You’ve heard the horror stories—food delivery apps leaking customer locations, payment data being compromised, and platforms being taken offline by security breaches overnight. As entrepreneurs rush to launch a white-label Grubhub app in 2025, one question dominates every serious discussion: Is it actually safe?
Food delivery apps today handle highly sensitive data—real-time GPS locations, saved payment credentials, personal addresses, order histories, and business revenue data. A single vulnerability can lead not only to financial loss, but permanent brand damage and regulatory penalties.
In 2025, safety is no longer a “technical feature.” It is the foundation of business trust, compliance, and long-term survival. With cyberattacks becoming more targeted and regulatory frameworks becoming stricter worldwide, ignoring security is no longer an option for founders entering the on-demand food delivery market.
This guide delivers an honest, practical security assessment of white-label Grubhub apps—covering real risks, current compliance standards, and the exact safeguards every serious founder must implement. You’ll learn what truly makes a white-label Grubhub app safe, what warning signs to avoid, and how to choose a provider that protects both your users and your business.
Understanding White-Label Grubhub App Security Landscape
What “White-Label App Security” Actually Means
White-label Grubhub app security refers to the protective layers built into the app’s code, servers, APIs, databases, and integrations that safeguard user data, payments, and business operations.
Common Security Myths vs Reality
Many founders believe white-label apps are inherently unsafe. In reality, risk depends on how the app is engineered, hosted, audited, and maintained—not on the white-label model itself.
Why People Worry About White-Label Apps
Concerns mainly arise from low-cost providers, lack of transparency, poor data handling, and absence of verified compliance certifications.
Current Threat Landscape for Food Delivery Apps
Food delivery apps face risks like payment fraud, account takeovers, GPS spoofing, data scraping, fake restaurants, and API abuse.
Security Standards in 2025
Modern food delivery apps must meet global data protection laws, encrypted communications, zero-trust infrastructure, and continuous vulnerability testing standards.
Real-World Security Statistics
In 2024–2025, over 38 percent of reported mobile app breaches were linked to payment APIs, location services, and third-party integrations in on-demand platforms.
Key Security Risks & How to Identify Them
Data Protection & Privacy Risks
User Personal Information
Names, phone numbers, delivery addresses, and order history are highly valuable to attackers and must be securely encrypted.
Payment Data Security
Saved cards, wallet balances, and transaction logs are primary targets for fraud and financial theft.
Location Tracking Concerns
Real-time driver and user GPS data can be abused if APIs and databases are not properly secured.
GDPR / CCPA Compliance
Improper consent management and data storage violations can lead to heavy legal penalties.
Technical Vulnerabilities
Code Quality Issues
Poorly written code creates backdoors for attackers and increases exploit risk.
Server Security Gaps
Weak cloud configuration exposes databases and user records to public access.
API Vulnerabilities
Unsecured APIs allow data scraping, fake orders, and account manipulation.
Third-Party Integrations
Payment gateways, maps, and SMS providers introduce indirect security risks.
Business Risks
Legal Liability
Data breaches expose founders to lawsuits and regulatory action.
Reputation Damage
User trust collapses instantly after a public breach disclosure.
Financial Losses
Fraud, refunds, chargebacks, and regulatory fines cause direct revenue damage.
Regulatory Penalties
Non-compliance can result in service shutdowns and multi-million-dollar fines.
Risk Assessment Checklist

Security Standards Your White-Label Grubhub App Must Meet
Essential Certifications
ISO 27001
Ensures structured information security management across systems and teams.
SOC 2 Type II
Verifies secure handling of customer data over extended operational periods.
GDPR Compliance
Mandatory for protecting personal data of users in the European Union.
HIPAA (If Applicable)
Required if health or medical food data is processed.
PCI DSS
Mandatory for handling online payments and card transactions securely.
Technical Security Requirements
End-to-End Encryption
Protects data from user device to server without exposure.
Secure Authentication
Two-factor authentication and OAuth-based login systems prevent account hijacking.
Regular Security Audits
Identifies vulnerabilities before attackers exploit them.
Penetration Testing
Simulates real-world cyberattacks to test system resistance.
SSL Certificates
Ensures all user communications are fully encrypted.
Secure API Design
Prevents unauthorized access to backend services and databases.
Security Standards Comparison Table
| Security Standard | Purpose | Mandatory for Food Delivery Apps |
|---|---|---|
| ISO 27001 | Information security management | Yes |
| SOC 2 Type II | Data processing controls | Yes |
| GDPR | Personal data protection (EU) | Yes |
| PCI DSS | Payment data security | Yes |
| HIPAA | Health data security | Conditional |
Read more : – Grubhub App Features Explained for Founders
Red Flags: How to Spot Unsafe White-Label Providers
No Security Documentation
Providers that cannot present formal security policies or audit reports often lack proper safeguards.
Unrealistically Cheap Pricing
Extremely low pricing usually means shortcuts in infrastructure, hosting, and security layers.
