You’ve heard the horror stories about dating apps — data breaches, fake profiles, and privacy violations. For entrepreneurs building a white-label Tinder app, these concerns hit even harder. After all, your platform will handle sensitive user data, including personal identities, chat histories, and location tracking.
In 2025, security is no longer optional. As global regulations tighten and user awareness grows, any compromise in safety can destroy credibility overnight. Building a dating platform that feels both exciting and secure is the challenge of this era.
This guide offers an honest, data-driven assessment of white-label Tinder app safety — exposing myths, clarifying risks, and outlining the exact standards you must meet. You’ll also see how Miracuves’ white-label solutions ensure enterprise-grade security, compliance, and user trust by design.
Understanding White-label Tinder App Security Landscape
What white-label security actually means
A white-label Tinder app is built on a pre-engineered dating platform framework that can be fully rebranded and customized. From a security perspective, this means the core architecture, encryption layers, authentication system, and server logic are already established before your customization begins. When engineered correctly, this provides a stable, tested, and hardened security base. When done poorly, it becomes a single point of failure replicated across many apps.
Common security myths vs reality
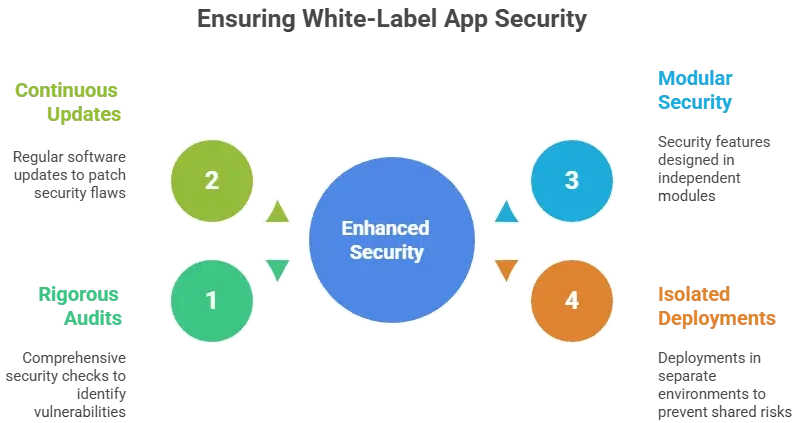
Why people worry about white-label apps
Dating apps deal with extremely sensitive information. Users fear that these systems may expose their identity, location, preferences, photos, and private conversations. Entrepreneurs worry about compliance liabilities, data theft, reputation damage, and legal consequences in case of breaches.
Current threat landscape for Tinder-type platforms
Dating platforms are among the top ten targets for cyberattacks globally due to the high value of identity data. Key threats include:
- Account takeovers via weak authentication
- Location tracking leakage
- API exploitation
- Fake profile fraud and impersonation
- Data scraping through unprotected endpoints
- Cloud misconfigurations exposing user images or chat logs
Security standards in 2025
The 2025 regulatory environment demands strict adherence to privacy and security frameworks:
- GDPR, CCPA, and global data protection laws
- ISO 27001 and SOC 2 Type II for organizational security
- PCI DSS for payment safety
- Robust encryption and zero-trust authentication
- Continuous vulnerability scanning and patching
- Penetration testing on infrastructure and mobile apps
Real-world statistics on app security incidents
- Dating apps saw a 38 percent rise in credential-stuffing attacks in 2024–2025.
- 1 in 5 dating platforms exposed user location due to poorly implemented GPS masking.
- Nearly 40 percent of breaches in social and dating apps were caused by insecure APIs.
- Over 55 percent of breached apps had no regular security audits in place.
- Apps storing unencrypted user images accounted for more than 30 percent of reported data exposure incidents.
These numbers show why white-label Tinder app security must be treated as a non-negotiable priority from day one.
Key Security Risks & How to Identify Them
A white-label Tinder-type app handles some of the most sensitive user information found in any consumer platform. Understanding the core risk areas is the first step toward building a safe, compliant, and trustworthy dating application.
