The food delivery industry has undergone a massive transformation over the past decade, fueled by advances in technology and shifting consumer preferences. The rise of food delivery app types has redefined convenience, with people now expecting food, groceries, and even meal kits to be delivered to their doorstep with just a few taps on their smartphones. This explosive growth of on-demand food delivery apps like ubereats clone has reshaped the way businesses operate, forcing restaurants and grocery stores to innovate rapidly to stay competitive.
In today’s hyper-connected world, consumers demand more than just quick delivery—they expect personalized experiences, seamless ordering processes, and reliable service. This blog aims to provide a detailed exploration of the different types of food delivery apps, their unique business models, and the strategies that have contributed to their success. Whether you’re a budding entrepreneur looking to enter the market or a developer seeking insights into building a successful platform, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
In this guide, we will walk you through the primary food delivery app types, their distinguishing features, and the secrets to their ongoing success. By understanding what sets each category apart and what contributes to their profitability, you can harness these insights to build or improve your food delivery service and capitalize on a booming industry.
With the rapid growth of on-demand food delivery apps, it’s not just about offering convenience anymore—it’s about providing an optimized, user-friendly experience that delivers value at every touchpoint. Let’s dive deeper into these app types and uncover the secret sauce behind their massive success.
2. Understanding the Different Types of Food Delivery Apps
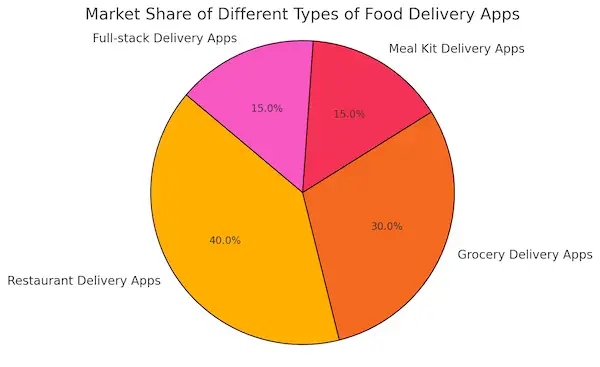
The food delivery app ecosystem is diverse, with various types of platforms catering to different segments of the market. These app categories differ not only in their operational models but also in the unique value they bring to customers and businesses. Whether focused on restaurant deliveries, groceries, or meal kits, each type of app has its own set of features that appeal to specific user needs. Understanding these food delivery app types is key to identifying opportunities for innovation and differentiation.
| Type of App | Description | Key Features | Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Restaurant Delivery Apps | Connect users with local restaurants | Real-time tracking, multiple payment options | Uber Eats, DoorDash, Grubhub |
| Grocery Delivery Apps | Deliver groceries from local stores | Inventory tracking, flexible delivery windows | Instacart, Amazon Fresh |
| Meal Kit Delivery Apps | Deliver ready-to-cook meal kits | Pre-portioned ingredients, subscription models | Blue Apron, HelloFresh |
| Full-stack Delivery Apps | Deliver both food and groceries | All-in-one platform, multiple delivery categories | Deliveroo, Postmates |
Below, we break down the primary categories of food delivery apps, exploring their core functionalities, business models, and the secrets to their success.
2.1. Restaurant Delivery Apps
Restaurant delivery apps are perhaps the most well-known in the food delivery landscape. These platforms connect users with local restaurants, allowing them to browse menus, place orders, and have meals delivered straight to their homes. Major players in this space include Uber Eats, Grubhub, and DoorDash, which have become household names by delivering food from a wide range of restaurants, from fast food to gourmet dining.
Success secret: The secret to success for restaurant delivery apps lies in their ability to form strong partnerships with local restaurants, offering users a variety of dining options while providing restaurants with a wider customer base. Additionally, the user experience plays a significant role; intuitive app design, real-time tracking, and seamless payment options contribute to customer satisfaction and loyalty. Data-driven insights allow these apps to personalize recommendations, further enhancing user engagement and repeat business.
2.2. Grocery Delivery Apps
With a focus on convenience, grocery delivery apps like Instacart and Amazon Fresh have gained substantial traction. These apps allow users to order groceries online and have them delivered within hours, often from local grocery stores. In a fast-paced world, the ability to have groceries delivered directly to your home without the hassle of physically going to a store is a major value proposition.
Success secret: The success of grocery delivery apps stems from their efficient order fulfillment and strong partnerships with local retailers. By offering real-time inventory tracking and user-friendly interfaces, these platforms make it easy for users to order products, substitute unavailable items, and schedule deliveries. Personalized promotions based on past purchases, as well as flexible delivery windows, contribute to their popularity and repeat usage.
2.3. Meal Kit Delivery Apps
A slightly different segment within the food delivery ecosystem, meal kit delivery apps like Blue Apron and HelloFresh have carved out a niche by offering ready-to-cook meal kits. These services provide pre-portioned ingredients along with easy-to-follow recipes, allowing users to cook gourmet meals at home without the hassle of meal planning or grocery shopping. Meal kit delivery apps appeal to users who want the satisfaction of home-cooked meals without the time investment.
Success secret: The subscription-based business model is the primary driver of success for meal kit delivery apps. Users commit to receiving meal kits on a weekly or bi-weekly basis, providing the app with predictable, recurring revenue. Furthermore, these platforms excel at offering a wide variety of meal options to cater to different dietary preferences, ensuring that users stay engaged and loyal.
2.4. Full-stack Delivery Apps
Full-stack delivery apps like Deliveroo and Postmates offer a wide range of services beyond just food delivery. These platforms are versatile, allowing users to order groceries, restaurant meals, and even retail products, all from a single app. This all-encompassing approach gives them an edge over niche-focused apps by serving multiple consumer needs through one platform.
Success secret: Flexibility is the cornerstone of full-stack delivery apps’ success. By offering a diverse range of services, these apps increase user engagement, as customers find more value in a single platform that can cater to all their delivery needs. Additionally, efficient logistics management, real-time tracking, and user-centric features such as customized delivery slots and loyalty programs help retain a broad customer base.
The various types of food delivery apps demonstrate the incredible potential within the industry. Whether focused on restaurant meals, groceries, or meal kits, the key to success for all these apps lies in the seamless integration of technology with user convenience. By offering intuitive user experiences and forming strategic partnerships, these platforms continue to scale and thrive in an increasingly competitive market.
