In 2025, the ride-hailing industry continues to revolutionize urban mobility—and Uber and Lyft remain at the forefront. While these giants share a common service—on-demand transportation—their business models, revenue strategies, and market approaches diverge in significant ways.
For startup founders and app entrepreneurs, choosing between building an Uber-style super app or a more focused Lyft-style service can dictate product roadmap, capital requirements, and market positioning. With emerging trends like electric fleets, AI-powered dispatch, gig economy regulation, and micromobility, the time has never been more critical to study and emulate the right model.
This blog breaks down the Uber vs Lyft business models, comparing them across core areas like revenue, cost structure, partnerships, and user growth. By the end, you’ll know exactly which blueprint suits your vision—and how to act on it.
What is Uber?
Uber is a global ride-hailing and mobility platform founded in 2009. Beyond traditional ridesharing, Uber has expanded into food delivery (Uber Eats), freight logistics, autonomous driving R&D, and micromobility.
Core Features:
- On-demand rides in 10,000+ cities worldwide
- Multi-vertical: rides, food, freight, bikes, EV rentals
- Real-time matching algorithm, surge pricing, safety tools
- Driver-partner network using personal or leased vehicles
Uber’s goal is to be the “Amazon of transportation”—a comprehensive platform that powers every form of urban movement.
What is Lyft?
Lyft is a U.S.-focused rideshare platform founded in 2012, known for its community-first approach and simplified service offerings. Unlike Uber, Lyft has remained focused on transportation services with less diversification.
Core Features:
- Ride-hailing across 600+ U.S. and Canadian cities
- Multiple ride types: standard, shared, luxury, rentals
- Integration with public transport and bike/scooter rentals
- Emphasis on sustainability and EV adoption
Lyft offers a leaner, user-centric experience designed for consistency, ethical gig work, and a strong domestic market presence.
Business Model of Uber
Revenue Streams
- Ride Commissions: 15–30% from each trip booked
- Uber Eats Delivery Fees & Restaurant Commissions
- Freight and Logistics Solutions
- Driver & Rider Fees (cancellation, service)
- Subscription Products (Uber One)
- Advertising: In-app promotions for restaurants & products
- Strategic Investments: Equity stakes in emerging tech
Cost Structure
- Driver incentives and loyalty programs
- Tech R&D (AI dispatch, AV development)
- Global expansion and regulatory compliance
- Customer acquisition, promotions, and refunds
- Platform maintenance, cloud hosting
Key Partnerships
- Vehicle rental/leasing (Hertz, Lime, Tesla)
- Fleet & delivery partners (Postmates, Cornershop)
- Payment providers (PayPal, Apple Pay)
- Municipalities for transit integration
- Ads & brand promotions (AdMob, Marquee Ads)
Growth Strategy
- Expand to Tier 2/3 cities in emerging markets
- Develop autonomous vehicles (Uber ATG divested to Aurora)
- Strengthen Uber Eats in competition with DoorDash
- Build advertising as a high-margin business vertical
- Bundle services under Uber One for higher LTV
Business Model of Lyft
Revenue Streams
- Ride Commissions: 15–25% of fare
- Vehicle Rentals (Lyft Rentals)
- Micromobility (Bikes, Scooters)
- Lyft Pink Subscriptions
- Fleet Management Software (Lyft Business)
- EV Partnerships: Charging services, carbon offsets
Cost Structure
- Driver incentives and bonuses
- Vehicle acquisition and micromobility maintenance
- Engineering & platform innovation
- Government lobbying and safety compliance
- Brand marketing and user discounts
Key Partnerships
- Rental and fleet partners (Hertz, GM, Ford)
- Public transport (integration with local transit apps)
- Google Maps, Apple Maps integrations
- EV infrastructure partners (ChargePoint)
- Universities and large employers (Lyft Business)
Growth Strategy
- Focus on profitable urban cores
- Transition to electric and autonomous fleets
- Expand Lyft Business for corporate transit
- Deepen public transport integrations
- Improve gig driver retention with flexible policies
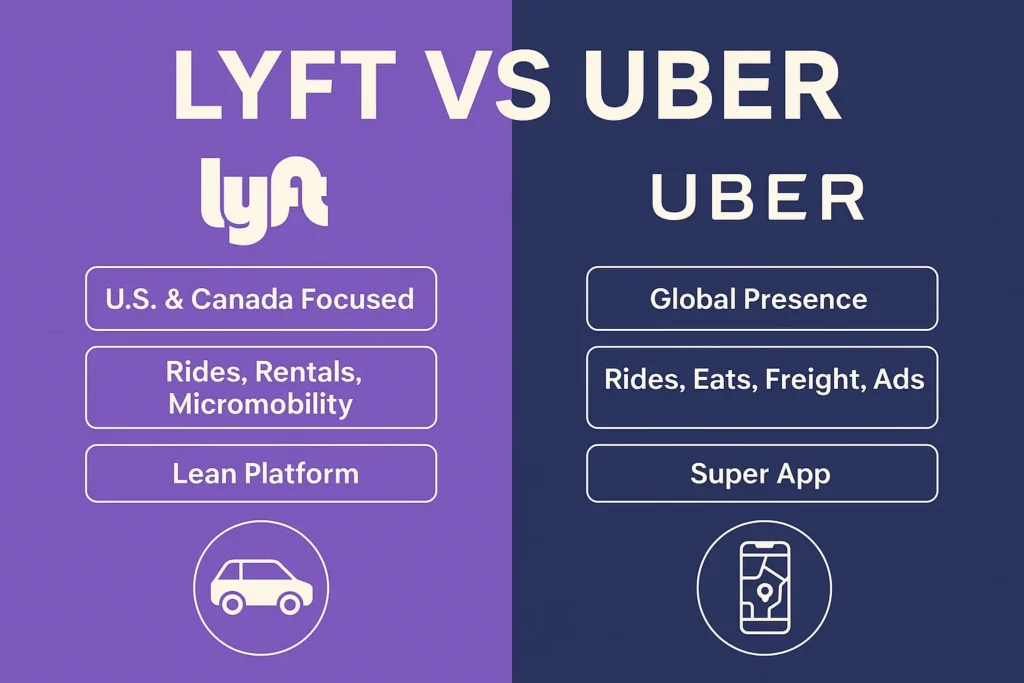
Comparison Table: Uber vs Lyft
| Feature | Uber | Lyft |
| Market Focus | Global | U.S. & Canada |
| Revenue Streams | Rides, Eats, Freight, Ads | Rides, Rentals, Micromobility |
| Diversification | High (super app strategy) | Medium (mobility only) |
| Subscription Plans | Uber One | Lyft Pink |
| Tech Investment | AVs, AI, Robotics, Ads | EV infrastructure, AVs |
| Partner Ecosystem | Restaurants, Couriers, Fleets | Fleets, Transit, Cities |
| Profitability Strategy | Cross-vertical monetization | Focused operational efficiency |
| Driver Dependency | High | High |
| Public Transit Integration | Growing | Strong in core markets |
| Link to Clone | /uber-clone | /lyft-clone |
Pros & Cons of Uber’s Business Model
Pros
- Diversified revenue reduces dependency on rideshare
- Global footprint enables cross-border scaling
- High brand visibility and app engagement
- Opportunities to upsell via Uber Eats and Freight
Cons
- Complex to manage across markets and services
- High regulatory and compliance cost globally
- Greater operational risk due to diversification
- Slower unit economics in newer markets
Pros & Cons of Lyft’s Business Model
Pros
- Focused operation leads to clearer vision and UX
- Easier to localize services for domestic markets
- Faster path to profitability via core strengths
- Leaner app experience, low tech debt
Cons
- Limited international growth potential
- Fewer monetization opportunities beyond rides
- High exposure to U.S. market volatility
- Reliant on EV incentives and infrastructure
Market Data: Growth, Revenue, and Funding (2025)
| Metric | Uber | Lyft |
| 2024 Revenue | $37.3B | $4.4B |
| Market Cap (2025) | ~$140B | ~$5.5B |
| Total Users (Riders) | 130M+ | 25M+ |
| Global Reach | 70+ countries | U.S. + Canada only |
| Monthly Active Drivers | 5M+ | 1.5M |
| Funding Raised (all-time) | ~$25B | ~$5B |
| Valuation Trends | Growing post-pandemic | Stabilized after cost cuts |
Which Model is Better for Startups in 2025?
Both models offer viable paths—but your decision should reflect your target market size, budget, and vision.
- Want to build a mobility super app with room for delivery, ads, and logistics? Uber-style is for you.
- Prefer a focused, lean platform optimized for local ride efficiency and driver loyalty? Go Lyft-style.
If you’re a startup in an emerging economy or urban transport hub, Uber’s breadth may open more doors. But if you’re building for one region with high density, Lyft’s tight model may help you scale faster.
Choose Uber-Style If…
- You want to bundle services like food, freight, and rides
- You’re entering multiple cities or countries
- You have funding to scale across verticals
- You aim to build a super app experience
Build Your Own Uber Clone with Miracuves
Choose Lyft-Style If…
- You prefer to master one region or country
- You aim to launch quickly with lower complexity
- You want to focus on rideshare, rentals & micromobility
- You plan to integrate with local transit or institutions
Build Your Own Lyft Clone with Miracuves
Conclusion
Whether you choose to replicate Uber’s expansive mobility empire or Lyft’s simplified, community-first service, Miracuves is your go-to partner for ride-hailing app development.
With deep expertise in on-demand platforms, geolocation, driver networks, and payment systems, we’ll help you launch a scalable, secure, and feature-rich platform tailored for 2025 and beyond.
Ready to build the next big thing in mobility
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Uber and Lyft’s business models?
Uber operates as a super app with rides, food, freight, and ads; Lyft focuses primarily on ride-hailing and micromobility in North America.
2. Which is more profitable in 2025—Uber or Lyft?
Uber has more diversified revenue streams and global scale, making it more profitable overall. Lyft has optimized its U.S. operations for leaner profitability.
3. Can startups still enter the ride-hailing space in 2025?
Yes—especially in underserved Tier 2/3 markets or by focusing on niche segments like EV fleets, safety-first apps, or women-only services.
4. Is it harder to build an Uber clone or a Lyft clone?
Uber clones require more infrastructure and vertical integration; Lyft-style platforms are easier to launch and operate at a smaller scale.
5. Does Miracuves offer white-label ride-hailing app solutions?
Absolutely! Miracuves builds custom Uber and Lyft clone apps with driver management, real-time tracking, in-app payments, and admin dashboards.