Data Protection and Privacy Risks
User personal information
Dating apps store names, photos, preferences, identities, and bios. If this data is unencrypted or poorly stored, attackers can easily retrieve and misuse it.
Payment data security
If your app offers premium features, insecure payment gateways can expose card details or transaction histories. PCI DSS non-compliance increases financial and legal risks.
Location tracking concerns
Real-time GPS misuse is one of the biggest risks in a Tinder-style platform. Poorly masked coordinates allow attackers to triangulate exact user locations.
GDPR/CCPA compliance failures
Non-compliant data handling, improper consent systems, or missing deletion policies can result in severe penalties from global regulators.
Technical Vulnerabilities
Code quality issues
Unoptimized or outdated codebases lead to exploitable bugs, insecure storage, and broken authentication flows.
Server security gaps
Weak server configuration, missing firewalls, or unpatched systems can expose entire databases to automated attacks.
API vulnerabilities
Dating apps rely heavily on APIs for login, swiping, chat, and profile data. Insecure API endpoints can leak user identities, photos, or conversations.
Third-party integrations
Chat services, analytics tools, and cloud storage can all introduce additional attack surfaces if not securely implemented.
Business Risks
Legal liability
If a breach occurs due to weak app security, the business owner — not the tech vendor — often bears legal responsibility.
Reputation damage
One security incident can permanently destroy user trust in a dating app, drastically reducing adoption rates.
Financial losses
Costs include breach mitigation, legal fees, regulatory fines, customer compensation, and PR damage control.
Regulatory penalties
Fines for mishandled user data under GDPR, CCPA, or other laws can reach millions depending on severity.
Risk Assessment Checklist
Use this checklist to immediately evaluate whether your white-label Tinder app is at risk:
- Is all user data stored with modern encryption standards?
- Does the app implement secure location masking?
- Are payment systems PCI DSS compliant?
- Are APIs protected with rate limiting, authentication, and secure design?
- Does the provider offer proof of penetration testing?
- Is there a clear data retention and deletion policy?
- Are third-party tools audited for security compliance?
- Does the server infrastructure include firewalls, WAF, and intrusion detection?
- Are regular security updates and patches guaranteed?
- Does the vendor provide documentation of audits and compliance certifications?
If the answer to any of these is unclear, the app requires an immediate security review.
Read more : – Top 5 Mistakes Startups Make When Building a Tinder Clone
Security Standards Your White-label Tinder App Must Meet
For a white-label Tinder app to be truly safe, it must adhere to globally recognized security frameworks and technical safeguards. These standards protect user data, reduce breach risks, and ensure the platform meets legal and industry-specific requirements.
Essential Certifications
ISO 27001 compliance
Ensures that the organization behind your app follows strict information security management practices, covering data handling, access control, and risk mitigation.
SOC 2 Type II
Validates that the service provider maintains high security, availability, processing integrity, confidentiality, and privacy standards with continuous monitoring.
GDPR compliance
A must for any app handling EU user data, ensuring lawful processing, consent management, right-to-delete mechanisms, and transparent privacy policies.
HIPAA (if applicable)
Relevant only if your dating app collects or processes health-related data, such as wellness or compatibility metrics tied to medical information.
PCI DSS for payments
Required if the app processes card payments for premium features. It ensures cardholder data is handled securely during storage, transmission, and processing.
Technical Requirements
End-to-end encryption
Critical for protecting user chats, images, and identity data from interception during transmission.
Secure authentication (2FA/OAuth)
Adds an extra security layer to prevent account takeovers, the most common dating-app attack vector.
Regular security audits
Third-party audits uncover vulnerabilities in code, servers, APIs, and configurations before attackers do.
Penetration testing
Simulated attacks help validate the app’s resistance to real-world threats, including social engineering and API exploitation.
SSL certificates
Every bit of data transferred between app and server must be encrypted via HTTPS with strong TLS protocols.