No Compliance Certifications
Absence of ISO, SOC 2, GDPR, or PCI documentation is a critical warning sign.
Outdated Technology Stack
Old frameworks, unsupported servers, and legacy databases increase breach risks.
Poor Code Quality
Messy or unreviewed code leads to vulnerabilities and unstable performance.
No Security Update Policy
Lack of regular patching exposes apps to known exploits.
No Data Backup Systems
Without automated backups, recovery after a breach becomes nearly impossible.
No Insurance Coverage
Providers without cybersecurity insurance shift all liability to the founder.
Questions to Ask Providers
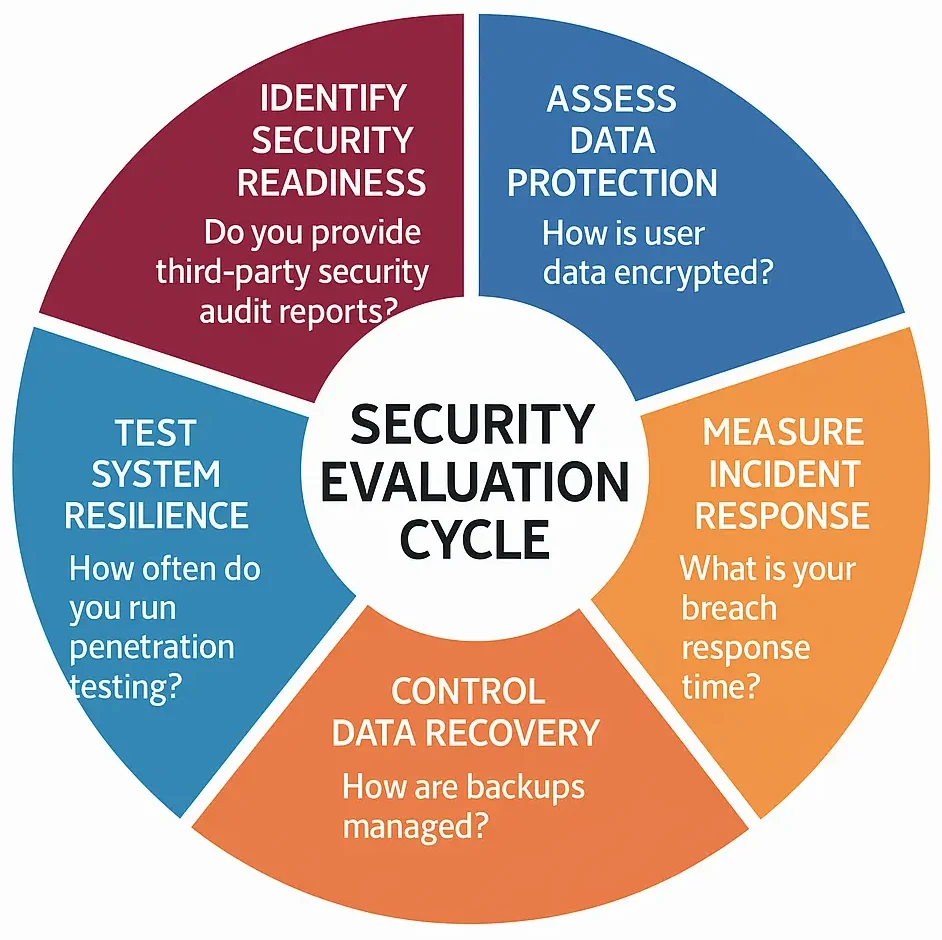
Documents to Request
- ISO 27001 certificate
- SOC 2 Type II report
- GDPR compliance statement
- PCI DSS compliance proof
Testing Procedures
- Vulnerability scanning
- API security testing
- Load and stress testing
- Manual code review
Due Diligence Steps
- Verify cloud security setup
- Review data storage laws by region
- Test payment gateway security
- Check historical breach records
Best Practices for Secure White-Label Grubhub App Implementation
Pre-Launch Security Measures
Security Audit Process
Conduct a full codebase and infrastructure audit before going live to eliminate hidden vulnerabilities.
Code Review Requirements
Every module must undergo manual and automated security code reviews.
Infrastructure Hardening
Use private servers, firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and segmented networks.
Compliance Verification
Validate GDPR, PCI DSS, and regional data protection laws before user onboarding.
Staff Training Programs
Operations, support, and technical teams must follow strict data handling protocols.
Post-Launch Monitoring
Continuous Security Monitoring
Real-time monitoring of server activity, login attempts, and API usage.
Regular Updates and Patches
Monthly security updates to prevent exploitation of newly discovered vulnerabilities.
Incident Response Planning
Defined breach response workflow with internal and legal teams.
User Data Management
Controlled access, encrypted storage, and strict retention policies.
Backup and Recovery Systems
Automated daily backups with tested disaster recovery plans.
Security Implementation Timeline
| Phase | Key Security Actions | Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Development | Compliance planning, risk assessment | 1–2 weeks |
| Development | Secure coding, encryption, API protection | 4–8 weeks |
| Pre-Launch | Security audits, penetration testing | 1–2 weeks |
| Post-Launch | Monitoring, patching, backups | Ongoing |
Read more : – Grubhub Marketing Secrets for Startups
Legal & Compliance Considerations
Regulatory Requirements
Data Protection Laws by Region
Different countries enforce different data protection laws such as GDPR in Europe, CCPA in California, DPDP Act in India, and PIPEDA in Canada.
Industry-Specific Regulations
Food delivery apps must comply with consumer protection laws, electronic transaction laws, and digital payment regulations.
User Consent Management
Clear user consent for data collection, tracking, notifications, and marketing communication is mandatory.
Privacy Policy Requirements
Privacy policies must clearly explain data usage, storage, third-party sharing, and user rights.
Terms of Service Essentials
Terms must define platform liability, dispute resolution, refunds, cancellations, and service limitations.
Liability Protection
Insurance Requirements
Cyber liability insurance and data breach insurance protect the business from financial shocks.
Legal Disclaimers
Clear disclaimers reduce legal exposure in case of service disruption or cyber incidents.
User Agreements
Digitally signed user agreements protect both the platform and users legally.
Incident Reporting Protocols
Mandatory timelines for reporting breaches to authorities and users must be followed.
Regulatory Compliance Monitoring
Ongoing legal audits ensure continued compliance with changing regulations.
Compliance Checklist by Region
| Region | Key Compliance Laws | Mandatory for Launch |
|---|---|---|
| Europe | GDPR | Yes |
| USA | CCPA, PCI DSS | Yes |
| India | DPDP Act, IT Act | Yes |
| Canada | PIPEDA | Yes |
| Australia | Privacy Act | Yes |
Read more : – How to Hire the Best Grubhub Clone Developer
Why Miracuves White-Label Grubhub App is Your Safest Choice
Miracuves Security Advantages
Enterprise-Grade Security Architecture
Miracuves builds its Grubhub-style app on hardened cloud infrastructure with multi-layer security controls across servers, databases, and APIs.
Regular Security Audits and Certifications
All platforms undergo routine internal audits and third-party vulnerability assessments to ensure continuous compliance.
GDPR and CCPA Compliant by Default
Data protection frameworks are implemented at the core level, not added later as extensions.
24/7 Security Monitoring
Real-time monitoring detects unusual activity, unauthorized access attempts, and system vulnerabilities.
Encrypted Data Transmission
All user, driver, restaurant, and admin data is protected through industry-standard encryption protocols.
Secure Payment Processing
PCI DSS-compliant payment infrastructure safeguards every transaction across cards, wallets, and gateways.
Regular Security Updates
Security patches and framework upgrades are deployed proactively to block emerging threats.
Insurance Coverage Included
Cybersecurity insurance adds an additional financial safety net for founders.
Conclusion
Launching a white-label Grubhub app in 2025 is not just a technology decision—it is a long-term trust commitment to your users, partners, and regulators. Security is no longer optional or secondary. It directly impacts your revenue stability, legal standing, user loyalty, and brand reputation.
A secure app is not defined by how fast it launches, but by how well it withstands real-world threats over time. Founders who treat security as an investment rather than a cost are the ones who build platforms that survive market shocks, cyber risks, and regulatory changes.
Choosing the right technology partner makes the difference between reactive damage control and proactive risk prevention. The strongest food delivery businesses of the next decade will be those built on secure, compliant, and continuously protected digital foundations.
FAQs
1. How secure is a white-label Grubhub app compared to custom development?
A properly built white-label Grubhub app can match or exceed custom app security when backed by certified infrastructure and continuous audits.
2. What happens if there is a security breach?
Immediate isolation, forensic investigation, user notification, legal reporting, data recovery, and system hardening are triggered.
3. Who is responsible for security updates?
The white-label app provider manages core security updates, while the business handles operational compliance.
4. How is user data protected in white-label apps?
Through encryption, secure servers, role-based access control, and continuous monitoring.
5. What compliance certifications should I look for?
ISO 27001, SOC 2 Type II, GDPR, PCI DSS, and regional data protection laws.
6. Can a white-label Grubhub app meet enterprise security standards?
Yes, when built on certified cloud infrastructure with regular penetration testing.
7. How often should security audits be conducted?
At least once every 6–12 months, with continuous vulnerability scanning.
8. What is included in the Miracuves security package?
Encrypted data, compliant payment systems, audits, monitoring, backups, and insurance coverage.
9. How is security handled across different countries?
By aligning data storage and privacy practices with local regulations such as GDPR, CCPA, and DPDP Act.
10. What insurance is needed for app security?
Cyber liability insurance and data breach insurance are essential.
Related Articles: