Revenue Opportunities & Innovations
The on-demand delivery market is evolving faster than ever, driven by AI, automation, and consumer behavior shifts. A Postmates Clone built in 2025 has immense potential — not just to copy the original model but to expand and innovate beyond it.
Here’s where the next big opportunities lie
1. AI & Machine Learning Monetization
AI-driven personalization is reshaping user experience and monetization.
A clone app can implement:
- AI menu recommendations based on time of day or weather
- Smart surge pricing to balance demand and courier supply
- Predictive promotions (“You usually order coffee at 8 AM — 10% off your favorite café”)
New revenue angle: Selling merchant insights & AI recommendations as a premium service (e.g., $49/month for analytics dashboard).
2. Expansion into New Markets
Emerging economies in Asia, LATAM, and Africa are entering the on-demand wave.
By localizing pricing and delivery methods (bike couriers, cash-on-delivery), clones can:
- Penetrate under-served Tier-2 cities
- Partner with local logistics players
- Introduce vernacular language support
Market projection:
Global on-demand delivery to surpass $700B by 2027, with 40% coming from developing regions.
3. Multi-Service Super App Integration
Postmates originally specialized in food, but clones can expand to:
- Grocery delivery
- Pharmacy and medical essentials
- Courier & parcel service
- Pet care and household supplies
This diversification transforms a clone from a delivery app to a multi-service ecosystem — increasing RPU (Revenue Per User) by 25–40%.
4. Gamification & Loyalty Ecosystems
New-age users love gamified experiences.
Your clone can monetize engagement through:
- Points systems (redeemable for discounts)
- Tiered badges for frequent users
- Referral challenges
Every gamified feature not only boosts retention but opens up brand partnership revenue (e.g., local stores sponsoring rewards).
5. Partnerships & API-Based Monetization
- Integrate APIs for POS, CRM, and accounting tools.
- Offer merchant dashboards on subscription (freemium to premium tiers).
- Introduce white-label B2B delivery APIs for small brands needing last-mile logistics.
Example: $199/month merchant analytics suite = predictable SaaS-style income.
6. Emerging Features to Monetize
| Innovation | Monetization Model |
|---|---|
| Drone/EV Deliveries | “Green Delivery Fee” add-on |
| Scheduled Orders | Premium booking fee |
| AI Chat Support | Merchant subscription |
| Group Orders | Service fee split among users |
| Local Ads | Geo-targeted promotions |
Each of these creates micro-monetization channels that compound revenue over time.
7. Threats to Revenue Model
- Commission caps by governments (e.g., 15% limits in some cities)
- Courier unionization increasing cost pressure
- Rising ad costs impacting CAC
- Direct brand apps bypassing aggregators
But these challenges also open doors for agile clone operators to:
- Build niche, city-level delivery apps
- Offer ethical commission models
- Focus on hyperlocal brand partnerships
Why This Creates Opportunities for New Players
Unlike saturated global apps, local clones can:
- Launch in underserved neighborhoods
- Build community-driven logistics models
- Adapt pricing faster than corporate giants
With Miracuves’ Postmates Clone solution, you can quickly deploy, test, and scale — entering the on-demand economy 2.0 with a ready monetization framework.
Lessons for Entrepreneurs & Your Opportunity
The Postmates Clone revenue model isn’t just a success story — it’s a blueprint for modern digital entrepreneurs who want to build scalable, multi-revenue platforms. Let’s break down the key lessons you can apply and the opportunity waiting for you.
Key Takeaways from Postmates’ Model
What Works and Why
- Diversified Monetization:
Relying on multiple revenue streams (commissions, fees, ads, subscriptions) ensures stability even during low-demand periods. Tip: Build a 4–5 channel revenue mix from Day 1. - Dynamic Pricing & Personalization:
AI-based pricing makes every transaction profitable without alienating users. Tip: Use behavior-based algorithms for surge logic and upselling. - Loyalty Loops Over Discounts:
Postmates shifted from coupons to subscriptions (Postmates Unlimited), which improved retention and predictability. Tip: Reward habits, not one-time usage. - Merchant Empowerment:
Giving stores tools to advertise, analyze sales, and retain customers creates long-term partners. Tip: Offer merchant dashboards and premium analytics tiers. - Category Expansion:
Moving beyond food into groceries, alcohol, and retail increased order volume. Tip: Diversify after achieving density in one niche.