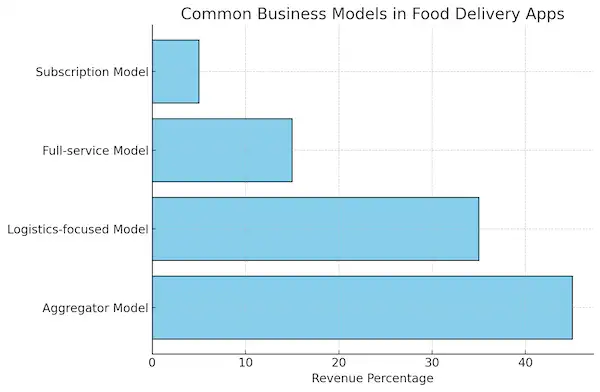
3. The Business Models Behind Food Delivery Apps
A successful food delivery app doesn’t just rely on technology or partnerships—its underlying business model plays a critical role in determining its long-term profitability. Various food delivery business models have emerged over the years, each tailored to different segments of the market. Understanding these models provides insights into how these platforms generate revenue, optimize operations, and scale to meet growing demand.
| Business Model | Description | Revenue Stream | Example Apps |
|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregator Model | Connects users to restaurants but doesn’t manage delivery logistics | Commission fees from restaurants | Grubhub, Just Eat |
| Logistics-focused Model | Manages both orders and deliveries | Delivery fees + restaurant commissions | Uber Eats, DoorDash |
| Full-service Model | Manages food preparation and delivery, often via cloud kitchens | Direct sales + delivery fees | Rebel Foods |
| Subscription Model | Offers users benefits such as free or discounted deliveries for a subscription | Recurring subscription fees | Uber Eats Pass, DashPass |
Let’s break down the core business models that power the most successful on-demand food delivery apps and examine the factors contributing to their success.
3.1. Aggregator Model
The aggregator model is one of the earliest and most widely adopted business models in the food delivery industry. In this setup, the app acts as a middleman between restaurants and customers. The app lists restaurants, facilitates ordering, and leaves the delivery logistics to the restaurant. This model is popular among apps like Grubhub and Just Eat, where the platform charges restaurants a commission for each order placed through the app.
Success secret: The aggregator model thrives on low operational costs since the platform doesn’t handle delivery logistics. By maintaining a large pool of restaurant partners, these apps offer users a wide variety of dining options, attracting a broad customer base. Their ability to scale quickly, with minimal overhead, gives them a competitive edge. Additionally, restaurant partnerships allow the platform to generate steady revenue without the complexities of managing a delivery fleet.
Many food delivery apps, like Grubhub, operate on a commission-based model, where they charge restaurants a percentage of each order processed through their platform.
3.2. Logistics-focused Model
In contrast to the aggregator model, the logistics-focused model involves the app managing both the ordering process and the delivery itself. Apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash have perfected this approach, where they not only connect customers with restaurants but also handle the entire delivery process through their own fleet of drivers. This model provides more control over the delivery experience, ensuring faster, more reliable service.
Success secret: The logistics-focused model excels because of its ability to offer a consistent delivery experience. By controlling the logistics, these platforms can optimize delivery routes, reduce delivery times, and provide real-time tracking for users. This level of service enhances customer satisfaction and loyalty. Additionally, having a dedicated delivery fleet allows these platforms to offer additional services like grocery delivery, further diversifying their revenue streams.
3.3. Full-service Model
The full-service model takes the logistics-focused approach a step further by managing the entire process—from food preparation to delivery. Apps operating on this model, like Rebel Foods (which operates cloud kitchens), control everything, including the kitchen, allowing them to streamline the entire customer experience. In this model, the app owns the entire value chain, from cooking the food to delivering it to the customer’s door.
Success secret: The full-service model offers unparalleled control over quality, speed, and customer satisfaction. By managing the entire process, these platforms can ensure food consistency and reduce delivery times, which in turn improves customer retention. Another significant advantage is the higher profit margins, as these apps don’t have to share revenue with third-party restaurants. Instead, they operate their own kitchens, retaining most of the profit while offering competitively priced meals.
4. Key Features of Successful Food Delivery Apps
The food delivery landscape is highly competitive, and simply offering a platform for users to order food is no longer enough. Successful on-demand food delivery apps differentiate themselves through features that not only attract users but also keep them coming back. These key features can make or break an app’s chances of standing out in a crowded market.
4.1. User Experience (UX)
The foundation of any successful food delivery app is its user interface and experience. An intuitive, easy-to-navigate interface is essential for a seamless ordering process. The most successful apps ensure that users can browse menus, place orders, and track deliveries effortlessly. Features like one-click reordering, personalized recommendations, and multiple payment options enhance the overall user experience.
Success secret: Personalization is critical. By using data analytics to provide personalized recommendations based on users’ past orders and preferences, these apps create a more engaging and tailored experience. A clean, responsive design, combined with real-time order tracking, makes the entire process more convenient and satisfying for the user.
4.2. Customer Support
In an industry where delays or mistakes can result in dissatisfaction, having robust customer support is non-negotiable. Offering 24/7 customer support through multiple channels (chat, email, phone) ensures that users can quickly resolve issues, whether it’s related to incorrect orders, delays, or payment problems. Fast, efficient customer service contributes to higher user satisfaction and retention.
Success secret: Rapid problem resolution is key to maintaining a positive brand image. Apps that offer instant support through chatbots or real-time customer service representatives have a distinct advantage. Handling disputes efficiently and compensating for mistakes (e.g., through vouchers or refunds) builds trust with the customer base.
4.3. Partnering with Local Businesses
For many food delivery apps, partnering with local businesses is crucial for gaining traction in new markets. Forming strong partnerships with local restaurants and grocery stores ensures faster deliveries, greater selection, and the ability to cater to local tastes and preferences. These partnerships can also help establish brand loyalty within specific regions.
Success secret: Collaboration with local businesses offers mutual benefits. The app gets access to a broader menu selection and regional cuisines, while local businesses gain exposure to a wider audience. Offering loyalty programs or exclusive deals with local restaurants further incentivizes users to order through the app, enhancing both engagement and retention.
The food delivery business models discussed here reflect the diverse approaches platforms can take to serve their customers while generating revenue. Whether focusing on logistics, full-service, or the aggregator model, the key to success lies in understanding consumer needs and optimizing the delivery experience. Apps that provide seamless ordering, efficient logistics, and personalized user experiences are well-positioned to dominate the competitive landscape.