Secure API design
Includes token-based authentication, rate limiting, encryption, and protection against injection attacks.
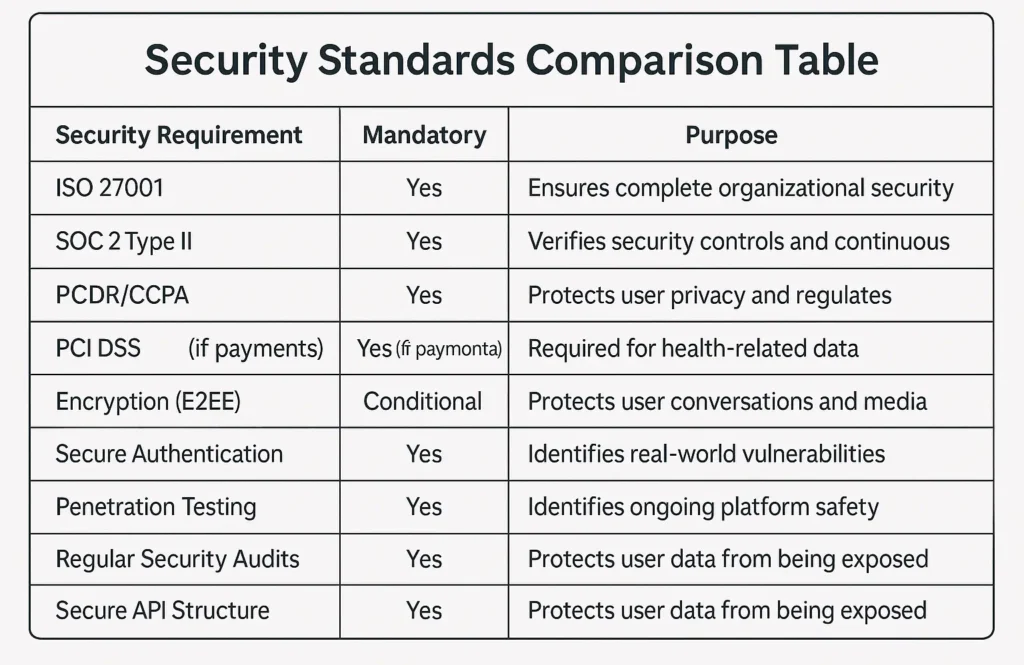
This is the absolute baseline for launching a safe and compliant dating app in 2025. Anything below this is a significant red flag.
Read more : – Tinder App Features Explained
Red Flags: How to Spot Unsafe White-label Providers
Not all white-label Tinder app providers prioritize security. Many focus on low pricing, fast delivery, or template-based development instead of building a robust and compliant security foundation. Identifying red flags early can save you from severe legal, financial, and reputational consequences.
No security documentation
If a provider cannot show detailed documentation on encryption, data flows, compliance procedures, or audit reports, the app is likely insecure from the core.
Cheap pricing without explanation
Significantly low prices often indicate outdated codebases, no audits, no compliance, reused vulnerable modules, and zero post-launch security support.
No compliance certifications
A provider without ISO 27001, SOC 2, GDPR compliance, or PCI DSS readiness is not equipped to build a safe dating platform.
Outdated technology stack
Old frameworks, deprecated libraries, and unmaintained dependencies are major sources of vulnerabilities.
Poor code quality
Signs include unoptimized scripts, no unit testing, missing encryption, or unsecured API structures.
No security updates policy
In dating apps, threats change rapidly. If a provider does not offer regular patches, your platform becomes unsafe within months.
Lack of data backup systems
Without automated and encrypted backups, recovery from system failure or breach is extremely difficult.
No insurance coverage
Security-first companies carry cyber liability insurance. Providers with no coverage usually lack professional-grade infrastructure and responsibility.
Evaluation Checklist
Use this checklist before signing with any white-label dating app provider:
Questions to ask providers
- How is user data encrypted at rest and in transit?
- Do you have ISO 27001 or SOC 2 Type II certification?
- Is the app architecture tested for OWASP vulnerabilities?
- How often do you release security updates?
- Do you offer logs and audit trails?
Documents to request
- Architecture diagrams
- API security documentation
- Audit reports or penetration test summaries
- Compliance certificates
- Server security policies
- Data backup and disaster recovery procedures
Testing procedures
- Perform third-party code audits
- Validate API encryption
- Test authentication for brute-force resilience
- Check SSL and TLS configurations
- Conduct load testing to detect failure points
Due diligence steps
- Review provider’s previous app launches
- Verify their infrastructure partners (AWS, GCP, Azure)
- Check marketplace ratings and security complaints
- Assess the age and quality of their codebase
- Confirm legal and cyber insurance coverage
If a provider fails more than two items on this checklist, they should be considered unsafe for high-risk app categories like dating platforms.
Best Practices for Secure White-label Tinder App Implementation
Launching a white-label Tinder app safely requires a structured approach before and after the platform goes live. Security is not a one-time activity but an ongoing discipline. Below are the essential best practices that every dating app entrepreneur must follow to ensure long-term protection, compliance, and user trust.
Pre-launch Security
Security audit process
Before launch, conduct a full security audit covering code structure, encryption mechanisms, server configurations, and third-party integrations. A professional audit identifies vulnerabilities that could otherwise go unnoticed.
Code review requirements
Have senior-level engineers review the entire codebase. This ensures secure coding standards, removes insecure logic, and validates the implementation of authentication and data protection measures.
Strengthen all components of the hosting environment
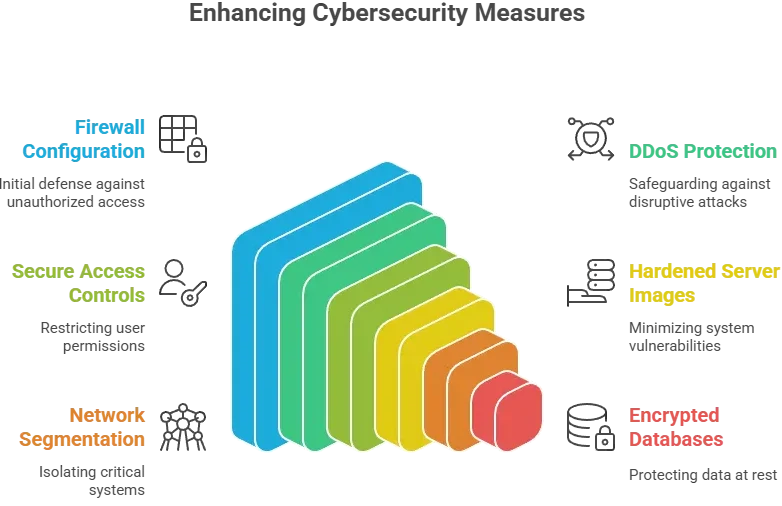
These measures reduce the chances of unauthorized access or service disruption.
Compliance verification
Ensure the app meets GDPR, CCPA, PCI DSS (for payments), and international data laws. Verify consent flows, data retention settings, deletion mechanisms, and privacy policy alignment.
Staff training programs
Your internal team must understand cybersecurity basics. Training should cover data handling, incident reporting, secure credentials, and phishing prevention.
Post-launch Monitoring
Continuous security monitoring
Use automated systems to monitor:
- Intrusion attempts
- Suspicious API traffic
- Authentication anomalies
- Server health
- Data access patterns
Real-time alerts help prevent breaches before they escalate.
Regular updates and patches
Dating platforms evolve constantly. Apply updates to:
- Fix vulnerabilities
- Patch libraries
- Update frameworks
- Strengthen encryption
- Improve API stability
Ignoring updates is one of the most common causes of breaches.
Incident response planning
Create a documented plan describing who does what in case of a security breach. It should include:
- Containment steps
- Communication protocols
- Legal notifications
- Data recovery actions
A strong response plan reduces damage significantly.