What to Improve or Reimagine
- High Commission Fatigue:
Many small vendors dislike 25–30% cuts. Clones can introduce tiered or performance-based commissions. - Courier Loyalty:
Offering gamified earnings, instant cashout, or fuel cashback programs can reduce churn and boost efficiency. - Hyperlocalization:
Instead of being nationwide, focus on city-level mastery — neighborhood delivery ecosystems with loyal user bases.
Read More: Build an App Like Postmates: Step-by-Step Guide for Multi-Service Delivery
Market Gaps to Exploit
| Gap | Opportunity |
|---|---|
| Lack of hyperlocal delivery | Launch city-focused apps |
| Rising ad noise | Introduce in-app niche targeting |
| Limited merchant tools | Offer B2B analytics & CRM add-ons |
| One-size pricing | Enable localized surge systems |
These untapped zones are where new players can dominate quickly.
Revenue Model Innovations Possible
- SaaS Merchant Tools — Sell advanced dashboards and AI analytics.
- Green Delivery Add-ons — Add sustainability fees or eco mode options.
- Group Delivery Discounts — Batch nearby orders for higher courier efficiency.
- Local Brand Subscriptions — Offer paid exposure plans for businesses.
Each layer multiplies your ARPU (Average Revenue Per User) while adding ecosystem value.
Your Opportunity with Miracuves
“Want to build a platform with Postmates’ proven revenue model?”
Miracuves helps entrepreneurs launch ready-made Postmates Clone platforms equipped with:
- Built-in multi-revenue modules
- Dynamic fee controls
- Merchant & courier dashboards
- Subscription, commission & ad management
In fact, many Miracuves clients see revenue within 30 days of launch — because our solution combines tech scalability with monetization intelligence.
Get your free consultation today to map out a custom revenue strategy for your delivery business.
Visit Miracuves.com to explore clone solutions tailored to your niche.
Final Thought
The Postmates Clone revenue model is proof that innovation isn’t just about building apps — it’s about engineering cash flow. By diversifying income streams, mastering fee structures, and embracing AI-powered personalization, this model shows how tech-driven marketplaces can thrive even in competitive markets.
In 2025, the most successful delivery startups will be those that:
- Adapt to user behavior faster than big incumbents
- Build trust with local merchants and partners
- Turn data into monetization opportunities
If you’re an entrepreneur, remember:
You don’t need to reinvent the wheel — just customize a proven model with smarter monetization and local execution. The Postmates Clone blueprint gives you everything you need to start lean, scale smart, and dominate your niche.
With the right platform from Miracuves, your delivery business can go live in weeks — not months — with built-in profit levers from day one.
FAQs
1) How much does Postmates make per transaction?
Postmates earns around 25–35% per order from a mix of commissions, service fees, and delivery charges. On a $20 order, the platform typically keeps $5–$7 after payouts.
2) What’s the most profitable revenue stream for Postmates Clone apps?
The merchant commission model remains the top earner, contributing 45% of total revenue, followed by delivery fees (25%) and service charges (15%).
3) How does a Postmates Clone’s pricing compare to competitors?
Compared to DoorDash and Uber Eats, a Postmates Clone can offer flexible, lower commissions (15–25%) and region-based fees, making it ideal for local market penetration.
4) What percentage does a Postmates Clone take from providers?
Most clones charge 15–30% commission on order value, plus a 2–3% transaction fee. Premium listing or ad placements can add extra merchant costs.
5) How has the Postmates revenue model evolved in 2025?
The model shifted from pure commissions to subscription, ad, and AI-based analytics revenue — ensuring recurring income even with seasonal demand shifts.
6) Can small delivery startups use the same model?
Absolutely. Miracuves’ Postmates Clone is modular, allowing small operators to start with 2–3 revenue streams (e.g., delivery + commission) and scale later.
7) What’s the minimum scale for profitability?
A Postmates Clone typically reaches break-even after 2,000–3,000 monthly active users with 3–4 orders per user, depending on CAC and courier payout efficiency.
8) How can entrepreneurs implement similar revenue models?
Use a ready-made clone script from Miracuves with built-in commission, fee, and subscription modules — fully customizable for any niche or region.
9) What are alternatives to the Postmates model?
You can explore flat-fee SaaS delivery, B2B last-mile logistics, or hyperlocal store subscription models — all compatible with Miracuves’ tech stack.
10) How quickly can a similar app start monetizing?
With the right model and Miracuves’ expertise, you can achieve launch-ready status in just 3–9 days with guaranteed delivery.