5. Market Trends in Food Delivery Apps
The food delivery app landscape is constantly evolving, driven by changes in consumer behavior, technological advancements, and shifting market demands. To remain competitive, it’s essential for food delivery platforms to not only adapt but to stay ahead of these trends. Understanding the latest food delivery trends can help businesses capitalize on new opportunities, improve user engagement, and scale their operations effectively.
Let’s explore the most significant trends shaping the future of on-demand food delivery apps and how these trends are contributing to the success of modern delivery platforms.
5.1. Contactless Delivery
One of the biggest trends to emerge in recent years, particularly due to the COVID-19 pandemic, is the rise of contactless delivery. This feature allows customers to have their food or groceries delivered without having any physical interaction with the delivery person. Apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash quickly adopted this model, providing customers with peace of mind and enhanced safety.
Success secret: The demand for contactless delivery isn’t going away anytime soon. Even as the world transitions into a post-pandemic era, consumers have grown accustomed to the convenience and safety of contactless options. By offering seamless contactless delivery as a standard feature, food delivery apps are able to cater to safety-conscious customers while boosting user retention. Enhancing this with real-time delivery tracking and notifications keeps users informed and satisfied.
5.2. Eco-friendly Delivery Options
With growing awareness around environmental sustainability, there is a rising demand for eco-friendly delivery options. Customers are increasingly looking for apps that offer environmentally conscious solutions, from using sustainable packaging to adopting green delivery methods, such as bicycles or electric scooters. Platforms like Deliveroo and Postmates have begun rolling out these options to appeal to eco-conscious users.
Success secret: Incorporating sustainability into the delivery process can differentiate a platform from competitors and attract a loyal, eco-conscious customer base. This can include offering customers the option to opt out of unnecessary items like plastic utensils, promoting carbon-neutral deliveries, or using biodegradable packaging. By aligning with consumer values around sustainability, food delivery apps can build stronger brand loyalty and trust.
5.3. Niche Delivery Services
Another notable trend in the food delivery app types landscape is the rise of niche delivery services. Beyond mainstream meal deliveries, apps are increasingly catering to specific dietary preferences and lifestyles. From vegan-only delivery services to organic and gourmet meal platforms, niche delivery apps are gaining traction. Apps like Vegin’ Out (focused on vegan meals) and Green Chef (offering organic ingredients) have capitalized on this trend by serving a dedicated and growing market segment.
Success secret: Niche delivery services thrive because they cater to the specific needs of target audiences, offering personalized experiences that mass-market platforms often can’t provide. By focusing on specialized diets, ethical sourcing, or gourmet offerings, these apps are able to create a loyal customer base that values quality and personalization. This trend highlights the importance of tailoring the delivery experience to meet the unique demands of specific consumer segments.
5.4. Subscription-Based Delivery Models
Subscription-based services are quickly becoming one of the most profitable trends in the food delivery industry. Platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats have introduced subscription services (e.g., DashPass and Eats Pass), where customers pay a monthly fee in exchange for benefits such as free delivery and exclusive discounts. This model not only incentivizes repeat business but also ensures a steady stream of predictable revenue.
Success secret: The subscription model is effective because it increases customer loyalty while providing regular, recurring revenue. Customers are more likely to choose platforms where they can save on delivery fees, especially if they frequently order food. Additionally, offering exclusive perks such as priority delivery or member-only promotions helps retain subscribers and drives long-term engagement.
5.5. Integration with Technology: AI and Automation
Advances in artificial intelligence (AI) and automation are significantly enhancing the efficiency of on-demand food delivery apps. From optimizing delivery routes using AI to implementing chatbots for customer support, technology is streamlining operations, reducing costs, and improving the customer experience. Apps like Domino’s are already experimenting with autonomous vehicle deliveries, while others are using AI to personalize the user experience by recommending meals based on past orders.
Success secret: Leveraging AI and automation not only helps reduce operational costs but also improves the speed and accuracy of deliveries. Real-time data analytics, predictive modeling for delivery times, and personalized recommendations based on AI-driven insights keep customers engaged and satisfied. Platforms that adopt these technologies early on gain a significant competitive advantage by offering faster, smarter, and more personalized services.
The food delivery market trends outlined here demonstrate how dynamic and fast-evolving this industry is. As customer expectations shift and new technologies emerge, food delivery apps must innovate to remain competitive. By embracing contactless delivery, eco-friendly practices, niche services, subscription models, and cutting-edge technology, these platforms can not only keep up with market demands but also position themselves as leaders in the food delivery space.
6. The Secret to Success in the Food Delivery Market
The success of any food delivery app goes beyond just delivering food to customers. In a competitive market, the key drivers of success are rooted in a platform’s ability to scale, engage users, and leverage cutting-edge technology. While the core functionality of delivering meals or groceries is essential, the platforms that excel in the food delivery space do so by optimizing user experiences, enhancing operational efficiency, and building strong relationships with both customers and partner businesses.
| Platform | Success Factor | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Uber Eats | Efficient Logistics | Utilized existing Uber infrastructure for fast, reliable deliveries |
| Instacart | Strong Partnerships with Grocery Chains | Partnered with major grocery retailers like Costco and Whole Foods |
| DoorDash | Personalization through Data Analytics | Uses data to offer personalized meal recommendations and promotions |
| Deliveroo | Full-stack Approach | Combines restaurant and grocery delivery on one platform, offering versatility to users |
In this section, we’ll uncover the core strategies that have enabled on-demand food delivery apps to thrive and achieve massive success.
6.1. Data-driven Personalization
One of the most powerful tools in the arsenal of successful food delivery apps is data. By collecting and analyzing user behavior, apps can create highly personalized experiences that cater to individual preferences. From recommending meals based on past orders to offering customized promotions, data-driven personalization ensures that users feel valued and catered to, which in turn drives repeat usage and loyalty.
Success secret: Platforms like Uber Eats and Grubhub use advanced analytics to personalize recommendations for users, whether it’s showing favorite restaurants at the top of the feed or offering deals on frequently ordered items. By leveraging machine learning algorithms, these apps can predict what users are likely to order next, enhancing the overall customer experience. This kind of personalization boosts user engagement, increases order frequency, and improves customer satisfaction.
6.2. Scaling Through Strategic Partnerships
The success of a food delivery platform often hinges on its ability to form strong partnerships. These partnerships, whether with local restaurants, grocery chains, or logistics providers, play a crucial role in expanding the platform’s reach and service offerings. Strategic partnerships help food delivery apps scale by allowing them to offer a wider variety of options and ensuring smooth, timely deliveries.
Success secret: Apps like DoorDash and Postmates have formed strategic partnerships with not just local restaurants but also large chain brands, grocery stores, and even retail businesses. This allows them to diversify their service offerings, catering to a broader audience. Partnering with recognized brands boosts credibility and trust, while local partnerships ensure fast, reliable service. The ability to integrate seamlessly with partners, providing them with tools to manage orders and deliveries efficiently, is key to scaling successfully.
6.3. Efficient Delivery Logistics
Logistics management is one of the most critical factors in the success of on-demand food delivery apps. Efficient logistics not only affect the speed and accuracy of deliveries but also the overall customer experience. Apps that excel in optimizing their delivery routes, managing fleets, and providing real-time tracking are more likely to win over customers and retain them.
Success secret: Platforms like Deliveroo and Instacart have mastered the art of delivery logistics by using AI and machine learning to optimize delivery routes, ensuring faster delivery times and minimizing delays. Real-time tracking features keep users informed about their order status, reducing anxiety and improving transparency. Additionally, apps that manage their own fleet (like Uber Eats) have greater control over the delivery process, allowing for quicker response times in case of issues.
6.4. Customer Retention Through Loyalty Programs
Retaining customers in the highly competitive food delivery space requires more than just fast deliveries and a good user interface. Loyalty programs are a proven strategy to keep users engaged and encourage repeat orders. Offering rewards, discounts, or points for frequent use incentivizes customers to stay within the platform rather than switching to competitors.
Success secret: Apps like Grubhub and Postmates use loyalty programs to build customer retention. Grubhub’s Perks program, for example, offers users exclusive deals, discounts, and points that can be redeemed for future orders. These programs not only keep users engaged but also foster a sense of belonging and reward, which reduces churn rates. Offering subscription models with benefits like free delivery (e.g., DashPass by DoorDash) further locks in customer loyalty.
6.5. User-friendly Design and Seamless Experience
In today’s competitive food delivery market, the user experience can make or break an app. A platform with a user-friendly design, intuitive navigation, and a seamless checkout process has a higher chance of retaining users and driving repeat business. Ensuring that the app loads quickly, works across multiple devices, and offers seamless payment options is essential for success.
Success secret: The success of apps like Uber Eats and DoorDash can be largely attributed to their focus on providing an outstanding user experience. From fast-loading pages to simple, clutter-free designs, these platforms ensure that users can place orders quickly and with minimal friction. Features like one-click reordering, multiple payment methods, and easy tip options further enhance the overall experience, encouraging customers to return.
The secret to success in the food delivery market lies in the careful balance of technology, partnerships, and customer engagement strategies. By focusing on personalization, scaling through partnerships, optimizing logistics, and improving user experiences, on-demand food delivery apps can create a sustainable and profitable business model. In a market saturated with competitors, these secrets help the best platforms stand out and continue to grow.
Looking to create the next big food delivery platform?
Get a custom-built app with real-time tracking,
AI recommendations,and effortless checkout.
7. Monetization Strategies for Food Delivery Apps
A key aspect of building a successful food delivery app is figuring out how to generate consistent revenue while offering value to both users and partner businesses. The monetization strategies employed by on-demand food delivery apps vary based on the business model and the services offered, but the most successful platforms have found ways to diversify their income streams. Whether through commissions, delivery fees, or subscription models, effective monetization is crucial to the long-term profitability of these platforms.
In this section, we’ll dive into the most common and effective monetization strategies used by food delivery app types, outlining how they contribute to business growth and sustainability.
7.1. Commission-based Fees
One of the primary ways food delivery apps make money is through commission-based fees charged to restaurants and food establishments. Platforms like Uber Eats, DoorDash, and Grubhub typically take a percentage of the total order value from the restaurant in exchange for providing the platform to list their menu, process orders, and deliver food. Commissions can vary, but they generally range from 15% to 30% of each order, depending on the terms of the partnership.
Success secret: Commission-based fees are a reliable source of revenue for food delivery apps, as they directly scale with the volume of orders placed on the platform. By forming partnerships with high-demand restaurants and chains, apps can ensure a steady flow of orders, driving consistent revenue. The more orders a restaurant processes through the app, the more commission revenue the platform generates. To maintain positive relationships with restaurants, many platforms offer additional marketing or visibility features in exchange for a higher commission rate.
7.2. Delivery Fees
In addition to charging restaurants, food delivery apps also generate revenue through delivery fees charged directly to customers. These fees typically depend on factors such as the distance between the restaurant and the customer, peak ordering times, or even the size of the order. Some platforms use dynamic pricing models where delivery fees increase during high-demand periods or for longer delivery distances. Postmates and Deliveroo are prime examples of apps that successfully utilize delivery fees as a revenue source.
Success secret: Delivery fees provide a direct and scalable way to monetize each transaction, ensuring that the platform is compensated for its logistical services. To minimize customer resistance to paying delivery fees, some apps offer free or reduced delivery through loyalty programs or during promotional periods. Dynamic pricing based on demand ensures that the platform maximizes revenue during peak hours without overburdening users with high fees during off-peak times.
7.3. Subscription Models
Many on-demand food delivery apps have introduced subscription services as a way to drive loyalty and generate predictable, recurring revenue. Platforms like Uber Eats (with Eats Pass) and DoorDash (with DashPass) offer customers the option to pay a monthly fee in exchange for benefits like free or discounted delivery and exclusive promotions. Subscription models not only increase user retention but also provide a steady stream of income, independent of order volume fluctuations.
Success secret: Subscription models are an effective way to create customer loyalty while ensuring consistent revenue for the platform. Users are more likely to place orders frequently if they feel they are getting more value through reduced delivery fees. Additionally, offering exclusive perks like priority support or access to premium restaurants can further incentivize users to sign up for the subscription. For the platform, this creates a reliable, recurring income stream that helps stabilize revenue during slower periods.
7.4. Advertising and Promotional Partnerships
Another revenue stream for food delivery apps is advertising and promotional partnerships with restaurants. Many platforms offer restaurants the ability to pay for featured listings, premium placement in search results, or inclusion in special promotional campaigns. Grubhub and DoorDash, for example, offer restaurant partners the option to boost their visibility by paying for higher placement within the app. These promotional partnerships create an additional revenue stream for the platform while providing restaurants with a competitive edge.
Success secret: By offering paid visibility options to restaurants, food delivery apps can generate significant advertising revenue while allowing smaller or less-known establishments to compete with larger chains. Sponsored placements are particularly effective during high-traffic times or during promotional events, where being at the top of the feed can result in more orders for the restaurant and more commission revenue for the platform. A win-win scenario for both the app and its partners.
7.5. Surge Pricing (Dynamic Pricing)
Similar to how ridesharing platforms like Uber use surge pricing, some food delivery apps also implement dynamic pricing models. During peak times, such as weekends or major events, the app may increase delivery fees or adjust commissions to maximize revenue. This strategy not only helps manage the higher demand but also ensures that the platform benefits financially from the increased order volume. Postmates and Uber Eats often use surge pricing during high-demand times.
Success secret: Surge pricing allows food delivery apps to capitalize on increased demand, ensuring that they maintain profitability during busy periods. By adjusting fees dynamically, platforms can also encourage more delivery drivers to be available, ensuring that customer wait times are minimized, and more orders can be processed. This dynamic model balances supply and demand while boosting revenue at crucial times.
The monetization strategies outlined above highlight how food delivery apps have evolved to diversify their revenue streams and create sustainable business models. By combining commission-based fees, delivery charges, subscriptions, and promotional partnerships, these platforms can maximize profitability while delivering value to both users and restaurants. For any entrepreneur looking to enter the food delivery space, understanding these strategies is essential to building a scalable and profitable app.
8. Challenges Faced by Food Delivery Apps
While on-demand food delivery apps have revolutionized the food service industry, they also face several challenges that can impact their growth and profitability. These challenges range from operational complexities and high competition to managing customer expectations and navigating regulatory environments. For entrepreneurs and developers, understanding these hurdles is crucial to creating solutions that can help mitigate risks and optimize success.
| Challenge | Description | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| High Competition | Saturated market with established players | Focus on niche services or unique user experiences |
| Managing Operational Costs | High costs related to logistics, delivery, and driver compensation | Use AI for route optimization, adopt surge pricing strategies |
| Customer Satisfaction | Issues with delivery delays or incorrect orders | Invest in 24/7 customer support, real-time tracking, and transparent communication |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating labor laws, food safety regulations | Stay updated with evolving laws, provide driver benefits |
In this section, we will explore the key challenges that food delivery apps encounter and offer insights into how some of the most successful platforms are overcoming these obstacles.
8.1. High Competition in the Market
The food delivery app industry is incredibly competitive, with numerous platforms vying for market share. Major players like Uber Eats, Grubhub, and DoorDash dominate the space, making it challenging for new entrants to carve out a niche. This intense competition forces apps to continuously innovate and differentiate themselves, often through aggressive marketing campaigns, partnerships, or by lowering fees.
Challenge analysis: Competing with established platforms requires significant investment in technology, logistics, and customer acquisition strategies. Newcomers to the market must offer unique value propositions, such as niche services or specialized delivery options, to stand out from larger competitors. Another challenge is customer retention, as users often switch between apps based on convenience, promotions, or restaurant availability.
Solution insight: To stay competitive, apps must focus on delivering a superior user experience, personalized features, and exceptional service. Leveraging technology to offer faster deliveries, real-time tracking, or niche delivery options (like vegan-only meals or eco-friendly packaging) can create differentiation. Additionally, partnering with local restaurants or forming exclusive deals can boost customer loyalty.
Keywords to include: best food delivery platforms, on-demand food delivery apps, food delivery app types
8.2. Managing Operational Costs
One of the most significant challenges for food delivery platforms is managing operational costs. This includes the costs of maintaining a fleet of drivers, handling customer service, and optimizing logistics to ensure efficient deliveries. For platforms that manage their own delivery logistics (like Uber Eats or DoorDash), balancing driver compensation with delivery fees is a constant challenge.
Challenge analysis: High operational costs can quickly erode profit margins, especially for platforms offering free or discounted delivery options. Ensuring that deliveries are timely, while also managing fuel costs, vehicle maintenance, and driver compensation, requires complex logistics management. Additionally, fluctuations in order volumes during peak or off-peak hours can make it difficult to maintain cost efficiency.
Solution insight: One solution is to implement dynamic pricing models (such as surge pricing) to balance demand and supply during peak hours. Additionally, leveraging automation and AI for route optimization can help reduce fuel costs and shorten delivery times. Platforms can also offer flexible working hours for drivers to ensure there is adequate workforce coverage during high-demand periods without overpaying during off-peak hours.
8.3. Customer Expectations and Satisfaction
In an age of instant gratification, customer expectations for food delivery services are higher than ever. Users expect fast deliveries, accurate orders, and consistent quality, regardless of the restaurant or grocery store they order from. However, managing these expectations, especially when working with multiple restaurant partners, can be a challenge. Late deliveries, incorrect orders, or poor customer service can lead to negative reviews, customer churn, and reputational damage.
Challenge analysis: Balancing customer expectations with the realities of delivery logistics is one of the toughest challenges food delivery apps face. Issues such as traffic, weather conditions, or restaurant delays can all impact delivery times, leading to customer dissatisfaction. Additionally, customers often expect high-quality customer service, quick problem resolution, and proactive communication.
Solution insight: To address this challenge, platforms should invest in robust customer support systems, including real-time chatbots, 24/7 customer service, and automated issue resolution for common problems. Transparent communication, such as real-time order tracking and delivery notifications, can help manage customer expectations. Additionally, offering compensation for delays (like free delivery on the next order) can help mitigate negative experiences.
8.4. Balancing Restaurant and Customer Needs
Food delivery apps face the unique challenge of serving two distinct groups: customers and restaurant partners. While it’s essential to provide a seamless user experience for customers, apps must also ensure that their restaurant partners are satisfied with the platform. Restaurants rely on delivery platforms for additional business, but high commission fees or unreliable delivery services can lead to strained relationships.
Challenge analysis: Many restaurant partners feel the pressure of commission fees, which can cut into their already thin margins. Additionally, poor delivery service can reflect negatively on the restaurant’s brand, even though the app is responsible for the delivery. Striking a balance between maintaining positive relationships with restaurant partners and ensuring customer satisfaction is a delicate act.
Solution insight: To foster strong relationships with restaurant partners, platforms should consider offering flexible commission structures, especially for smaller businesses. Providing restaurants with tools for managing orders, such as real-time order notifications and delivery updates, can help streamline the process. Additionally, ensuring that delivery personnel are trained to represent both the platform and the restaurant in a professional manner can help mitigate reputation issues.
8.5. Regulatory and Legal Challenges
Operating in the food delivery industry means navigating various legal and regulatory challenges. These include adhering to food safety regulations, managing driver employment classifications (contractor vs. employee), and complying with local laws regarding delivery services. As the industry continues to grow, regulatory scrutiny is also increasing, particularly in areas such as driver benefits and the environmental impact of food delivery services.
Challenge analysis: Regulatory compliance can be both costly and time-consuming for food delivery apps. Ensuring that food safety standards are maintained, especially for grocery delivery apps, is crucial. Additionally, the legal classification of drivers—whether they are independent contractors or employees—has been a contentious issue, with labor laws evolving rapidly in various regions.
Solution insight: Platforms must stay up-to-date with evolving regulations and ensure compliance to avoid fines or legal challenges. This may involve offering additional benefits to drivers, such as health insurance, or ensuring that all food deliveries meet stringent safety standards. Proactively engaging with regulators and working toward sustainable, ethical business practices can help reduce the risk of legal complications.
The challenges faced by on-demand food delivery apps are numerous, but the platforms that succeed are those that can adapt, innovate, and optimize their operations. From managing costs and logistics to meeting customer and partner expectations, the ability to overcome these challenges is what sets successful apps apart from their competitors. By understanding and addressing these hurdles head-on, food delivery platforms can continue to grow and thrive in a highly competitive market.
9. Case Studies of Successful Food Delivery Apps
Examining real-world examples of successful food delivery apps provides valuable insights into how platforms have navigated challenges, scaled their operations, and achieved widespread adoption. Case studies showcase practical applications of the strategies and business models we’ve discussed, illustrating what it takes for a food delivery app to thrive in a competitive marketplace.
In this section, we’ll explore two case studies: Uber Eats and Instacart, both of which have become leaders in their respective niches by leveraging innovative approaches to logistics, customer engagement, and technology.
9.1. Uber Eats: Scaling Through Logistics and Partnerships
Overview: Launched in 2014, Uber Eats has become one of the leading on-demand food delivery apps globally, serving millions of users across more than 6,000 cities. The platform quickly rose to prominence by leveraging Uber’s existing infrastructure of drivers and its robust logistics network. Uber Eats capitalized on the growing demand for convenient, fast food delivery by forming strong partnerships with restaurants, both large chains and local establishments.
Success Factors:
- Logistics Efficiency: Uber Eats used Uber’s existing network of drivers to establish a fast, reliable delivery service. By integrating its technology with real-time traffic data, Uber Eats optimized delivery routes, reducing wait times and improving customer satisfaction.
- Strategic Partnerships: The platform formed exclusive partnerships with major fast-food chains like McDonald’s and Starbucks, ensuring a steady flow of high-volume orders. These partnerships gave Uber Eats an edge over competitors by offering users exclusive access to popular brands.
- Data-Driven Personalization: Uber Eats uses data analytics to enhance the user experience, offering personalized restaurant recommendations and promotions based on past orders. This not only boosts user engagement but also drives repeat business.
Takeaway: Uber Eats’ ability to scale rapidly is rooted in its efficient logistics and strategic partnerships. By leveraging its parent company’s existing infrastructure, Uber Eats was able to enter the market with a distinct advantage, quickly establishing itself as a top-tier food delivery platform.
9.2. Instacart: Dominating the Grocery Delivery Space
Overview: Instacart, founded in 2012, is the leading grocery delivery app in the United States. Unlike traditional restaurant delivery platforms, Instacart focuses on delivering groceries from local stores directly to consumers. The platform’s success has been driven by its ability to cater to consumer demand for convenient, same-day grocery delivery, especially during the COVID-19 pandemic, which dramatically increased the need for contactless delivery services.
Success Factors:
- Partnering with Major Grocery Chains: Instacart’s success is largely attributed to its partnerships with major grocery chains like Costco, Whole Foods, and Safeway. These partnerships allow Instacart to offer a wide range of products, appealing to different customer segments. By partnering with well-known retailers, the platform has gained credibility and trust among consumers.
- Scalable Logistics Model: Instacart operates on a gig economy model, employing independent contractors to handle deliveries. This flexible workforce model allows the platform to scale quickly based on demand, ensuring that customers can receive groceries within hours of placing an order.
- Customer-Centric Features: Instacart offers a highly personalized user experience. The platform saves past shopping lists, suggests frequently purchased items, and provides real-time updates on product availability. Additionally, customers can choose specific delivery windows, adding a layer of convenience that sets it apart from competitors.
Takeaway: Instacart’s dominance in the grocery delivery space is a result of its strong retail partnerships, scalable logistics model, and focus on delivering a personalized, user-friendly experience. The platform’s ability to adapt quickly to market demand, especially during the pandemic, solidified its position as the go-to grocery delivery app for millions of consumers.
9.3. Lessons from the Case Studies
Both Uber Eats and Instacart have demonstrated the importance of building a scalable logistics infrastructure and forming strategic partnerships with key players in their respective industries. Their success underscores the value of data-driven personalization, which not only enhances user engagement but also drives repeat orders.
Key takeaways from these case studies include:
- Efficient logistics are critical to scaling: Both platforms invested in optimizing delivery routes and managing fleets to ensure fast, reliable service.
- Strategic partnerships drive growth: By aligning with major brands and retailers, these platforms were able to offer exclusive services and products that attracted large customer bases.
- Personalization is key to user retention: By using data analytics to customize the user experience, these platforms increased customer loyalty and engagement, leading to higher retention rates.
For entrepreneurs and developers, these case studies provide a roadmap for building and scaling successful food delivery apps. Focusing on logistics, partnerships, and personalization will be crucial in navigating the competitive landscape and delivering a winning solution to users.
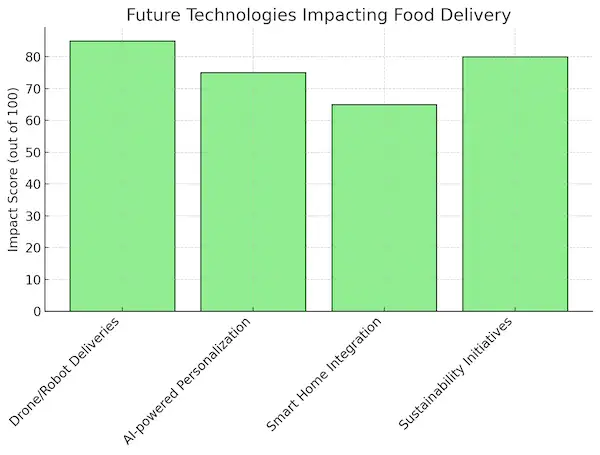
10. Future of Food Delivery Apps
The food delivery app market is constantly evolving, driven by rapid technological advancements and changing consumer expectations. As the industry grows more competitive, platforms must innovate to stay ahead. From the integration of AI and automation to the use of drones and robots for delivery, the future of on-demand food delivery apps holds exciting possibilities.
| Technology | Description | Impact on Industry |
|---|---|---|
| Drone and Robot Deliveries | Use of autonomous drones and robots for last-mile deliveries | Faster, more efficient deliveries with less reliance on human labor |
| AI-powered Personalization | Use of AI to recommend meals and optimize delivery routes | Enhanced user experience and reduced operational costs |
| Smart Home Integration | Integrating food delivery apps with smart devices for voice-activated ordering | Streamlined, hands-free ordering experiences |
| Sustainability Initiatives | Adoption of eco-friendly packaging and carbon-neutral delivery options | Attract eco-conscious consumers and reduce environmental impact |
In this section, we’ll explore the most promising trends and technologies that will shape the future of food delivery and how these innovations can help platforms scale, improve efficiency, and enhance customer satisfaction.
10.1. Drone and Robot Deliveries
One of the most anticipated developments in the food delivery space is the use of drones and autonomous robots for last-mile delivery. Companies like Wing (owned by Alphabet) and Amazon have already started experimenting with drone delivery services, while platforms such as Starship Technologies are using robots for short-distance deliveries. These technologies promise to make food delivery faster, more efficient, and less reliant on human labor.
Future potential: Drones and robots have the potential to revolutionize food delivery, particularly in urban areas where traffic congestion often causes delays. These autonomous delivery systems can significantly reduce delivery times and costs, making on-demand food services more accessible to consumers. Additionally, with fewer human touchpoints, these technologies can offer more hygienic delivery options—an increasingly important factor in the post-pandemic world.
Challenge: However, widespread adoption of drones and robots will depend on overcoming regulatory hurdles and addressing logistical challenges such as battery life, weather conditions, and the safe integration of autonomous systems into busy urban environments.
10.2. AI-powered Systems for Personalization and Optimization
Artificial intelligence (AI) is already being used to improve customer experiences, but its role will continue to expand in the coming years. AI can power recommendation engines, optimize delivery routes, and automate customer support, making on-demand food delivery apps smarter and more efficient. Platforms like Uber Eats and Domino’s are already leveraging AI for everything from predictive analytics to voice-activated ordering systems.
Future potential: AI can enhance the personalization of food delivery services by predicting what users are likely to order based on past behavior, dietary preferences, and even real-time data such as weather or time of day. This level of personalization will lead to higher customer satisfaction and increased order frequency. Additionally, AI-powered systems can help platforms optimize logistics by dynamically adjusting delivery routes based on traffic patterns or driver availability, reducing delivery times and operational costs.
Challenge: While AI offers enormous potential, it requires significant investment in data infrastructure and machine learning algorithms. Additionally, ensuring data privacy and security will be paramount as more personal information is used to create tailored customer experiences.
10.3. Integration with Smart Homes and IoT Devices
The future of on-demand food delivery apps is also likely to include deeper integration with smart home devices and the Internet of Things (IoT). As more consumers adopt smart speakers like Amazon Alexa and Google Home, they will expect seamless voice-activated ordering systems that allow them to place orders without needing to interact with their phones or computers. This hands-free convenience is poised to become a key differentiator for food delivery apps in the near future.
Future potential: By integrating with smart home devices, food delivery apps can create an even more frictionless experience for users. Imagine being able to order your favorite meal while driving home, and having it delivered just as you arrive, or receiving alerts from your smart fridge when you’re running low on groceries, prompting a grocery delivery order. The ability to connect with other IoT devices like smart refrigerators, ovens, and even fitness trackers (to suggest meals based on dietary goals) will further personalize and streamline the food ordering experience.
Challenge: The challenge lies in creating seamless integrations that work across a variety of devices and platforms while ensuring security and privacy. Furthermore, the development of APIs and partnerships with smart home providers will be necessary to expand these capabilities.
10.4. Subscription-Based Models and Tiered Services
Subscription-based models, which we touched upon earlier, are expected to play a more significant role in the future of on-demand food delivery apps. Offering tiered subscription services with benefits such as free delivery, faster delivery times, and exclusive deals will become the norm. Platforms like DoorDash and Uber Eats already offer subscription services (DashPass and Eats Pass), and this trend is expected to expand as platforms look for ways to generate steady revenue.
Future potential: By offering more personalized and value-driven subscription options, platforms can increase customer loyalty and retention. Tiered services could include premium memberships that offer perks like VIP customer support, early access to new features, or discounts on large orders. This would allow platforms to diversify their revenue streams while offering users additional incentives to stick with a single service.
Challenge: To succeed, platforms must strike a balance between offering enough value to justify the subscription cost and maintaining profitability. Additionally, they must avoid alienating non-subscribers by ensuring that the basic service remains attractive and competitive.
10.5. Sustainability and Eco-friendly Initiatives
As consumers become more environmentally conscious, the future of food delivery apps will likely involve a greater focus on sustainability. Many platforms are already experimenting with eco-friendly initiatives such as offering carbon-neutral deliveries, using biodegradable packaging, and encouraging customers to opt out of plastic utensils. Moving forward, these efforts will become even more critical as consumers demand more sustainable practices from the businesses they support.
Future potential: Platforms that adopt eco-friendly practices will not only reduce their environmental impact but also attract eco-conscious consumers. Offering green delivery options, such as bike couriers or electric vehicle deliveries, could become a selling point for platforms looking to differentiate themselves in a crowded market. Additionally, food delivery apps that partner with sustainable restaurants or offer vegan and organic food options will appeal to an increasingly health- and environment-conscious audience.
Challenge: Implementing sustainable practices can be costly and operationally challenging, especially for platforms that rely on large-scale logistics. Ensuring that sustainability initiatives are both scalable and cost-effective will be crucial for their success.
The future of food delivery apps is poised to be shaped by a combination of advanced technology, innovative business models, and an increasing focus on personalization and sustainability. From drone deliveries to AI-powered systems, the platforms that embrace these trends and adapt to changing consumer demands will be best positioned to succeed in an increasingly competitive market. For developers and entrepreneurs, keeping an eye on these trends will be critical to staying ahead of the curve.
Conclusion
The food delivery app industry has transformed into a multi-faceted, highly competitive space, with platforms ranging from restaurant delivery services to niche grocery and meal kit apps. As consumer expectations continue to rise, platforms must leverage a combination of innovative technology, operational efficiency, and customer-centric features to stay ahead. Throughout this guide, we’ve explored the different types of food delivery apps and the strategies that make them successful, offering insights into how you can build and scale your own platform.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Different App Types: Each type of food delivery app, whether focused on restaurant meals, groceries, or meal kits, serves a unique market segment. Successful platforms differentiate themselves by addressing the specific needs of their users, such as convenience, variety, or customization.
- Business Models That Drive Success: From commission-based fees to subscription models and surge pricing, successful food delivery platforms have diverse monetization strategies that maximize profitability while delivering value to customers and restaurant partners.
- Overcoming Challenges: Despite the significant opportunities, food delivery apps must navigate challenges such as high competition, managing operational costs, balancing customer and restaurant expectations, and adhering to evolving regulatory requirements.
- The Secret to Success: Platforms like Uber Eats and Instacart demonstrate that the key to success lies in logistics optimization, strong partnerships, and data-driven personalization, which foster both user loyalty and operational scalability.
- The Future of Food Delivery: Innovations such as drone deliveries, AI-powered systems, and deeper integration with IoT devices will shape the future of food delivery apps, providing exciting opportunities for both entrepreneurs and consumers. Sustainability initiatives and eco-friendly delivery options will also play an increasingly important role.
As the industry continues to evolve, food delivery apps must remain agile and innovative to meet the shifting demands of customers. Whether you are developing a new platform or enhancing an existing one, staying ahead of the trends—such as adopting AI-driven features, partnering with local businesses, and offering personalized user experiences—will be crucial to your success.
If you’re ready to build or enhance your food delivery app, now is the time to start. With the insights from this guide, you can create a platform that stands out in the crowded market. Whether you need expert guidance on app development, logistics, or scaling your platform, working with experienced developers can help you achieve your goals and bring your vision to life.
Build Your Food Delivery App with Miracuves
Ready to bring your food delivery app idea to life and stand out in the competitive market? At Miracuves, we specialize in developing customized, scalable, and innovative on-demand delivery solutions tailored to your business needs. Whether you’re building a platform for restaurant deliveries, groceries, meal kits, or niche markets, our expert team will guide you through every step—from conceptualization to deployment.
With a proven track record of delivering high-performance apps, we integrate the latest technologies like AI-powered personalization, real-time tracking, and seamless payment gateways to ensure your platform offers the best user experience. Plus, our deep understanding of logistics, scalability, and strategic partnerships ensures your app is built to grow and thrive.
- Develop a feature-rich, user-friendly app that meets the demands of modern consumers.
- Scale your platform effortlessly with efficient logistics and robust backend architecture.
- Stay ahead of the curve with AI-powered analytics, personalized user experiences, and sustainable delivery options.
- Get expert support, from ideation to launch, ensuring your app succeeds in the competitive food delivery market.
Your vision, our expertise—let’s build a successful food delivery app that drives growth and delivers excellence. Contact us today to discuss your project and take the first step toward creating a standout app with Miracuves.
Scale your food business with a
feature-rich app!
From real-time order tracking to secure payments,
get a fully customizable solution.
FAQs
What are the different types of food delivery apps?
Food delivery apps come in several categories, including restaurant delivery apps (e.g., Uber Eats, DoorDash), grocery delivery apps (e.g., Instacart, Amazon Fresh), meal kit delivery apps (e.g., Blue Apron, HelloFresh), and full-stack delivery apps (e.g., Postmates, Deliveroo). Each type caters to different customer needs, from ordering takeout to receiving groceries or meal kits directly at home.
How do food delivery apps make money?
Most food delivery apps use a combination of monetization strategies, including commission fees from restaurants, delivery fees paid by customers, and subscription services (e.g., DashPass or Eats Pass). Additionally, many apps offer promotional partnerships with restaurants or use surge pricing during peak hours to increase revenue.
Which food delivery apps are the most successful?
Some of the most successful food delivery apps include Uber Eats, Grubhub, and DoorDash for restaurant delivery, while Instacart dominates the grocery delivery space. These apps succeed by offering fast, reliable service, forming strong partnerships, and providing personalized user experiences.
What challenges do food delivery apps face?
Food delivery apps face multiple challenges, including high competition, managing operational costs like driver wages and logistics, customer satisfaction, and navigating regulatory compliance around food safety and driver classification. Platforms that overcome these challenges through innovation and optimization tend to be more successful.
How are food delivery apps evolving with new technology?
The future of food delivery apps includes advancements like drone and robot deliveries, AI-powered personalization, and integration with smart home devices. These technologies promise faster, more efficient delivery services, enhanced customer experiences, and new ways to automate the order process.
How can I start my own food delivery app?
To build a food delivery app, you need to define your target market (e.g., restaurants, groceries, or niche services), choose a suitable business model (e.g., commission-based or subscription), and focus on developing key features such as real-time tracking, seamless payments, and customer support. Partnering with experienced developers like Miracuves can help you create a scalable, high-performance platform.
Check out the top-rated delivery solutions offered by Miracuves – built for performance and scale:
- Postmates Clone Solution – Imagine one powerful platform that lets you book a stay, order your favorite meals, hail a ride, pay bills, and much more all in a single app.
- Doordash Clone Solution – Book stays, order food, hail rides, make payments, and more all in one seamless app designed to move with you.
- Amazon Fresh Clone Solution – From farm-fresh produce to snacks, pantry staples, and household must-haves shop in seconds and get what you need, when you need it.
- FedEx Clone Solution – A smart logistics and courier platform for real-time shipment tracking, instant pickups, and secure, on-time delivery.