User data management
Define strict rules for storing, accessing, and deleting user data. Sensitive information must never be retained unnecessarily or stored without encryption.
Backup and recovery systems
Perform automated, encrypted backups daily or hourly depending on scale. Test restoration procedures to ensure your team can recover quickly after failures or attacks.
Security Implementation Timeline
| Phase | Timeline | Key Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Planning | Week 1 | Security architecture, compliance mapping, threat analysis |
| Development | Weeks 2–6 | Secure coding, API protection, encryption implementation |
| Pre-launch | Week 7 | Security audit, code review, penetration testing |
| Launch | Week 8 | Infrastructure hardening, SSL setup, monitoring activation |
| Post-launch | Ongoing | Updates, patches, continuous monitoring, periodic audits |
A structured timeline like this ensures the app launches securely and stays secure throughout its lifecycle.
Legal and Compliance Considerations
A white-label Tinder app must follow strict legal and regulatory frameworks because it handles highly sensitive user information such as identities, preferences, chat histories, and location data. Non-compliance can lead to lawsuits, platform bans, and severe financial penalties. This section outlines the legal requirements, regional regulations, and essential documentation needed to operate safely and responsibly.
Regulatory Requirements
Data protection laws by region
Dating apps must comply with global and region-specific privacy regulations. Key frameworks include:
- GDPR (Europe): Requires lawful data processing, transparency, consent management, and deletion rights.
- CCPA/CPRA (California): Governs data sales, user rights, and disclosure obligations.
- UK GDPR and PECR (United Kingdom): Regulates cookies, consent, and data sharing.
- PDPA (Singapore), LGPD (Brazil), NDPR (Nigeria): Region-specific obligations around data storage and user consent.
- India DPDP Act 2023: Requires explicit consent, data minimization, and security safeguards.
Failure to comply can lead to multi-million-dollar fines, especially for dating apps where user data is extremely sensitive.
Industry-specific regulations
Although dating apps aren’t medical or financial apps, they still fall under:
- PCI DSS (if processing card payments)
- Local telecom or digital regulations for OTP, messaging, or phone verification
- Age verification laws for adult content regions
User consent management
You must collect explicit user consent for:
- Data storage
- Location tracking
- Image and media uploads
- Behaviour analytics
- Marketing communication
Consent must be recorded, traceable, and revocable.
Privacy policy requirements
A compliant privacy policy should clearly explain:
- What data is collected
- How it is used
- Who it is shared with
- How users can request deletion
- Data retention periods
- Security measures applied
Policies must be accessible within the app, not hidden behind multiple layers.
Terms of service essentials
Your ToS must include:
- Acceptable use guidelines
- Safety expectations for users
- Rights and responsibilities of the business
- Prohibited activities
- Liability disclaimers
- Refund and cancellation policies for paid subscriptions
Liability Protection
Insurance requirements
A secure dating app should be backed by:
- Cyber liability insurance
- Data breach response insurance
- Errors and omissions (E&O) coverage
These protect your business against lawsuits, user claims, regulatory penalties, and data recovery costs.
Legal disclaimers
Clear disclaimers help limit liability for:
- User-generated content
- Misuse of the platform
- Fake profiles or fraudulent actors
- User interactions outside the app
User agreements
Every user should digitally sign or agree to:
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
- Community guidelines
- Age confirmation
This creates legal protection for your business.
Incident reporting protocols
You must have a system to report breaches to:
- Local authorities
- Users
- Regulatory bodies
GDPR requires breach reporting within 72 hours.
Regulatory compliance monitoring
Regulations change frequently. Your app must undergo periodic audits to stay legally compliant in all the regions it serves.
Compliance Checklist by Region
| Region | Key Law | Mandatory Requirements |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | GDPR | Consent, deletion rights, DPIA, encryption |
| USA | CCPA/CPRA | Opt-out options, transparency, breach notifications |
| UK | UK GDPR/PECR | Cookie consent, lawful processing, privacy notices |
| India | DPDP Act | Explicit consent, purpose limitation, secure processing |
| Brazil | LGPD | User rights, data minimization, legal basis for processing |
| Global | PCI DSS (if payments) | Secure card data, audits, encrypted transactions |
This compliance framework ensures your white-label Tinder app meets international standards and avoids legal risk.
Read more : – How to Hire the Best Tinder Clone Developer Company
Why Miracuves White-label Tinder App is Your Safest Choice
Choosing the right technology partner directly determines how secure your dating platform will be. Miracuves is engineered from the ground up as a security-first provider, ensuring that every white-label Tinder-style app delivers enterprise-level protection, compliance, and reliability. Our infrastructure, code practices, data governance systems, and monitoring frameworks are purpose-built to eliminate the common vulnerabilities found across dating apps.
Miracuves Security Advantages
Enterprise-grade security architecture
Miracuves uses hardened server configurations, encrypted databases, secure API gateways, and advanced firewalls to protect user identities, chat logs, images, and real-time location data.
Regular security audits and certifications
The platform undergoes frequent third-party audits, penetration tests, and vulnerability assessments to ensure compliance with international security standards.
GDPR/CCPA compliant by default
Consent management, data deletion mechanisms, traceable permissions, and transparent privacy flows are integrated into the app, helping you stay legally compliant without extra development work.
24/7 security monitoring
Miracuves offers real-time monitoring to detect malicious activities such as brute-force attempts, API abuse, suspicious login patterns, and intrusion events.
Encrypted data transmission
All communication is protected with strong TLS protocols and secure encryption layers. User content, including media and chat messages, is safeguarded against interception.
Secure payment processing
If your dating app includes premium features, Miracuves ensures PCI DSS compliance, secure payment gateways, and tokenized transaction handling.
Regular security updates
The threat landscape evolves constantly. Miracuves delivers continuous updates, patches, and security enhancements to keep your platform protected and compliant year-round.
Insurance coverage included
Unlike low-tier providers, Miracuves maintains cyber liability and infrastructure insurance, protecting you from unexpected risks beyond the development stage.
Conclusion :
Don’t compromise on security. Miracuves white-label Tinder app solutions come with enterprise-grade security built in. Our 600 plus successful projects have maintained zero major security breaches. Get a free security assessment and see why businesses trust Miracuves for safe, compliant dating platforms.
Building a white-label Tinder app in 2025 is no longer just about features, matching algorithms, or sleek design. It is fundamentally about trust. Users will only engage with platforms that make them feel safe, respected, and protected. A single vulnerability can compromise thousands of users and permanently damage your brand.
When you choose the right provider, follow strict security standards, and maintain continuous monitoring, a white-label Tinder app can be just as secure—if not more secure—than a fully custom-built solution. The key is partnering with a development company that treats security as a non-negotiable priority.
FAQs
1. How secure is a white-label app compared to custom development?
With proper audits and compliance, a white-label Tinder app can be equally secure because its architecture is already tested and hardened.
2. What happens if there’s a security breach?
You must follow an incident response plan including containment, notifications, recovery, and compliance reporting.
3. Who is responsible for security updates?
A reliable provider like Miracuves handles continuous updates, patches, and monitoring.
4. How is user data protected?
Through encryption, secure servers, strong authentication, and GDPR-compliant data handling practices.
5. What certifications should I look for?
ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, CCPA, PCI DSS (if payments), and regular audit reports.
6. Can white-label apps meet enterprise security standards?
Yes, provided the provider follows strict compliance, audits, and secure coding practices.
7. How often should security audits be conducted?
At least quarterly, with penetration testing done annually or before major releases.
8. What does Miracuves include in its security package?
Encryption, audits, monitoring, compliance setup, secure APIs, and infrastructure hardening.
9. How do I handle cross-country data security?
Follow regional laws (GDPR, CCPA, DPDP Act) and store data in compliant regions.
10. What insurance is needed for dating app security?
Cyber liability, breach response coverage, and errors and omissions insurance.
Related Articles: